- Home
- »
- Organic Chemicals
- »
-
Gas Hydrates Market Size & Share, Industry Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![Gas Hydrates Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Gas Hydrates Market (2025 - 2030) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Grade (Onshore Gas Hydrates, Offshore/Marine Gas Hydrates), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Vehicle Fuel, Energy), By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-528-4
- Number of Report Pages: 80
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Bulk Chemicals
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Gas Hydrates Market Summary
The global gas hydrates market size was estimated at USD 2.92 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 3.99 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2025 to 2030. Gas hydrates, often referred to as "flammable ice", are crystalline substances consisting of water and natural gas (primarily methane) trapped in a solid lattice structure.
Key Market Trends & Insights
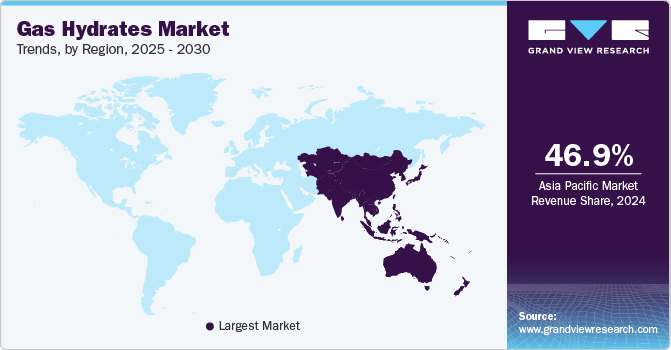
- Asia Pacific dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of over 46.9% in 2024.
- China held over 53.8% revenue share of the overall Asia Pacific gas hydrates industry.
- By grade, onshore gas hydrates segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 54.5% in 2024.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 2.92 Billion
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 3.99 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2030): 5.4%
- Asia Pacific: Largest market in 2024
These compounds are predominantly found in permafrost regions and deep ocean sediments, where low temperatures and high pressures create suitable conditions for their formation. Recognized as a potential game-changer in the global energy market, gas hydrates hold immense promise as an alternative energy source due to the vast reserves distributed worldwide.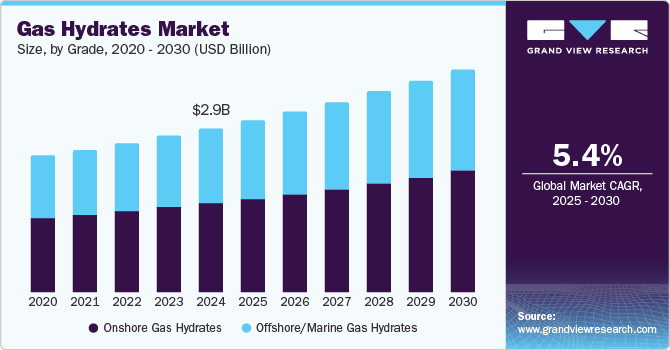
The demand for gas hydrates is driven by the growing global energy requirements and the need for sustainable alternatives to conventional fossil fuels. With depleting oil and gas reserves, industries and governments are exploring gas hydrates as a viable solution to bridge the energy gap. Moreover, advancements in extraction technologies have made the commercial utilization of gas hydrates increasingly feasible, especially in energy-hungry regions like Asia-Pacific. Countries such as Japan, India, and China are already investing heavily in research and development to harness the potential of these resources.
Despite its promise, the gas hydrate market faces several challenges, including complex extraction processes, environmental concerns, and high production costs. However, technological innovations, combined with a growing focus on energy security and sustainability, are expected to drive further exploration and development. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, gas hydrates could play a pivotal role in meeting future energy demands while reducing carbon footprints, provided the environmental and technical hurdles are addressed effectively.
Drivers, Opportunities & Restraints
The gas hydrate industry is primarily driven by the increasing global demand for energy and the depletion of conventional fossil fuel reserves. Gas hydrates, with their vast and untapped reserves, present a promising solution to meet this growing energy need. Additionally, advancements in extraction technologies, such as depressurization and thermal stimulation, have made the commercial recovery of gas hydrates more feasible, further boosting their market potential. The involvement of government and private entities in research and exploration, particularly in energy-hungry regions like Asia-Pacific-has also contributed significantly to the growth of the market.
The market for gas hydrates offers immense opportunities, especially as the world pivots toward sustainable energy solutions. Gas hydrates are seen as a transitional energy source that can bridge the gap between traditional fossil fuels and renewable energy systems. Countries like Japan, India, and China are investing in pilot projects to commercialize gas hydrate extraction, creating pathways for economic and energy security. Furthermore, the potential discovery of new reserves in underexplored regions, coupled with ongoing innovations in extraction and environmental impact mitigation, opens doors for significant market expansion in the coming years.
