- Home
- »
- Market Trend Reports
- »
-
Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market: Geopolitical Impact Analysis And Opportunity Outlook
Report Overview
The global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is witnessing notable shifts driven by intensifying geopolitical developments, trade policy interventions, and industry-led capacity expansions. These factors are reshaping outsourcing strategies across the value chain, further accelerating regional diversification, accelerating investments in advanced therapy manufacturing, and reshaping competitive positioning of CDMOs worldwide. For instance, in the U.S., the federal government has taken several initiatives to reduce dependence on foreign pharmaceutical supply chains. The country has established a Strategic API Reserve and is providing direct funding to boost local production of APIs and essential medicines, while also indicating that it may impose wider tariffs on imported drugs and raw materials. These changes are already being translated into significant private sector investments by several pharmaceutical companies. For instance, Eli Lilly announced to invest USD 5 billion in a manufacturing facility in Virginia, which aims to strengthen the company’s ability to secure domestic production of important therapies. Thus, these geopolitical realignments are not only mitigating supply chain risks but also creating new growth avenues for CDMOs that can balance cost efficiency with regional resilience and advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Supply Chain Outlook
The supply chain outlook for pharmaceutical contract manufacturing is witnessing significant transition from cost-centricity to resilience and risk diversification. China and India previously accounted for the bulk of API and intermediate production, however the supply chain disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic, compounded by escalating trade frictions, have compelled governments and pharmaceutical companies to accelerate onshoring and nearshoring initiatives. In the U.S., tariff risks and national security concerns are accelerating contracts for local formulation and packaging facilities, while in Europe, energy cost fluctuations and logistic challenges are prompting stronger regional self-reliance. India continues to capture significant market share by securing long-term supply agreements for APIs and generic formulations, reinforced by large-scale investments in manufacturing clusters. Thus, the pharmaceutical contract manufacturing supply chain is expected to evolve into a multi-tier structure where critical drugs and injectables are sourced locally or regionally under strategic contracts, while commoditized generics remain heavily outsourced to Asia for cost advantages..
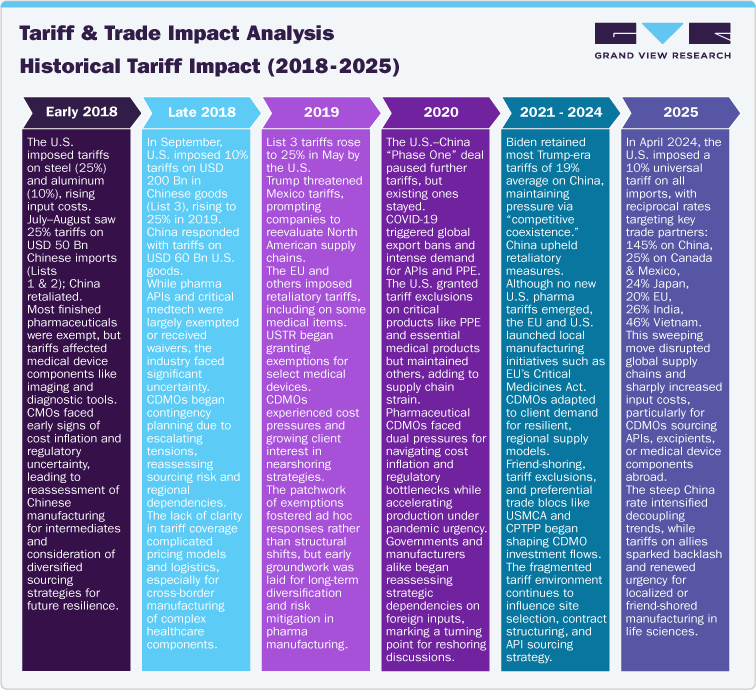
Input cost inflation: The initial U.S. tariffs on steel (25%) and aluminum (10%) in early 2018 and the 25% Section 301 import tax on Chinese imports raised raw material costs for CDMOs. Sector analyses indicate API and excipient costs rose by 10–25%, squeezing CDMO margins by approximately 3 percentage points on average. Similarly, medical device component costs such as precision metals, electronic parts, etc. spiked 15–20%, driving device CMO input costs higher.
