Pioneering Progress: The UAE and Middle East Accelerate Global Innovation in Wound Care
The healthcare landscape across the Middle East is undergoing a rapid and fundamental transformation. Driven by strategic national visions such as Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and the United Arab Emirates’ Vision 2050, the region is actively reshaping its healthcare delivery models. The focus is moving beyond traditional hospital-based care toward a more proactive ecosystem centered on prevention, patient engagement, and the integration of advanced technologies.
Within this broader evolution, wound care, historically considered a secondary area of clinical focus, has emerged as a strategic priority. Chronic wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers and pressure injuries, pose a growing burden on healthcare systems due to their complexity, high recurrence rates, and extensive treatment costs. These conditions contribute significantly to hospital remissions, extended inpatient stays, and productivity losses, ultimately straining both healthcare budgets and workforce capacity.
However, this growing challenge also presents a unique opportunity for innovation and investment. The wound care segment is increasingly becoming a convergence point for biotechnology, advanced materials, digital health, and supply chain innovation. The UAE is positioning itself as a regional hub for testing and implementing next-generation solutions-from bioengineered dressings and regenerative therapies to AI-driven monitoring platforms that support precision wound management.
This renewed focus signals a shift in how healthcare leaders and policymakers view wound care-not merely as a clinical necessity but as a critical area for technological advancement and sustainable healthcare delivery.

Pioneering Wound Care: The Middle East's Journey to Innovation
The Middle East is rapidly advancing in healthcare innovation, with wound care emerging as a critical area of focus. Driven by rising chronic diseases, an aging population, and significant government investments, the region is fostering strategic partnerships and innovative research to meet growing demand. This infographic highlights the key drivers, collaborations, and investments shaping the future of wound care in the Middle East.
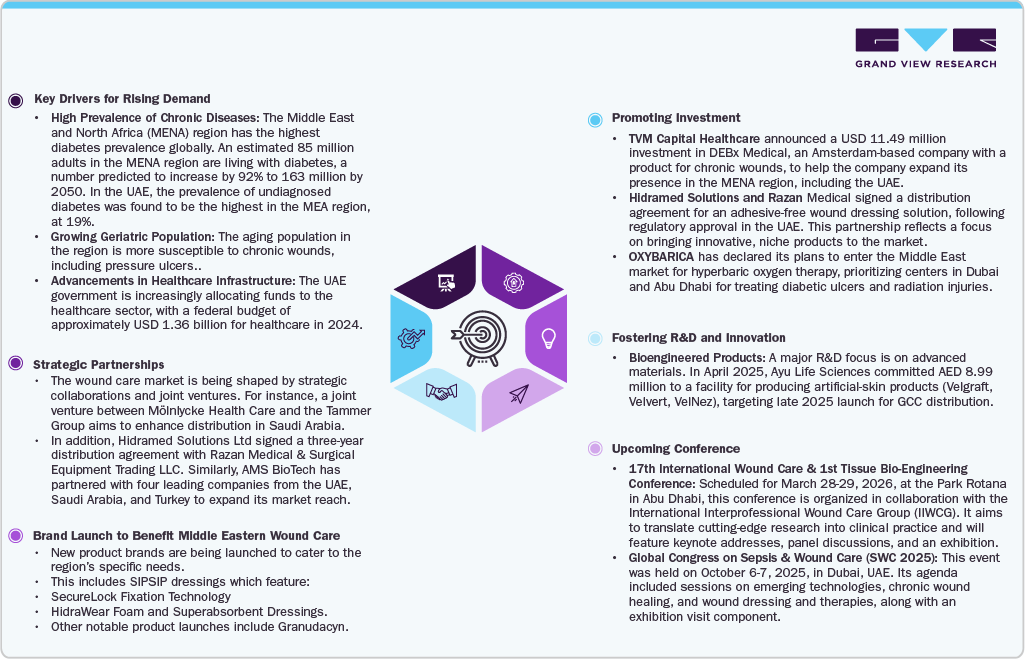
The Market Challenge: Complex Needs, Rising Expectations
Patients in the Middle East are no longer passive recipients of care. They expect comfort, continuity, and convenience, from hospital to home. This shift is driving systemic challenges:
-
Hospitals face pressure to discharge patients earlier.
-
Home-care providers must ensure wound safety and monitoring.
-
Suppliers must create reliable, home-ready solutions suited for regional climates and logistics.
The question facing the industry is clear:
How can we make wound care scalable, sustainable, and seamlessly integrated into everyday healthcare?
Backing Claims with Evidence: Policies Driving Change
Regional governments are already taking strong action. In the UAE, the National Strategy for Industry and Advanced Technology and Operation 300bn aim to boost local production of key medical products, such as wound dressings and medical devices. The Digital Health Strategy 2025–2033 focuses on creating connected healthcare systems that support remote patient monitoring and AI-powered diagnostics.
