Minimal Invasive Surgeries: Transforming Healthcare with Technology, Strategy, and Resilience
The shift towards minimal invasive surgeries (MIS) represents a fundamental transformation in surgical healthcare, marked by rapid technological progress, significant market uptake, and measurable improvements in patient outcomes across the Middle East and globally. This article discusses risk-reframing, data-driven, and leadership-forward techniques to explore how MIS is redefining market strategies, clinical decision-making, and operational baselines for providers and policymakers.
The Quiet Revolution: Why Minimal Invasive Surgeries Matter
Surgical risk profiles and cost structures are slowly but fundamentally transforming. Minimal invasive surgery (MIS) techniques, covering laparoscopic, endoscopic, and robotic procedures, have progressed far beyond their initial niche status and are increasingly recognized as standard practice, thanks to major advances in visualization, robotics, and instrumentation that enable less invasive treatment and faster recovery times.
In leading GCC markets, such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, over 60.0% of major surgeries today utilize MIS approaches, while traditional open procedures continue to decline. At American Hospital Dubai, robotic-assisted surgeries have averaged 500 cases per year since 2020, accounting for 20.0% of all surgeries. In Saudi Arabia’s public sector, nearly half of non-critical surgeries are performed laparoscopically. These numbers show a decisive shift in surgical practice; minimally invasive surgery is becoming the norm, not the exception.
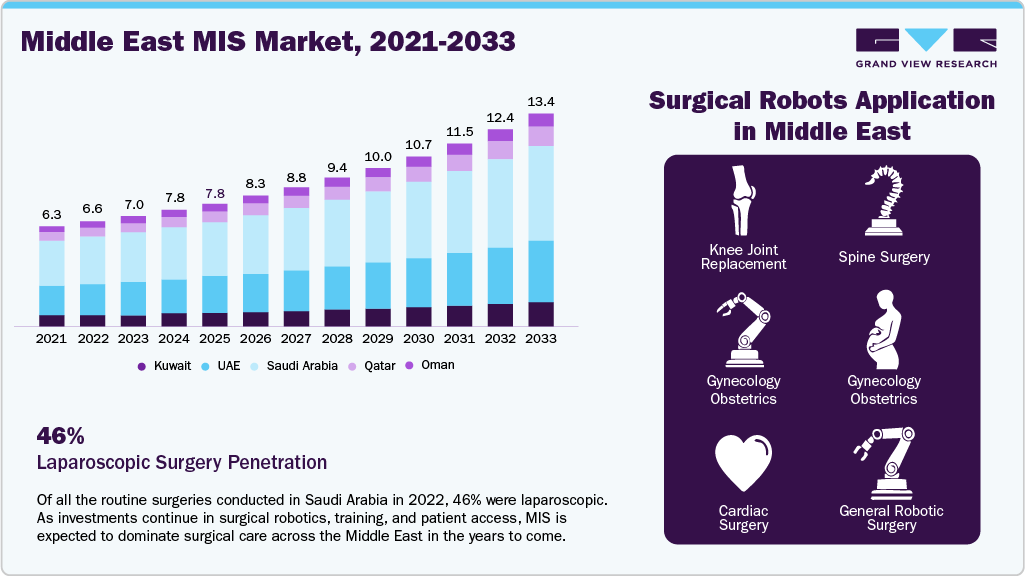
Data Tells the Story: Measurable Gains for Patients and Systems
Clinical data provides compelling evidence of the measurable advantages linked to the adoption of minimally invasive surgery (MIS):
-
A 2020 patient survey in Saudi Arabia showed 46.0% of patients underwent laparoscopic surgery versus 41.0% choosing open procedures.
-
King Faisal Specialist Hospital completed 400 robotic cardiac MIS surgeries since 2019, with reported outcomes of 98.0% survival, 50.0% shorter hospital stays, and 40.0% lower costs compared to open cardiac surgeries.
-
Myomectomy complication rates favor MIS: laparoscopic procedures resulted in average blood loss of 333 mL vs 576 mL for open, durations of 57 minutes vs 103 minutes, and complication rates of 2.9% versus 10.8%, consistently supporting the value proposition.
These outcomes are driving transformations in hospital strategy, prompting the expansion of day surgery programs, innovations in cost-sharing practices, and increasingly value-driven procurement models. The effectiveness and benefits of MIS are now central considerations in organizational planning and care delivery across leading health systems.
Technology and Surveillance: The New Surgical Assistant
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone of both preventive and precision medicine, leveraging technology to enable earlier intervention, greater accuracy, and enhanced surgical outcomes.
-
Hospitals like Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi have completed more than 400 advanced robotic procedures in 2024, from cancer surgeries to organ transplants and lung operations.
-
Robotic programs like at Burjeel Medical City in Abu Dhabi have expanded from one to fifteen certified surgeons since August 2023 and aim for 1,000 cases by end of 2025.
-
Simulation workshops, often run by American Hospital Dubai, focus on upskilling surgeons with robotic systems like da Vinci and Versius, highlighting technology as a surgical assistant rather than a replacement.
