- Home
- »
- Biotechnology
- »
-
Microfluidics Market Size And Share, Industry Report, 2033GVR Report cover
![Microfluidics Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Microfluidics Market (2026 - 2033) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product (Microfluidic-based Devices, Microfluidic Components), By Application (Medical, Non-Medical), By Material (Silicon, Glass), By Technology, By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-1-68038-056-9
- Number of Report Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2021 - 2024
- Forecast Period: 2026 - 2033
- Industry: Healthcare
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Interactive Charts
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Microfluidics Market Summary
The global microfluidics market size was estimated at USD 41.92 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 105.13 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.22% from 2026 to 2033. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing adoption of microfluidic devices across various fields of research and diagnostics.
Key Market Trends & Insights
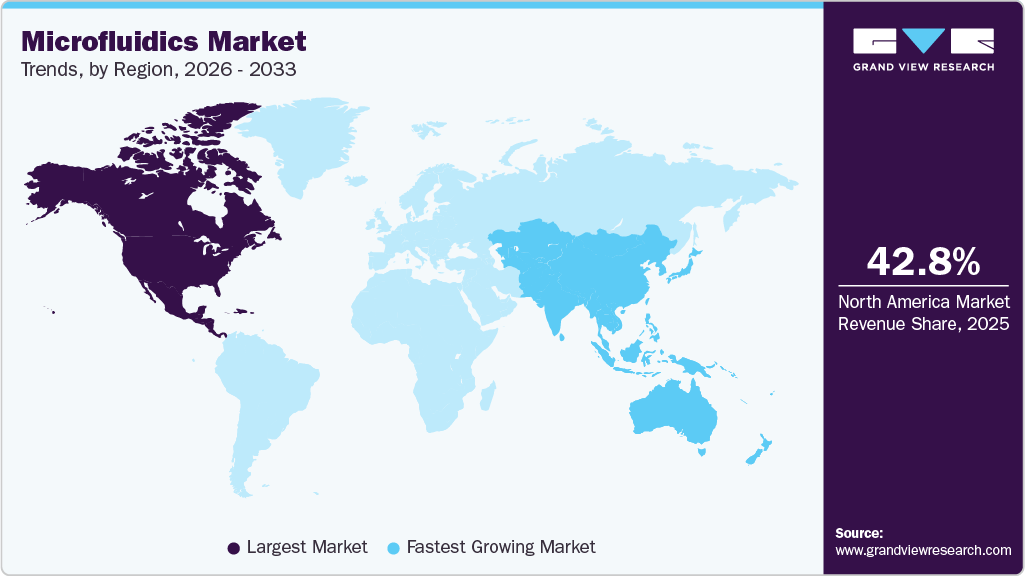
- The North America microfluidics industry held the largest share of 42.85% of the global market in 2025.
- The microfluidics industry in the U.S. is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period.
- By material, the polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) segment held the largest revenue share of 34.99% in 2025.
- By technology, the lab-on-a-chip segment held the largest market share in 2025.
- By product, the microfluidic components segment held the largest revenue share in 2025 and is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 41.92 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 105.13 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 12.22%
- North America: Largest market in 2025
- Asia Pacific: Fastest growing market

Advancements and Adoption of Microfluidics in Diagnostic Healthcare
The demand for reliable diagnostic tools is increasing due to the soaring hospital charges and frequent patient readmissions, while prehospital and point-of-care (POC) solutions, including at-home monitoring, are minimizing hospital visits and inpatient stays. Major players such as Abbott, Roche, and Danaher are pushing the growth of the IVD market by incorporating microfluidics into their diagnostic platforms for earlier disease detection, faster turnaround times, enhanced accuracy, and, at the same time, non-invasive sampling.
Some commercialized POCT devices based on Nucleic-Acid Testing (NAT).
Product Name
Manufacturer
Method
Target
Sample Type
ID NOW COVID-19
Abbott Diagnostics Scarborough, Inc.
