- Home
- »
- Clinical Diagnostics
- »
-
Neurological Biomarkers Market Size, Industry Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![Neurological Biomarkers Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Neurological Biomarkers Market (2025 - 2030) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Application (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis, Autism), By Type, By End Use, By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-3-68038-823-7
- Number of Report Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2024
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Healthcare
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Interactive Charts
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Neurological Biomarkers Market Summary
The global neurological biomarkers market size was estimated at USD 9.1 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 18.75 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 12.9% from 2025 to 2030. Some of the major factors expected to drive the market are the increasing prevalence of neurological diseases and growing awareness about the condition among physicians & patients.
Key Market Trends & Insights
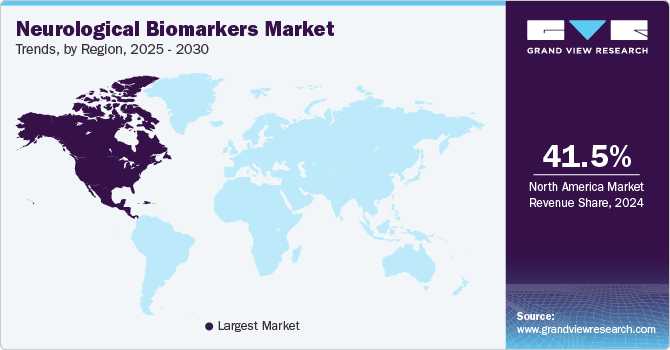
- The North America region commanded the highest share of around 41.47% of the neurological biomarkers market in 2024.
- The U.S. is expanding rapidly due to growing research funding, increasing neurodegenerative disease prevalence, and technological advancements.
- Based on applications, the Alzheimer’s disease accounted for the largest share of 34.80% of the market in 2024.
- Based on type, the proteomic biomarkers accounted for the largest share of 30.62% of the market in 2024.
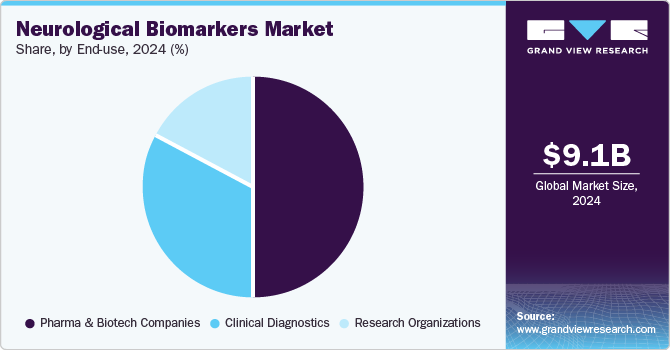
- Based on end use, the pharma & biotech Companies segment accounted for a significant share of 50.39% of the market in 2024.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 9.1 Billion
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 18.75 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2030): 12.9%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
Furthermore, technological advancements and growing R&D efforts for neurological disease drug development further propel the overall market.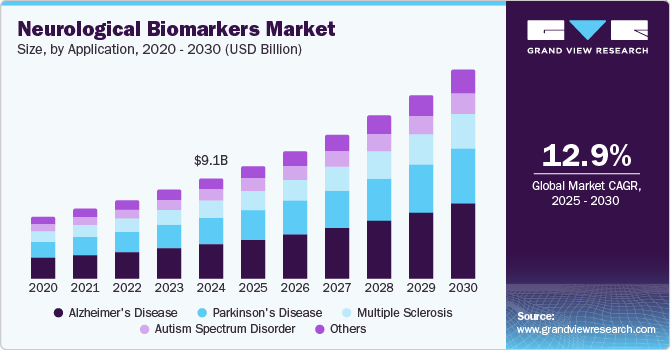
The increasing integration of biomarkers into clinical practice and neurological research has significantly propelled market growth. Technological advancements have enhanced the precision and sensitivity of biomarker assays, enabling faster and more accurate disease detection. Cross-disciplinary developments in neurology continue to expand the biomarker landscape, driven by an improved understanding of disease pathophysiology and the ability to measure multiple biological variables with high accuracy.