Medical device manufacturers have accelerated their responses, rapidly scaling the deployment of specialized instruments and technologies to support this surge in MIS adoption. Companies such as Medtronic (Hugo RAS), Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon staplers and Ottava robotics), Olympus (endoscopy tools), Stryker (orthopedic MIS), and Intuitive Surgical (da Vinci systems) are expanding their footprints throughout the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and across the GCC to meet rising demand for advanced minimally invasive solutions.
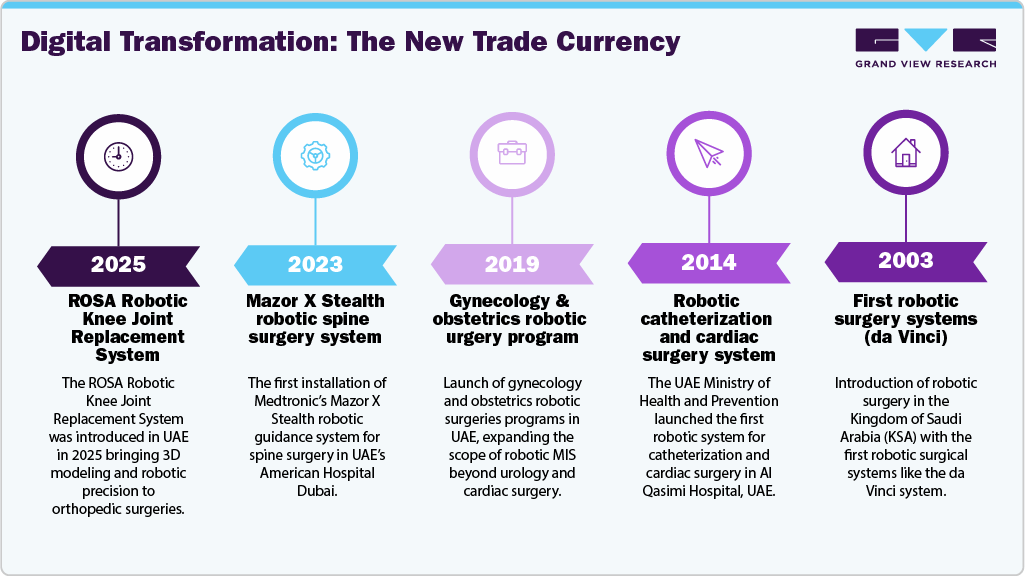
The timeline of minimal invasive surgery adoption in the Middle East illustrates a progressive journey from early experimentation to modern technological leadership.
Market and Leadership: Reframing Costs, Integrating Value
Healthcare leaders must adopt a comprehensive approach to managing costs and capabilities by integrating risk management and scenario planning specifically tailored to the evolving demands of minimally invasive surgery (MIS). For hospitals and national health authorities, this approach translates into several key strategic actions:
-
Embedding MIS adoption into procurement and reimbursement models, aligning financial incentives with best clinical outcomes.
-
Breaking silos between departments—integrating OR planning, radiology, and IT data systems to optimize scheduling and understand risk-adjusted resource utilization.
-
Investing heavily in surgeon training, simulation platforms, and cross-border credentialing to prevent gaps in skill as technologies outpace workforce readiness.
The growing devices market, valued at approximately USD 1.7 billion in Saudi Arabia for laparoscopic and robotic surgical tools in 2024, underscores not only a volume growth trend but suggests accelerated diffusion of new technologies. This dynamic landscape introduces both fresh risks and opportunities for healthcare policy makers and clinical management to navigate thoughtfully and proactively.
Resilience and Strategic Positioning: Preparing for the Future
Gaining a competitive edge in healthcare today increasingly pivots around resilience. The capacity to scale minimally invasive surgery (MIS) services efficiently, adapt quickly to fluctuations in patient demand (such as surges triggered by pandemics), and respond promptly to challenges like rapid technological changes or disruptions in supply chains is critical to building a resilient, future-ready healthcare system. Building this resilience requires strategic foresight and comprehensive planning tailored specifically to the surgical environment.
Forward-looking hospitals should:
-
Map out capacity expansion based on historical throughput and future case-mix predictions.
-
Stress-test reimbursement and staffing models for disruptions caused by new technology adoption or shifts in regulatory requirements.
-
Use patient outcome dashboards to identify opportunities for further reducing open surgery rates and benchmarking cost savings.
The Bottom Line: Minimal Invasive Surgery as the New Operating Baseline
This is not a passing trend. The market data, clinical outcomes, and investment cycles all point to a lasting restructuring of how surgery is performed, billed, and valued across the Middle East and beyond. Just as shipping lanes have become embedded frontlines, MIS is now the frontline of modern surgical care.
Healthcare leaders who integrate MIS into strategic planning, combining patient-centered outcomes, technology adoption, and financial resilience, are most likely to put their institutions and systems ahead in delivering care that is not just less risky, but markedly more valuable. Because in today’s healthcare market, those who cost innovation into their strategy aren’t just protected from the next disruption, they’re prepared to grow through it, setting a reference standard for the region and the world.