NEAR
COVID-19 RdRp gene
Nasal, Throat, and Nasopharyngeal swabs
VitaPCR SARS-CoV-2 Gen2 Assay
Credo Diagnostics Biomedical Pte. Ltd.
Real-Time RT-PCR
N1, N2-Nucleocapsid Gene
Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal swabs
The BioFire Respiratory 2.1-EZ (RP2.1- EZ) Panel (EUA)
BioFire Diagnostics, LLC
Nested multiplex PCR
Spike protein gene, Membrane protein gene
Nasopharyngeal swabs
1copy COVID-19 qPCR Kit
1drop, Inc
RT-PCR
E gene for beta coronavirus and the RdRp gene for SARS-CoV-2
Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal swabs
Source: PMC, Secondary research. Grandview research.inc
Microfluidics-enhanced PoCT solutions offer improved sensitivity, specificity, and faster turnaround times, prompting manufacturers to launch microfluidics-based diagnostic kits to address urgent testing needs. For example, in October 2021, LumiraDx received Emergency Use Authorization from India’s CDSCO for its COVID-19 antigen test, underscoring the critical role of microfluidics in pandemic response and public health diagnostics.
Technological Advancements in Microfluidics
Microfluidic devices are gaining popularity in the market because they can work with very small sample volumes, they can also help to lower the consumption of reagents, and improve the possibility of providing fast, accurate, and non-invasive diagnostics. The increasing costs in hospitals, together with the ever-growing transition to diagnostics at the point-of-care and even at home, are not only minimizing hospital visits but also facilitating the detection of diseases at their early stages. Moreover, partnerships between hospitals and universities, which are the academic-industry collaborations, are speeding up the flow of microfluidics into IVD.
Simultaneously, the increasing application of microfluidics in research and diagnostics is pushing the firms to bring to the market advanced technologies through collaboration. Laboratory-on-a-chip and microfluidic sensor technologies are the main factors for the precision, efficiency, and integration development in compact systems, which therefore makes their use wider in the medical and scientific fields and helps market growth.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The microfluidics industry is undergoing a major transformation due to the introduction of new technologies such as AI-based systems, digital microfluidics, modular platforms, and wearable sensors, the application of which is being widened in the fields of healthcare, biotechnology, and environmental monitoring.
Mergers and acquisitions in the microfluidics industry are increasing as companies pursue technological advancement, R&D expansion, and market consolidation. As market growth continues, M&A activity is expected to intensify, with strategic collaborations focused on strengthening technology portfolios and expanding market presence.
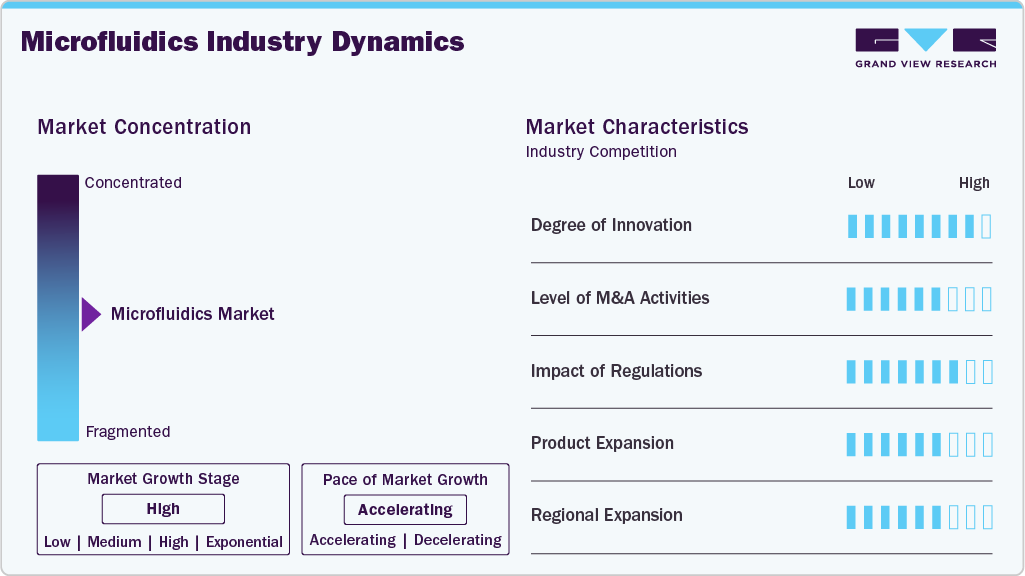
Regulations play a critical role in the microfluidics industry by ensuring product safety and efficacy, particularly in healthcare and biotechnology. Although compliance requirements from authorities such as the FDA and EMA can raise costs, slow innovation, and complicate global market entry, and also reduce risks associated with faulty products. Ongoing efforts to streamline regulatory approvals aim to balance patient safety with the need for faster innovation as the market expands.