Trade Diversion and Manufacturing Shifts: As U.S. imports of Chinese medical devices fell by around 30% in H2 2018–H1 2019, importers shifted USD 10 billion of device sourcing to Mexico and Vietnam, boosting Mexico’s share of U.S. device imports from 17% in 2018 to 20% in 2019. In pharmaceuticals, India’s API export volume to the U.S. increased by over 12% year-on-year in 2019 as Chinese APIs became costlier, supporting India’s pharma CDMO market growth from USD 7.4 billion in 2018 to USD 12.5 billion in 2023.
U.S.-Mexico-Canada Trade Analysis
The U.S.-Mexico-Canada trade framework, particularly under the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), is significantly influencing pharmaceutical contract manufacturing strategies across North America. For CMOs, this trilateral agreement provides a stable and predictable regulatory and tariff environment that encourages regional sourcing of both APIs and finished formulations. Mexico, with its lower labor costs and growing industrial infrastructure, has emerged as a nearshore manufacturing hub for U.S. sponsors seeking cost efficiency while maintaining supply chain proximity, particularly for generic drugs and sterile formulations.
Canada offers a highly regulated environment and advanced manufacturing capabilities, making it attractive for high-value products requiring stringent quality standards. The USMCA framework has also encouraged cross-border investment in capacity expansion, allowing contract manufacturers to optimize production networks by leveraging Mexico for cost-sensitive production, the U.S. for high-security or strategic drug manufacturing, and Canada for compliance-intensive formulations. Consequently, sponsors are increasingly restructuring their outsourcing strategies to exploit this regional advantage, balancing cost, regulatory alignment, and supply chain resilience while mitigating exposure to global trade frictions.
Tariff Escalation
Pharmaceutical trade policies underwent a major transformation, introducing customs duties that span from basic raw ingredients to final drug products in 2025. Firms are now evaluating the impact and formulating strategies to navigate these increasing tariff levels.
The updated tariff framework introduces a stepwise escalation approach aimed at encouraging the growth of domestic pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Phase 1: Minimal initial tariffs to allow companies time to adapt
Phase 2: Tariffs increase to 150% after 12–18 months of enforcement
Phase 3: Tariffs reach a maximum of 250%, compelling full-scale supply chain adjustments
Immediate Implementation: A 10% baseline duty on all pharmaceutical imports effective from 2025
Product Category
Country/Region
Current Tariff Rate
Target Impact
Medical Devices
Canada/Mexico
25%
Reduce NAFTA dependencies
Manufacturing Equipment
Switzerland/Germany/India
25%
Increase domestic facility costs
Finished Pharmaceuticals
All Countries
10% baseline
General import reduction
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
China
Up to 245%
Force domestic production
Immediate Market Impact and Price Projections
The proposed 25% tariff on pharmaceutical imports is projected to increase U.S. drug costs by approximately USD 51 billion annually, potentially raising prices by up to 12.9% if manufacturers pass these costs to consumers. This tariff would significantly impact generic medications, which constitute over 90% of U.S. prescriptions. Due to their reliance on imported active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), particularly from countries like India and China, generic drug prices could rise by approximately 17.5%. Such increases may lead to affordability challenges for patients, especially those dependent on essential treatments.
Global API and Intermediates Supply Concentration Analysis
APIs and intermediates are the backbone of contract manufacturing, and their geographic concentration contributes to the market risk. While India and China dominate volume production, this concentration introduces systemic vulnerability, as disruptions in either country can have cascading effects on global supply chains. Thus, these factors have led governments and sponsors to incentivize diversification, including multi-country sourcing and strategic stockpiling of critical APIs. Contract manufacturers that can establish integrated sourcing networks across multiple geographies, coupled with robust quality and compliance protocols, are positioned to capture long-term outsourcing contracts, particularly for essential medicines and high-demand generics.