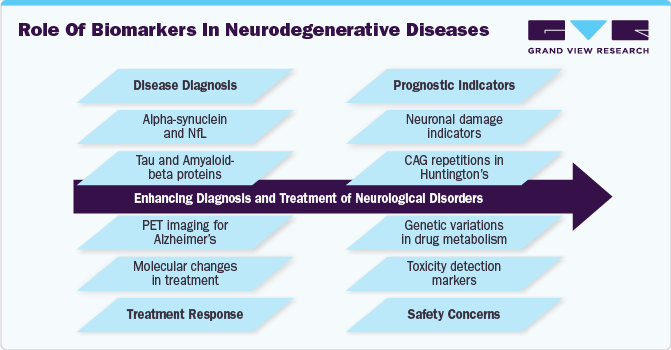
Neurological biomarkers are crucial in guiding clinical diagnosis, estimating disease risk, assessing prognosis, evaluating disease progression, and monitoring therapeutic response. In clinical trials, biomarkers are instrumental in patient stratification, ensuring therapeutic target engagement, tracking downstream effects of treatment, and assessing drug efficacy and safety. Their growing importance in drug development and personalized medicine has led to increased adoption by pharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
The discovery and implementation of biomarkers have revolutionized neurology, particularly in neurodegenerative diseases. A landmark development was identifying low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid-β42 levels in Alzheimer’s disease, leading to the widespread clinical adoption of CSF biomarkers, including Aβ42/40, total tau, and phosphorylated tau. The success of these biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease has driven further research in Parkinson’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies. Advanced protein aggregation assays originally developed for prion diseases now offer new diagnostic opportunities for tauopathies and α-synucleinopathies.
The shift toward blood-based biomarkers has been a major market driver, overcoming past challenges related to the blood-brain barrier. Highly sensitive technologies such as Simoa (Single Molecule Array) and Mass Spectrometry now allow the detection of neurological biomarkers in biofluids at extremely low concentrations. This has led to the development of blood-based neurofilament light protein (NfL) assays, which serve as reliable indicators of neuronal damage in multiple neurological conditions, including multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, neurodegenerative disorders, and even neurological complications of COVID-19. The ease of sample collection and the ability to monitor disease progression using blood biomarkers have accelerated their adoption in both clinical practice and trials.
Imaging biomarkers have also seen notable advancements, significantly contributing to market expansion. High-resolution 7-Tesla MRI enables the detection of microscopic changes in brain structure, improving the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. The development of radiotracers, such as amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) using Pittsburgh Compound B and 18F-based tracers, has transformed Alzheimer’s disease diagnostics. Tau-specific tracers have further expanded the market, with applications extending to Alzheimer’s disease, chronic traumatic encephalopathy, and other tauopathies. Emerging tracers targeting synaptic loss and neuroinflammation hold promise for a wide range of neurological disorders, further driving market growth.
The increasing demand for early and accurate diagnosis, the expansion of precision medicine, and continuous technological innovations are key factors fueling market growth. The expanding use of biomarkers in both clinical settings and drug development is expected to drive significant investments and regulatory approvals, further solidifying their role in neurology.
The table below presents a compilation of potential biomarkers in neurological disorders.
Chronic neurological conditions/ neurodegenerative diseases
Pathological traits
Biomarkers
Parkinson’s disease
Lewy bodies and neurites containing α-synuclein aggregates lead to dopaminergic nigrostriatal neuron loss in the substantia nigra pars compacta
α-Synuclein, orexin, caspase-3, TCS, NfL, Aβ42, p-tau, CRP, D3R, 8-OHG, YKL-40, MCP-1, MHPG, GCase, GlcCer, cathepsin D, DJ-1
Alzheimer’s disease
Extracellular aggregates of amyloid β (Aβ) plaques, intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, and inflammation result in synapse dysfunction, neuronal loss, and brain atrophy
Tau, p-tau, NfL, FABP, A1-42, MCP-1, YKL-40, TREM2, neurogranin, amyloid PET, NSE, VLP-1, HFABP, albumin, GFAP, α -synuclein, t-tau, pT181-tau, pS396-tau
Huntington’s disease
CAG repeat expansion in the huntingtin gene causes progressive degeneration and atrophy of the striatum, resulting in neuronal loss and cell death
mHTT, tau, NFL, NFH, miRNA, TDP-43, NPY, PDE10A, MRI, PET
Multiple sclerosis
Inflammatory lesions form plaques in the brain and spinal cord’s gray and white matter, causing neuronal demyelination, axonal degeneration, and neurological dysfunction.