Product expansion is a key strategy in the microfluidics industry as companies seek to meet rising demand in advanced diagnostics, drug delivery, and biotechnology. The recent developments, among which the improved PDMS SlipChip microfluidic device created by seven scientists from different countries, solved the troubles such as the blocking of channels and the killing of cells, thus allowing the conducting of efficient and safe biomedical research and drug development.
Regional expansion is a key strategy in the microfluidics industry as companies seek to capture growth in emerging markets and rising demand for advanced technologies. While North America remains the largest market due to strong R&D investment and a mature healthcare ecosystem, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a high-growth region driven by expanding biotechnology capabilities, increased healthcare spending, and growing adoption of point-of-care diagnostics.
Product Insights
The microfluidic components segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2025 and is expected to register the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. This increase in demand can be attributed to the indispensable role played by such components as pumps, valves, chips, and sensors in providing accurate fluid control for diagnostics, drug delivery, and lab-on-a-chip applications, among others.
The segment of microfluidic-based devices is projected to grow remarkably during the forecast period due to their increasing application in diagnostics, drug delivery, and life sciences research. The ongoing progress in miniaturization and automation, plus the growing support of both public and private sector investment in biomedical R&D, are speeding up the emergence of commercialization and the acceptance of the market.
Technology Insights
The lab-on-a-chip segment held the largest market share at 38.71% in 2025, driven by its ability to control cells at the single-cell level and process large cell volumes efficiently. Studies indicate that these devices need to be made more accessible, easier to use, and cheaper to manufacture to move them from the laboratory to the clinic and thus increase their importance in the areas of diagnostics and personalized medicine.
The organs-on-a-chip segment is expected to grow fastest over the forecast period, driven by its role in drug discovery and personalized medicine. Initiatives like the European Commission’s 2025 roadmap for standardizing OoC technologies, in collaboration with ISO, aim to integrate these devices into drug development and chemical safety testing, reducing animal testing and supporting industry growth.
Material Insights
The polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) segment accounted for the largest revenue share at 34.99% in 2025, driven by its widespread use in microfluidics. This is because its main attributes are biocompatible, optically transparent, flexible, permeable to gases, and low-cost. Moreover, the PDMS is significantly appreciated in soft lithography because it allows the creation of complex, multilayer microfluidic structures, which in turn are suitable for sophisticated biological and chemical experiments.
The polymers segment is expected to grow strongly over the forecast period, driven by demand for cost-effective, flexible, and customizable materials in microfluidic device fabrication. Besides, the large-scale production, flexibility in designing, and the wide range of usages from drug delivery to environmental monitoring make polymers the most liked material for innovation and mass production.
Application Insights
The medical segment had the largest revenue contribution in 2025, which was mainly due to the extensive usage of microfluidics in both biological analysis and clinical applications. Newer technologies, like digital microfluidic platforms for simultaneous drug testing on cancer samples, are not only increasing shuffling but also backing tailor-made cancer treatment, thereby promoting growth of the segment even more.
