- Home
- »
- Market Trend Reports
- »
-
Innovations In Hernia Surgery
Overview of the Hernia Surgery and Devices Industry
The global hernia surgery and devices market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by increased hernia cases and heightened awareness of early diagnosis. The Cleveland Clinic estimates that approximately 20 million hernia surgeries are performed worldwide each year, including procedures like inguinal, femoral, and abdominal wall repairs. Consequently, hernia repair ranks among the most common general surgical procedures globally.
In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration reports that over 1 million hernia repairs are performed each year, with inguinal hernia surgeries making up a large part of these procedures.
Breakthroughs in surgical methods, including laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures, have driven up the use of hernia repair surgeries. These advancements bring benefits like lower post-op pain, quicker recovery times, and better cosmetic results, which are all helping to grow the hernia surgery and devices market.
Rising Global Burden of Hernias
One of the most frequent surgeries done all over the world is hernia repair, which is an indication of how common and easily accessible the surgeries are. The total of these kinds of operations is different from one region to another, depending on factors such as population, health systems, the level of surgeons' skills, and the use of minimally invasive surgeries. Although inguinal hernias are the leading cause of hernias worldwide, diseases such as ventral, umbilical, and incisional hernias significantly contribute to the global requirement for hernia surgeries. The differences in surgical approaches between the various regions can be observed through the analysis of local surgical preferences, where some areas are more inclined towards open operations, while others are quickly changing to laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries.
Table 1: Annual Hernia Repair Volumes, by Country
Regions/Countries
Approximate Number of Hernia Repairs
U.S.
1,000,000
Germany
200,000
China
2,000,000
Japan
110,324
Australia
90,000
India
2,000,000
UK
100,000
Source: WHO, NHS England, Japan Surgical Society, China National Knowledge Infrastructure
Several key factors affect how many hernia surgeries are performed in different countries. Countries like China and India have some of the highest numbers of procedures, mainly because of their large populations, a high number of untreated hernias, and increasing access to surgical care. On the other hand, countries such as Germany, Japan, and Australia have lower overall volumes, partly because they have smaller populations and well-established screening, preventive care, and advanced surgical practices that reduce the need for repeat surgeries. The United States, with its mix of advanced healthcare and high demand for surgery, remains one of the top countries in annual hernia repair volumes. These differences show how demographics, access to healthcare, and public health priorities all shape the number of surgeries performed.
Surgical Approach Preferences in Hernia Repair
Surgeons continually refine their approach to hernia repair, but open surgery remains the most common method in many areas. This is mainly because it's familiar to surgeons, less expensive upfront, and widely available expertise. However, minimally invasive techniques like laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries are gaining traction, especially in busy hospitals with advanced surgical equipment. Patients and healthcare providers are attracted to these methods because they offer less pain after surgery, quicker recovery, and lower recurrence rates in certain cases. The balance between open and minimally invasive surgeries depends on medical considerations and access to technology, training, and hospital resources.
For example, a large-scale study of Medicare patients found that open hernia repairs were still the most common approach among 160,378 procedures in the U.S. This is mainly because surgeons are familiar with traditional methods, patient needs vary, and hospitals have the necessary resources. Although minimally invasive methods like laparoscopic and robotic surgeries were becoming more popular, they needed specialized training and equipment, which slowed their adoption early on.
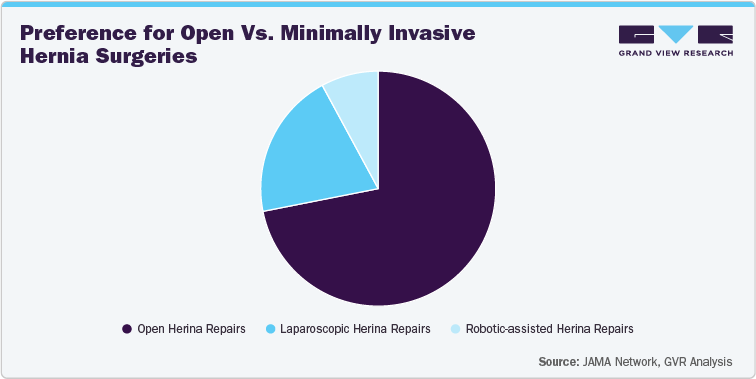
Such research keeps on notably emphasizing the fact that the learning process when it comes to the use of robots in hernia repairs is really challenging and that surgeons need to carry out no less than 19 robotic-assisted operations to be able to get reoperation rates that are comparable with those obtained through laparoscopic and open repairs. Nevertheless, this setting is not static as the change is always there. Over the last ten years, the use of minimally invasive procedures has been on the rise. This is a sign of several things, among which are the development in surgical technologies, the growing trust of health care providers, and the advantages that these surgeries have brought about, e.g. lesser postoperative pain, shorter convalescence period, and better cosmetics results in minimally invasive approaches. As the advantages get more acknowledged, the use of minimally invasive techniques in hernia repair will likely be the future trend upward.