Tau, NFL, NFH, CXCL13, ApoE, MBP, OPN, NCAM1, NGF, CNTF, GFAP, tau, S100B, Ferritin, CD163, YKL-40, Kir4
Frontotemporal dementia
Aberrant tau aggregate accumulation in the brain leads to frontal lobe atrophy.
Aβ42, t-tau, pT181-tau, pS396-tau, NfL
Epilepsy
Neuronal signaling imbalance causes unpredictable, recurrent seizures, leading to neurodegeneration, blood-brain barrier (BBB) damage, and inflammation.
NeuN, PV, FJB, GFAP, IBA1, Timm, DCX, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, UCH-L1, NSE, MMP-9, S100B
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The degree of innovation in neurological biomarkers is advancing rapidly, enhancing early diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and personalized medicine. Cutting-edge biomarkers like neurofilament light chain (NfL) in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) provide real-time insights into neurodegeneration, aiding in conditions like multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. Innovations such as alpha-synuclein detection for Parkinson’s disease and PET imaging for amyloid-beta plaques in Alzheimer’s enable precise disease characterization. In addition, machine learning integration with biomarker analysis enhances predictive accuracy. These advancements improve early intervention, optimize therapeutic strategies, and reduce healthcare costs, making neurological biomarkers a crucial frontier in modern neurodiagnostics and treatment.
The neurological biomarkers industry has witnessed increasing M&A (mergers and acquisitions) activity, driven by the demand for advanced diagnostics and precision medicine. Large pharma and biotech firms are acquiring companies specializing in biomarker-based diagnostics to enhance drug discovery and neurodegenerative disease management. For example, Roche acquired Foundation Medicine to expand biomarker-driven neurology research. Similarly, Biogen acquired Neurimmune’s Alzheimer’s biomarker platform, strengthening its position in neurodegenerative research. Thermo Fisher Scientific’s acquisition of PPD bolstered its biomarker-driven clinical research capabilities. These deals reflect a strong industry push toward leveraging biomarkers for early disease detection, personalized treatments, and clinical trial optimization.
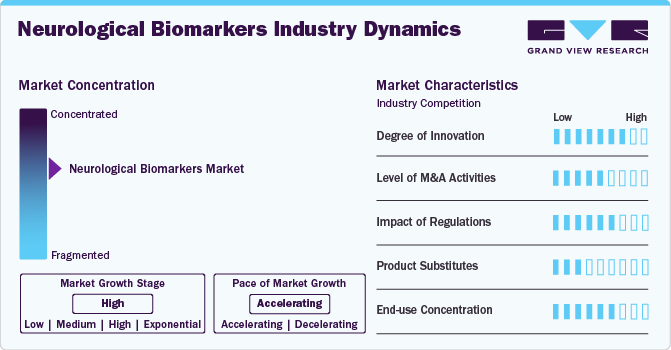
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence neurological biomarkers' development, approval, and commercialization. Agencies like the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), and PMDA (Japan) impose stringent guidelines to ensure biomarker accuracy, reliability, and clinical utility. For example, the FDA’s Biomarker Qualification Program streamlines approval processes but requires extensive validation, delaying market entry. EU’s In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) has introduced a stricter classification for diagnostic biomarkers, increasing compliance costs. Data privacy laws such as HIPAA (U.S.) and GDPR (Europe) also impact biomarker-based research by regulating patient data usage. These evolving regulations shape market dynamics, innovation speed, and investment trends.
The neurological biomarkers industry faces competition from various alternative diagnostic technologies. Neuroimaging techniques such as MRI, PET, and CT scans remain widely used for diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson’s, reducing dependence on biomarkers. Genetic testing, including whole genome sequencing and polygenic risk scoring, provides predictive insights, potentially replacing biomarker-based early detection. Clinical assessments, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), offer cost-effective diagnostic approaches. Electrophysiological tests like EEG and EMG also measure brain and nerve activity, serving as non-invasive alternatives. These substitutes influence biomarker adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive healthcare markets where affordability and accessibility are crucial.
The neurological biomarkers industry is expanding geographically due to increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure, rising disease prevalence, and growing R&D activities. North America dominates due to strong funding, regulatory support, and the presence of key market players. Europe follows with robust research initiatives and government-backed neurological programs. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a high-growth region, driven by expanding healthcare access, rising neurodegenerative disease cases, and increasing biomarker research in China, Japan, and India. Latin America and the Middle East are gradually adopting advanced biomarker technologies, supported by improving healthcare policies and international collaborations, creating new opportunities for market penetration.