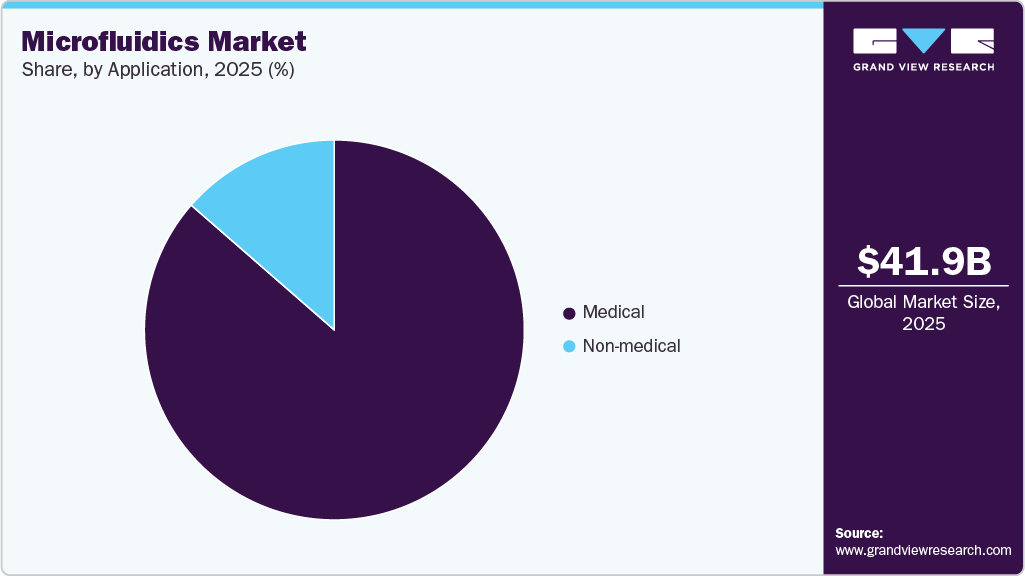
The non-medical segment of the market is expected to grow at a strong pace during the forecast period, driven by expanding applications across industries such as oil extraction, food processing, and materials science. Textile-integrated microfluidic systems for real-time sweat monitoring highlight how advanced fabrication enables compact designs, low sample volumes, and continuous biosensing, driving adoption beyond healthcare.
Regional Insights
North America microfluidics industry dominated the global market in 2025 with the largest share of 42.85%, driven by strong government and private research funding. Growing demand in research and diagnostics has spurred academia-industry collaborations, accelerating the commercialization and adoption of microfluidic innovations in healthcare and life sciences.
U.S. Microfluidics Market Trends
The U.S. microfluidics industry is driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong R&D investments, and industry-academia-government collaborations. For example, in April 2025, Mepsgen launched a microfluidics platform that enables rapid, precise cell-based assays for drug discovery, toxicology, and personalized medicine.
Europe Microfluidics Market Trends
The European microfluidics industry is steadily growing, thanks to the supportive regulations, strong research environments and the interest in personalized medicine. Besides, the combination of microfluidics with genomics and proteomics leads to more exact and personal medical treatments that are in line with the overall healthcare objectives of the continent.
The UK microfluidics industry is on an upward trajectory, mainly due to the government-backed projects such as ARIA, financial aid from BBSRC and EPSRC, and the backing of academia. UCL spin-off Young Owl Microfluidics (YOM) Ltd. introduced a modular microreactor system in March 2025 for high-throughput drug testing, biotransformation, and organoid culture.
Germany’s microfluidics industry is growing rapidly, supported by strong research infrastructure, industrial expertise, and strategic investments. Institutions like the Max Planck and Leibniz Institutes drive innovations, positioning the country as a leader in healthcare, diagnostics, and environmental microfluidic applications.
Asia Pacific Microfluidics Market Trends
The Asia Pacific microfluidics industry is set for fastest growth with a CAGR of 13.08% throughout the forecast period, driven by advanced research, a developing economy, and affordable labor. For example, INST Mohali developed droplet microfluidics to produce PVDF microspheres with enhanced piezoelectric properties for wearable sensors. While international players dominate diagnostics, regional companies are introducing innovative, cost-effective solutions to expand their market share.