Key Drivers of the Hernia Surgery and Devices Market
The global landscape of hernia surgery is evolving rapidly, driven by rising prevalence and a growing demand for innovative treatment options. Each year, around 20 million hernia repairs are performed worldwide, underscoring the scale of the condition and the pressing need for surgical approaches that deliver safer, faster, and more effective outcomes.
One of the most significant trends is the rapid growth of minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries. These methods are gaining popularity because they can reduce post-operative pain, shorten recovery times, and produce better cosmetic results. These advantages lead to higher patient satisfaction and improved quality of life. The global shift is evident. For instance, the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) has announced plans to increase robotic surgeries from 70,000 annually to nearly 500,000 by 2035, making robotic-assisted procedures the standard for keyhole surgeries. Similarly, in August 2025, doctors at Hamidia Hospital in Bhopal, India, performed a minimally invasive procedure on a 46-year-old woman for a complex hernia, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these advanced techniques.
Meanwhile, changing regulatory and reimbursement frameworks are impacting the adoption of new techniques. In 2023, the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) made coding changes that tie reimbursement rates for anterior abdominal hernia repairs to the size of the hernia defect. Although meant to standardize payments, these updates may lower reimbursement for smaller repairs, influencing provider decision-making and limiting access to certain advanced surgical options. This highlights the need to balance innovation with cost-effectiveness to ensure equal access to high-quality hernia care.
Notable Innovations Shaping Hernia Devices
Technological advancements are a major competitive force in the hernia surgery and devices market. Firms are making substantial R&D investments to boost image clarity, shorten scanning durations, and enhance patient comfort during procedures.
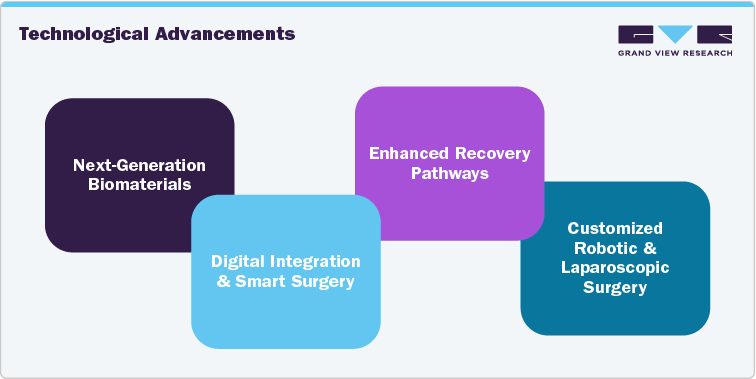
Next Generation Biomaterials
- Absorbable and Non-absorbable Meshes
Mesh implants continue to be the foundation of hernia repair. The decision between absorbable and non-absorbable materials largely depends on the patient's condition and the surgical goals. Non-absorbable meshes, such as polypropylene, offer long-term reinforcement and have a proven track record of durability, making them a good fit for standard hernia cases. On the other hand, absorbable meshes break down over time, lowering the risk of chronic inflammation or foreign body reactions. These are especially useful in cases where the surgical field is contaminated or the patient has fragile health, although they may provide less support over time.
Table 2: Comparison Between Absorbable and Non-absorbable Mesh
Features
Non-absorbable Mesh
Absorbable Mesh
Material
Polypropylene, Polyester
Polyglycolic acid, Polylactic acid
Longevity
Permanent support
Degrades over time
Durability
Proven long-term strength
Limited long-term support
Best Use Case
Standard, long-lasting repairs
Contaminated fields, fragile patients
Risks
Chronic inflammation, complications
Possible recurrence if support is insufficient
Source: GVR Analysis
- Biologic & Composite Meshes
Biomaterial breakthroughs have produced biologic meshes from human or animal tissue, aiding tissue integration in high-risk or contaminated cases. Their main drawbacks are higher cost and inconsistent strength compared to synthetics. Composite meshes, combining absorbent and non-absorbent layers, address these issues. For example, coated polypropylene meshes are used in intra-abdominal repairs, offering reinforcement and fewer adhesions.