These national frameworks are accelerating three simultaneous shifts:
-
From Hospital to Home: Home-care licenses in the UAE have increased year-on-year, supported by digital health portals. Suppliers must now create portable, patient-friendly dressings that include educational materials and QR-based instructions for caregivers.
-
From Import to Local Production: Partnerships with free-zone manufacturers in Jebel Ali or Dubai Science Park are enabling localized assembly and temperature-resilient packaging-critical for supply reliability in the Gulf’s climate.
-
From Product to Platform: Smart dressings with built-in sensors, tele-wound platforms, and cloud-based analytics are moving wound care into the digital health ecosystem, allowing remote clinicians to track healing and prevent infection.
Actionable Solutions: How Companies Can Lead
To align with this transformation, wound-care suppliers must move beyond selling consumables. The winning approach is partnership-driven, emphasizing integration, education, and sustainability.
-
Develop “Home-Ready” Kits: Bundle antimicrobial dressings, remote nurse-support services, and educational materials in one easy-to-use package.
-
Embed Digital Health Features: Design smart dressings compatible with tele-wound applications, and offer dashboards that help hospitals measure healing outcomes and efficiency metrics.
-
Localize Production Strategically: Establish partnerships within UAE free zones to enable regional assembly and ensure agility during import disruptions.
-
Prioritize Sustainability: With COP28 hosted in Dubai, health systems are embedding sustainability into procurement. Offer biodegradable materials, recyclable packaging, and ESG-compliant processes that align with hospital mandates.
To illustrate how these opportunities are materializing across the UAE, the following key national initiatives highlight where technology, policy, and industry innovation are intersecting-and how each is shaping market demand for advanced wound-care supplies.
|
Focus Area / Initiative Name |
Lead Authority / Institution |
Project Goal and Key Technology |
Market Impact for Medical Supplies |
|
Regenerative Medicine Center |
Ministry of Health and Prevention (MoHAP) / Al-Qassimi Hospital |
Goal: Revolutionize treatment for diabetic, chronic wounds, and burns. |
Creates High-Value Demand for: Bioengineered skin substitutes, 4D Bioprinting materials (for self-adipose tissue), advanced wound care biologics, and specialized laser/plasma therapy supplies. |
|
Centre of Excellence (CoE) for Burn Treatments |
Department of Health – Abu Dhabi (DoH) / Sheikh Shakhbout Medical City (SSMC) |
Goal: Consolidate expertise and advanced resources for severe and complex burn care. |
Drives Adoption of: Innovative technologies like Allograft Skin, Biodegradable Temporising Matrix (BTM), and high-specification surgical and anti-infective dressings. |
|
Digital Health / Tele-Wound Platforms |
Various Hospitals / Health Authorities (e.g., DHA/EHS) |
Goal: Enable remote monitoring, data-driven clinical decision-making, and high-quality home healthcare. |
Creates Demand for: Smart dressings with sensors, portable Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) systems, and user-friendly dressings compatible with home care and digital documentation standards. |
|
Reduction of Chronic Wound Burden |
Various Hospital Quality Improvement Programs (DHA-mandated KPIs) |
Goal: Improve healing rates and reduce complications, specifically for Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs) and Pressure Ulcers (PIs). |
Drives Volume for: Advanced Wound Dressings (Foam, Hydrocolloid, Alginate), premium pressure relief devices (mattresses, cushions), and evidence-based debridement products. |
|
International Wound Care Conferences |
Various Scientific Groups (e.g., International Inter-Professional Wound Care Group) |
Goal: Foster global collaboration, introduce the latest research, and set new clinical standards for the region. |
Validates Demand for: NPWT Systems, advanced tissue repair products, and emerging technologies like Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) and specific laser applications. |
Key Takeaways: From Commodity to Care Partner
The transformation of wound care in the Middle East is about more than innovation-it’s about integration.
To lead in this space, companies must:
-
Localize supply chains and align with national industrial strategies.
-
Deliver home-ready, digitally integrated kits tailored for patient empowerment.
-
Adopt sustainable practices that meet regulatory and ethical expectations.
-
Collaborate across healthcare ecosystems, from research to community care.
-
Deliver home-ready, outcome-oriented kits.
As the UAE positions itself as a regional test bed for healthcare innovation, the companies that will thrive are those that see wound care not as a product line-but as a platform for better living.
Conclusion: Healing the Future
The Middle East is redefining what it means to heal. With visionary policy, technological openness, and cross-sector collaboration, wound care has become a symbol of healthcare’s next chapter-one rooted in science, compassion, and shared responsibility.
For organizations shaping this transformation, the opportunity is clear: to lead not by selling products, but by building solutions that heal both people and systems-sustainably and intelligently.