China’s microfluidics industry is poised for strong growth, supported by government initiatives like Made in China 2025 and the National Key R&D Program. Rising chronic diseases and an aging population are driving demand for efficient diagnostic solutions, making microfluidics a key technology.
Japan’s microfluidics industry is growing, driven by an aging population and demand for advanced diagnostics and personalized medicine. In March 2025, JAIST developed a nanoparticle-based platform using magnetically guided carbon nanohorns for targeted cancer therapy, highlighting Japan’s innovation in healthcare microfluidics.
MEA Microfluidics Market Trends
The Middle East and Africa microfluidics industry is expected to grow due to rising healthcare investments, demand for personalized medicine, diagnostic advancements, and point-of-care testing. Supportive government initiatives and expanding biotech R&D further drive applications in drug delivery, diagnostics, and lab-on-a-chip devices.
The Kuwait microfluidics industry is projected to grow steadily over the forecast period. The increasing prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases is driving the need for rapid diagnostic solutions. This demand for efficient diagnostic solutions is also being fueled by the growth of pharmaceutical and biotechnology research in Kuwait. Emerging applications in drug delivery and wound care also provide momentum for the microfluidics industry, which is unique and newer than the Middle East microfluidics industry.
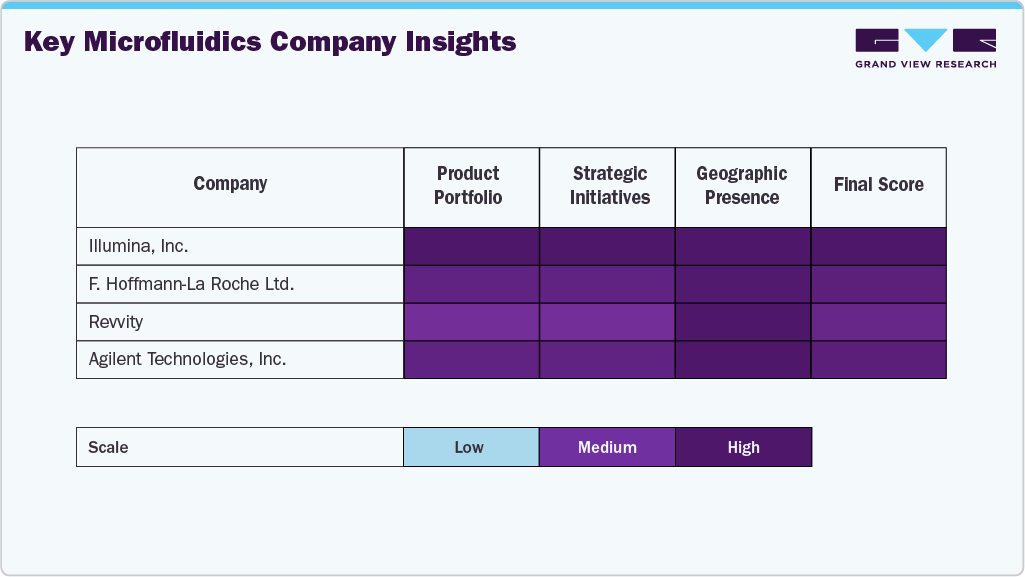
Key Microfluidics Company Insights
Leading companies such as Danaher Corporation, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, and PerkinElmer have maintained significant market share due to their global presence and integrated solutions spanning diagnostics, drug discovery, and genomics.
Leading companies-including Illumina, Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, PerkinElmer, Agilent Technologies, Inc., and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.-continue to dominate the landscape through comprehensive product portfolios, robust global distribution networks, and sustained investment in R&D.
Firms such as Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., DH Life Sciences, LLC, and Abbott are expanding their footprint by focusing on advanced microfluidic applications in molecular diagnostics, infectious disease testing, and personalized medicine.
Emerging players such as Standard BioTools Inc. and Parallel Fluidics, Inc. are steadily gaining market traction by offering customizable, cost-efficient microfluidic solutions tailored to specialized research and diagnostic needs. Companies that balance scientific validation with lifestyle relevance and ethical sourcing will be best positioned to capture long-term value in the evolving women’s health and beauty supplements landscape.