- Antimicrobial-coated Meshes
Another innovative research area in hernia repair is the production of antimicrobial-coated meshes. Such meshes are designed to lower the occurrence of infections at the surgical site, which is a substantial problem in abdominal surgeries. Using substances such as silver and triclosan for coating, mesh implants can become a barrier that protects them from bacteria. Preliminary clinical trials show that these meshes can substantially lower infection rates, which might result in the long-term efficacy of treatment and less reoperation. When these technologies develop, they will be relied upon to play a vital part in a safer and more efficient hernia management.
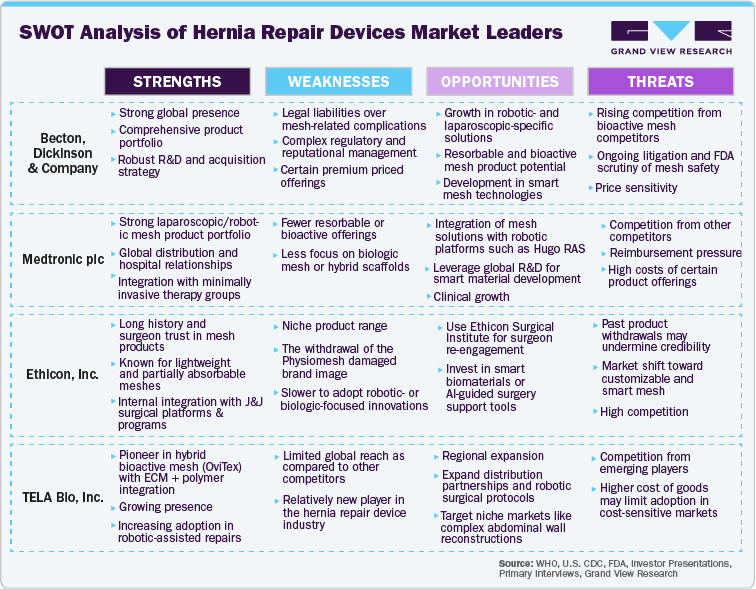
Competitive Scenario of the Hernia Repair Devices Industry
The hernia surgery and devices market is moderately competitive. It features several established leaders who continuously innovate and expand their market presence. Key players include Medtronic plc, Ethicon Inc., Novus Scientific AB, and B. Braun SE. These companies leverage advanced technologies and strategic partnerships to enhance their competitiveness.
Table 3: Types of Hernias, Common Surgical Approaches, and Primary Devices Used
Types of Hernia
Common Surgical Approach
Primary Devices Used
Inguinal Hernia
Open or Laparoscopic
- Mesh
- Sutures or tackers
- Laparoscope & trocars (if MIS)
Femoral Hernia
Open or Laparoscopic
- Mesh plug or flat mesh
- Sutures or fixation tacks
- Energy devices for dissection
Umbilical Hernia
Open or Laparoscopic
- Circular mesh or composite mesh
- Sutures, glue, or tackers
- Laparoscope if MIS
Epigastric Hernia
Open or Laparoscopic
- Mesh patch (synthetic or biologic)
- Sutures or fixation devices
- Insufflation system (if MIS)
Incisional/Ventral Hernia
Open, Laparoscopic, or Robotic
- Large composite/dual-layer mesh
- Tackers, sutures, or adhesive fixation
- Robotic arms (if robotic repair)
Hiatal Diaphragmatic Hernia
Laparoscopic or Robotic
- Mesh (biologic or absorbable)
- Sutures for crural closure
- Energy devices (for dissection)
- Endoscopic stapler (if needed)
Source: Company Website, GVR Analysis
Becton Dickinson and Company (BD), through its Davol division (formerly Bard), is a global leader in the hernia repair devices market. It offers one of the most comprehensive and clinically trusted portfolios of surgical mesh products.
They are a prominent leader with a global presence in countries such as Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, Greater China, Japan, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and South America. BD has manufacturing operations outside the United States in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Canada, China, Dominican Republic, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, the Netherlands, Singapore, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
BD’s extensive range includes synthetic, composite, resorbable, and robotic-compatible meshes, making it a go-to provider for surgeons using open and minimally invasive hernia repair approaches. Their product line is designed to address diverse clinical needs, from simple hernia repairs to complex, contaminated, or high-risk reconstructions.
The report analyses the competitive landscape in this industry based on the parameters mentioned below:
Competitive Landscape: Top 10 Hernia Repair Devices Manufacturers Overview
Market Outlook
Company Categorization
Company Share Analysis (Top 10 companies)
Company Position Analysis
List of Key Companies by Region
Company Overview
Product Benchmarking
Financial Performance
Recent Strategic Initiatives
SWOT Analysis
Emerging Players: Overview of 30+ Emerging Players and Startups in the Hernia Repair Devices Industry
Company Overview
Establishment Year
Headquarters
Business Verticals
Employee Count
Investor Information
Total Funding (USD)
Product Benchmarking
Strategic Initiatives
SWOT Analysis
Company Profiles
BECTON, DICKINSON AND COMPANY
Company Overview:
Headquarters: Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, U.S.