Despite its potential, the gas hydrate market faces several challenges and restraints. The complex and costly extraction processes remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Environmental concerns, such as the potential release of methane (a potent greenhouse gas) during extraction, also raise questions about the sustainability and safety of commercial operations. Additionally, the lack of mature infrastructure for hydrate recovery and the uncertainty surrounding long-term ecological impacts further hinder market growth. Addressing these restraints will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of the gas hydrate market in the future.
Grade Insights
Onshore gas hydrates are naturally occurring methane hydrates found beneath permafrost regions or within continental landmasses where low temperatures and sufficient pressure conditions exist. These deposits are typically located in areas with permanently frozen grounds, such as Siberia, Alaska, or northern Canada. Onshore gas hydrates are considered more accessible compared to their offshore counterparts due to their location on land, which eliminates the need for subsea operations. This accessibility makes them an appealing option for exploration, especially in regions where traditional oil and gas projects are already established.
However, extracting onshore gas hydrates comes with its own set of challenges. The permafrost layers that host these hydrates are sensitive to climatic changes, meaning extraction activities must be conducted carefully to avoid environmental degradation and the release of methane. Additionally, the logistical difficulties of operating in remote and harsh conditions can escalate project costs. Despite these challenges, onshore gas hydrates are gaining attention as an energy resource due to their potential to supplement local energy supplies in isolated regions.
Offshore or marine gas hydrates are found under deep-sea sediments along continental margins, where high-pressure and low-temperature conditions are ideal for their formation. These deposits are far more abundant than onshore hydrates, making them a critical focus for global energy exploration. Marine gas hydrates are often located in the gas hydrate stability zone, a layer beneath the seafloor where water pressure and temperature create a stable environment for hydrate formation. Regions such as the Gulf of Mexico, the Arctic Ocean, and the Indian Ocean hold significant offshore gas hydrate reserves.
Application Insights
Gas hydrates have diverse applications across several sectors, making them a promising alternative energy source. In the residential sector, gas hydrates can be utilized to provide natural gas for household heating, cooking, and electricity generation. With an increasing focus on clean and efficient energy solutions, the potential use of gas hydrates in residential applications could reduce dependency on conventional fuels like coal and oil, particularly in remote areas where hydrate reserves are abundant.
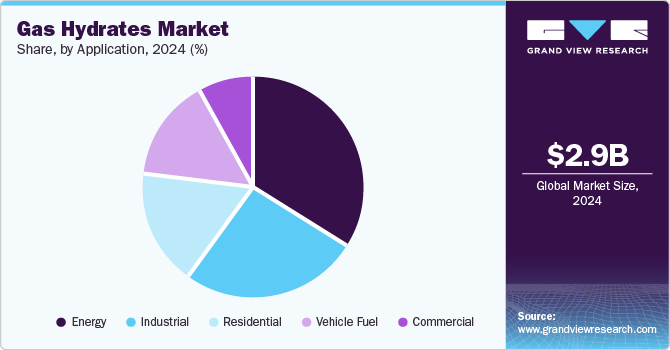
The commercial sector can leverage gas hydrates for large-scale energy needs, such as powering office spaces, shopping complexes, and public infrastructure. This application becomes especially relevant in urban areas seeking sustainable and reliable energy solutions. Similarly, the industrial sector stands to benefit significantly from gas hydrates, given the high energy demands of manufacturing, refining, and chemical production. Industries can use the extracted methane from hydrates as a feedstock or fuel, reducing reliance on dwindling traditional natural gas reserves.
Another promising application lies in the vehicle fuel sector, where methane obtained from gas hydrates can be processed into compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). These fuels are cleaner alternatives to diesel and gasoline, offering reduced emissions and improved energy efficiency for transportation. Lastly, gas hydrates hold immense potential as a source of energy generation, where methane can be used in power plants to meet growing electricity demands while transitioning toward cleaner energy systems. As technology evolves, these diverse applications of gas hydrates could redefine the global energy landscape.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific has emerged as a key focus area for gas hydrate exploration and development, driven by its rapidly growing energy demands and limited conventional energy resources in many countries. Countries like Japan, India, and China are leading the charge in gas hydrate research, recognizing the immense potential of these resources to bolster energy security and reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. The region is home to significant marine gas hydrate reserves, particularly along the continental margins of the South China Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Sea of Japan, which provide a strong foundation for the growth of the gas hydrates industry.
China Gas Hydrates Market Trends
The China gas hydrates market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the nation's increasing demand for energy and its focus on achieving energy security. As the world's largest energy consumer, China is actively exploring alternatives to conventional fossil fuels, and gas hydrates have emerged as a promising solution. The country has made substantial progress in identifying and developing marine gas hydrate reserves, particularly in the South China Sea, which is believed to hold vast untapped deposits.
North America Gas Hydrates Market Trends
One of the key trends in the North America gas hydrates industry is the focus on technological innovation and environmental sustainability. Companies and research institutions are exploring advanced extraction methods, such as depressurization and thermal stimulation, to make hydrate production more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Additionally, North America’s strong infrastructure for oil and gas exploration, combined with the region's expertise in deepwater drilling, positions it as a leader in the development of marine gas hydrates.