Key Microfluidics Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the microfluidics market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Illumina, Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Revitty
- Danaher Corporation
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Abbott
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Standard BioTools, Inc.
- Qiagen N.V.
Recent Developments
-
In December 2024, Dapu Biotechnology (DPBIO) and Leveragen announced a strategic partnership to advance antibody discovery. DPBIO's Cytospark platform utilizes droplet microfluidics to rapidly screen millions of single cells, reducing antibody discovery timelines from months to just 1-2 days. This collaboration addresses complex therapeutic targets and accelerates the development of novel antibody-based treatments.
-
In November 2024, Parallel Fluidics secured a USD 7M seed round to accelerate the development of its microfluidic manufacturing platform for life science applications. The company aims to solve engineering challenges in diagnostics, drug discovery, and precision medicine by delivering production-ready devices, reducing development time and cost. Parallel Fluidics is revolutionizing the field by enabling faster and more scalable product development, particularly for applications like point-of-care diagnostics and fertility treatments.
-
In July 2024, Bio-Rad Laboratories launched Celselect Slides 2.0, a microfluidics-based solution designed to enhance the capture of rare and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) for cancer research. The upgrade leverages the power of microfluidic technology to drive advancements in cancer research by enabling higher throughput and better recovery of valuable CTCs.
Microfluidics Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2026
USD 46.90 billion
Revenue forecast in 2033
USD 105.13 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 12.22% from 2026 to 2033
Base year for estimation
2025
Historical data
2021 - 2024
Forecast period
2026 - 2033
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2026 to 2033
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Product, technology, material, application, region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; UK; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; India; China; Japan; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; UAE; South Africa; Kuwait
Key companies profiled
Illumina, Inc.; Agilent Technologies, Inc.; Revitty; Danaher Corporation; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Abbott; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Standard BioTools, Inc.; Qiagen N.V.
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analyst’s working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Global Microfluidics Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth and provides an analysis on the latest trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this report, Grand View Research has segmented the microfluidics market report based on product, technology, material, application, and region.
-
Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Microfluidic-based Devices
-
Microfluidic Components
-
Chips
-
Micro-pumps
-
Sensors
-
Others
-
-
-
Technology Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Lab-on-a-chip
-
Organ-on-a-chip
-
Continuous Flow Microfluidics
-
Optofluidics & Microfluidics
-
Acoustofluidics & Microfluidics
-
Electrophoresis & Microfluidics
-
-
Material Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Silicon
-
Glass
-
Polymer
-
PDMS
-
Others
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Medical
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Medical Devices
-
In-vitro Diagnostics
-
Others
-
-
Non-medical
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
UK
-
Germany
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Denmark
-
Sweden
-
Norway
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
Japan
-
China
-
India
-
South Korea
-
Australia
-
Thailand
-
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
South Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
UAE
-
Kuwait
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global microfluidics market size was estimated at USD 41.92 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 46.90 billion in 2026.
b. The global microfluidics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 12.22% from 2026 to 2033 to reach USD 105.13 billion by 2033.
b. The medical technology segment dominated the microfluidics market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 86.42% in 2025. Microfluidics is gaining significant traction in Point-of-Care (POC) diagnostics since it is associated with several advantages that facilitate the development of novel POC diagnostics.
b. The Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) segment dominated the microfluidics market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 34.99% in 2025. The material offers several advantages, such as biocompatibility, permeability, and low levels of autofluorescence, which broaden its applications in biotechnology & biomedical engineering.
b. North America dominated the microfluidics market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 42.85% in 2025. Research institutes are showing extensive participation in the development of novel microfluidic devices, which is expected to maintain regional dominance in the global market.
b. The lab-on-a-chip segment dominated the microfluidics market with a share of 38.71% in 2025. This is because lab-on-a-chip offers high detection speed while maintaining the same sensitivity during DNA or RNA amplification and detection procedures. Lab-on-a-chip also allows the rapid sequencing of DNA probes.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.