Supply Chain Challenges and Opportunity Analysis, by Key Countries
Several structural challenges affect contract manufacturing supply chains, including rising raw material costs, logistical bottlenecks, regulatory divergence, and capacity constraints in regional hubs. On the opportunity side, these pressures are driving sponsors toward onshoring initiatives in North America and Europe, nearshoring in Latin America, and multi-site collaborations in Asia, creating openings for CMOs capable of providing both volume and resilience. For instance, the U.S. emphasis on local API reserves and formulation manufacturing has accelerated investment in domestic facilities, while India continues to leverage cost competitiveness and scale for contract manufacturing of generics and intermediates. These dynamics underscore the growing importance of strategically located contract manufacturing sites and diversified supply chains to meet global demand while mitigating geopolitical and operational risks.
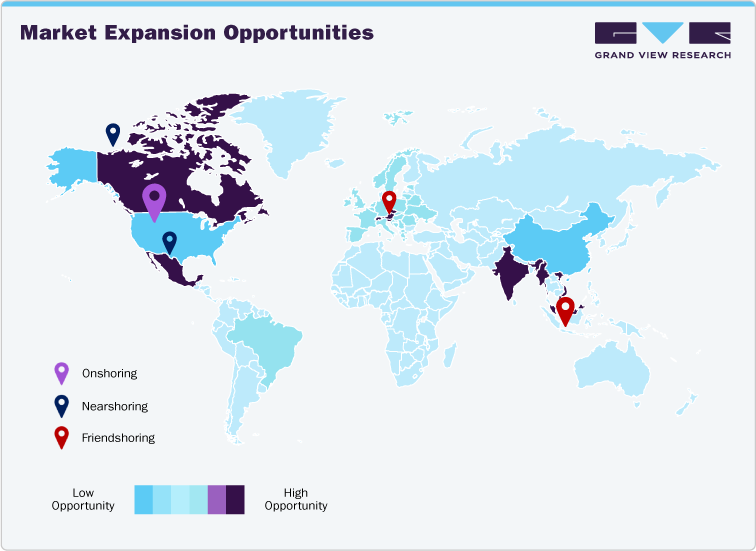
Onshoring Strategies
Onshoring involves relocating pharmaceutical manufacturing back to the domestic market to reduce exposure to tariffs and supply chain risks. For instance, Pfizer has expanded its U.S.-based vaccine and injectable production lines to avoid import duties on finished products. Similarly, Johnson & Johnson has shifted some of its API processing from India to U.S. facilities, ensuring continuity of supply while minimizing additional tariff costs. These measures allow companies to maintain control over production quality and timelines while mitigating financial risks associated with escalating international tariffs.
Nearshoring & Friendshoring Strategies
Nearshoring and friendshoring focus on moving production closer to key markets or to allied countries to reduce tariffs and geopolitical risk. A practical example is a generic drug manufacturer relocating tablet formulation operations from China to Mexico to efficiently serve the U.S. market under USMCA trade benefits. Similarly, Roche has opted to source certain intermediates from Canada instead of higher-tariff countries, stabilizing costs and ensuring smoother supply chain operations. These strategies help companies maintain competitive pricing while strengthening regional supply resilience.
Regional Expansion/Collaboration Strategies
Regional expansion and collaborative approaches involve extending manufacturing capacity or forming partnerships within strategic markets. Novartis, for example, has entered a joint venture with a European pharmaceutical company to expand biologics production within the EU, sharing infrastructure and R&D costs. Sanofi has expanded its Indian production facility in collaboration with a local firm, enabling it to serve both domestic and Asian markets while mitigating import tariffs on finished products. Such strategies enhance market access, optimize resource utilization, and provide flexibility to navigate complex tariff regimes.

Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