Europe Gas Hydrates Market Trends
The market in Europe is being driven by the region's strong focus on energy security and environmental sustainability. As European countries reduce their dependence on imported energy, particularly natural gas, gas hydrates are being considered as an alternative resource for future energy needs. Additionally, Europe's leadership in green energy technologies is playing a role in driving investments in sustainable gas hydrate extraction and utilization methods. Research initiatives supported by the European Union and collaborations with institutions globally are helping to advance knowledge about hydrate formation, extraction, and environmental impact.
Latin America Gas Hydrates Market Trends
Latin America's abundant natural resources and growing energy needs are key drivers for the development of the gas hydrates industry. Countries in the region, such as Mexico and Brazil, are already major players in offshore energy production and possess advanced infrastructure and expertise in deep-sea oil and gas drilling. This positions them well to explore and potentially exploit gas hydrate reserves. Additionally, as the global energy landscape shifts toward cleaner fuels, the methane extracted from gas hydrates is being considered as a low-carbon alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Middle East & Africa Gas Hydrates Market Trends
The region's growing energy demand, driven by rapid industrialization and population growth, presents an opportunity for gas hydrates to emerge as a supplementary energy source in the future. Countries in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) are actively pursuing energy diversification strategies to reduce reliance on oil and gas exports, which could eventually lead to investments in unconventional resources like gas hydrates. Additionally, Africa's offshore basins, particularly along the coasts of countries like Mozambique and Tanzania, are believed to hold untapped gas hydrate reserves, which could be explored as part of the region's broader energy development initiatives..
Key Gas Hydrates Company Insights
Some of the key players operating in the gas hydrates industry include China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec); Shell Plc.; TotalEnergies SE; PetroChina Company Limited; Japan Petroleum Exploration Company Limited; Oil and Natural Gas Corporation; and Gail Limited.
-
China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec) is one of the largest state-owned energy and chemical companies in China, headquartered in Beijing. The company operates as a vertically integrated energy giant, engaging in a wide range of activities, including oil and gas exploration, production, refining, storage, transportation, and marketing.
-
TotalEnergies SE, formerly known as Total S.A., is a French multinational and one of the world's largest integrated energy companies. The company operates across the entire energy value chain, including oil and gas exploration, production, refining, transportation, and marketing, as well as renewable energy and low-carbon solutions.
Key Gas Hydrates Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the gas hydrates market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- TotalEnergies SE
- Sinopec
- Shell Plc.
- PetroChina Company Limited
- Japan Petroleum Exploration Company Limited
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation
- Gail Limited
- Chevron Corporation
- Woodside Inc.
- Japan Drilling Co., Ltd.
- Schlumberger Limited
- PJSC Gazprom
Recent Developments
-
In March 2024, geologists from the University of the Philippines Diliman College of Science National Institute of Geological Sciences (UPD-CS NIGS) discovered evidence of gas hydrates in the Manila Trench, located west of Luzon and Mindoro. This discovery highlights the potential of the western Philippines as a significant source of this unconventional energy resource.
Gas Hydrates Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 3.07 billion
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 3.99 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 5.4% from 2025 to 2030
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2018 - 2023
Forecast period
2025 - 2030
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million/billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Grade, application, region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; France; Italy; Spain; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; South Africa
Key companies profiled
TotalEnergies SE; Sinopec; Shell Plc.; PetroChina Company Limited; Japan Petroleum Exploration Company Limited; Oil and Natural Gas Corporation; Gail Limited; Chevron Corporation; Woodside Inc.; Japan Drilling Co., Ltd.; Schlumberger Limited; PJSC Gazprom
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Gas Hydrates Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue and volume growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global gas hydrates market report based on grade, application, and region.
-
Grade Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Onshore Gas Hydrates
-
Offshore/Marine Gas Hydrates
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Residential
-
Commercial
-
Industrial
-
Vehicle Fuel
-
Energy
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
Italy
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
South Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global gas hydrates market size was estimated at USD 2.92 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 3.07 billion in 2025.
b. The global gas hydrates market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.4% from 2025 to 2030 to reach USD 3.99 billion by 2030.
b. Asia Pacific dominated the gas hydrates market with a share of 46.9% in 2024. The growth and expansion of end-use industries in key markets like India, China, South Korea, and Japan are expected to drive the demand for gas hydrates in the region.
b. Some key players operating in the gas hydrates market include TotalEnergies SE; Sinopec; Shell Plc.; PetroChina Company Limited; Japan Petroleum Exploration Company Limited; Oil and Natural Gas Corporation; Gail Limited; Chevron Corporation; Woodside Inc.; Japan Drilling Co., Ltd.; Schlumberger Limited; PJSC Gazprom.
b. High demand for clean and renewable energy to boost gas hydrates in pipelines rises demand for gas hydrates market.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.