Founded: 1897
Ownership: Public
Revenue: Approx. USD 20,178 Million
Specialization: BD operates globally, with international regions organized as EMEA (Europe, Middle East, Africa), Greater Asia (including China, Japan, South and Southeast Asia, Korea, Australia, and New Zealand), Latin America (Mexico, Central and South America, and the Caribbean), and Canada. The company manufactures products in multiple countries across North America, Europe, Asia, and South America, including major sites in China, Mexico, Germany, India, and Ireland.
Product Benchmarking:
SorbaFix Absorbable Fixation System
Purpose: Provides secure fixation of surgical mesh to tissue during laparoscopic and open hernia repairs.
Features:
-
Use absorbable fasteners that gradually dissolve, reducing long-term foreign body presence.
-
Spiral fastener design ensures strong mesh fixation with controlled depth of penetration.
-
Ergonomic, lightweight handle allows precise one-handed operation and consistent deployment.
Clinical Use: Frequently employed in ventral, incisional, and inguinal hernia repairs, particularly when surgeons prefer absorbable fixation to minimize chronic pain or complications linked to permanent tackers.
Ventralight ST Mesh
Purpose: The Ventralight ST Mesh is designed for laparoscopic intraperitoneal onlay mesh (IPOM) procedures in ventral and incisional hernia repairs.
Features:
-
Lightweight polypropylene base for flexibility
-
Sepra hydrogel barrier on the visceral side to prevent adhesions
-
Barrier resorbs in ~30 days
-
Macroporous design promotes tissue ingrowth
Clinical Use: Used in minimally invasive (laparoscopic or robotic) ventral hernia repairs, preferred in Intraperitoneal onlay mesh (IPOM) placement, where direct contact with bowel occurs, and also enables easier port insertion and unrolling due to its flexible profile.
Phasix Mesh / Phasix ST Mesh
Purpose: The Phasix Mesh / Phasix ST Mesh is designed for long-term reinforcement in soft tissue where permanent mesh is not desired (e.g., patients at risk of infection or complications).
Features:
-
Made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) – fully resorbable
-
Phasix ST includes a Sepra barrier for intraperitoneal use
-
Absorbed over 12–18 months, providing sustained strength
-
Reduces chronic foreign body response
Use Case:
-
Ideal for contaminated or high-risk fields
-
Used when mesh removal later is undesired or impractical
-
Excellent in complex abdominal wall reconstruction
Sepramesh IP Composite
Purpose: The Sepramesh IP Composite mesh is a mesh that is used for intraperitoneal placement with adhesion prevention.
Features:
-
Polypropylene mesh base for strength and flexibility
-
Sepra barrier coating to reduce adhesions to viscera
-
Barrier absorbs in 30 days; mesh integrates into tissue
Use Case: Used in IPOM procedures via open or laparoscopic techniques and is best suited for repairs near bowel or visceral contact
Composix L/P Mesh
Purpose: The Composix L/P Mesh offers strong mechanical support with a barrier for intra-abdominal use
Features:
-
Dual-sided design: polypropylene mesh + expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
-
ePTFE prevents tissue adhesion on the visceral side
-
Heavyweight mesh for robust reinforcement
Use Case: Used in ventral/incisional hernia repairs with a significant defect size. It is particularly useful when strong mechanical support is needed, and is often used in open surgeries or procedures.
Bard Soft Mesh
Purpose: The Bard Soft Mesh is a general-purpose and traditional polypropylene mesh used for hernia repair.
Features:
-
Soft, monofilament, polypropylene
-
Macroporous structure for tissue ingrowth
-
Non-coated, non-resorbable
Use Case: This mesh is primarily used for onlay, sublay, or preperitoneal repairs. It is not suited for intraperitoneal use due to risk of adhesions, and is commonly used for inguinal, umbilical, and small ventral hernias.
3DMax Mesh
Purpose: The 3DMax Mesh is an anatomically contoured mesh for inguinal hernia repair and small ventral defects.
Features:
-
3D shape conforms to the inguinal and ventral anatomy
-
Lightweight, monofilament polypropylene
-
Comes in left/right orientation for specific placement
Use Case: This mesh is primarily used for preperitoneal/laparoscopic inguinal repair, but is also used off-label for small ventral or umbilical hernias, and is generally preferred in TAPP (Transabdominal Preperitoneal) or TEP (Totally Extraperitoneal) laparoscopic procedures.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