Applications Insights
Alzheimer’s disease accounted for the largest share of 34.80% of the market in 2024 and is expected to dominate the market over the forecast period due to a rise in the prevalence of the disease and increasing awareness for early diagnosis and timely treatment. In addition, Labcorp's launch of the pTau217 test in 2024 represents a major advancement in Alzheimer's disease diagnostics. This biomarker, a crucial indicator of tau pathology, enhances early detection and disease monitoring, particularly in patients undergoing anti-amyloid therapy. Given that Alzheimer's affects 6.7 million Americans-a number projected to reach 13.8 million by 2060-the demand for accurate, minimally invasive testing is growing. This test complements Labcorp's existing biomarker portfolio, which includes the beta-amyloid 42/40 ratio, neurofilament light chain (NfL), and the ATN Profile-a combined panel assessing Alzheimer’s-related pathologies. The introduction of pTau217 provides physicians and biopharma partners with a powerful new tool for clinical trials, early intervention, and treatment monitoring, marking a significant step forward in neurodegenerative disease diagnostics.
Moreover, the Parkinson’s disease segment is also expected to grow fastest during the forecast period. Increasing R&D activities in biomarkers may offer new opportunities for Parkinson’s therapeutics. For instance, Merck and The Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF) are advancing Parkinson’s disease (PD) research with the SMCxPRO® immunoassay technology, enabling the detection of pS65 ubiquitin (pS65-Ub), a biomarker linked to cell dysfunction. With MJFF’s support, this technology is now available to the scientific community, helping track therapeutic responses to PD progression. Since 60-80% of nerve cells are already impaired when motor symptoms appear, detecting early dysfunction is crucial. The SMCxPRO platform allows researchers to measure low biomarker concentrations, enhancing diagnostics, patient stratification, and therapy development. Given that PD affects 10 million people globally, with cases projected to reach 20 million by 2050, this collaboration aims to develop disease-modifying treatments, as current therapies only address symptoms without slowing progression.
Type Insights
Proteomic biomarkers accounted for the largest share of 30.62% of the market in 2024. Proteomic biomarkers are increasingly pivotal in the market, especially for neurodegenerative diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Parkinson's disease (PD). These biomarkers facilitate early diagnosis and monitor disease progression by identifying specific protein alterations associated with neuronal degeneration. For instance, in ALS, proteomic analyses have revealed changes in proteins such as TDP-43, accumulating abnormally in affected neurons. Similarly, in PD, alterations in α-synuclein and its post-translational modifications have been identified, providing insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Technological advancements in mass spectrometry and bioinformatics have enhanced the detection and quantification of these protein changes in biological samples like cerebrospinal fluid and plasma, driving the adoption of proteomic biomarkers in clinical and research settings. The growing prevalence of neurodegenerative disorders and the demand for personalized medicine further propel the integration of proteomic biomarkers into neurology.
The others segment which includes transcriptomic and phenomicis, is anticipated to witness significant growth over the forecast period. Advancements in multi-omics technologies fuel this expansion, the growing need for personalized medicine, and the increasing prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases. Transcriptomic biomarkers analyze RNA expression levels to identify gene activity associated with neurological disorders. For instance, studies have found that altered RNA expression patterns in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can serve as early indicators of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. A notable example is the identification of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) that differentiate Parkinson’s patients from healthy individuals, offering a non-invasive diagnostic tool. Phenomic biomarkers integrate biochemical, imaging, and behavioral data to comprehensively view neurological diseases. For example, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based phenomic biomarkers help detect white matter changes in multiple sclerosis (MS) before clinical symptoms appear-similarly, phenomic profiling of metabolic alterations in CSF aids in distinguishing Alzheimer’s disease from other dementias. These biomarkers drive innovation in neurological research, supporting early diagnosis, treatment response monitoring, and the development of targeted therapies.
End Use Insights
Pharma & Biotech Companies segment accounted for a significant share of 50.39% of the market in 2024, driven by increasing investment in neurodegenerative disease drug development and the demand for highly sensitive biomarker assays. These companies are crucial in advancing biomarker research to support diagnostics and therapeutic interventions for conditions such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson’s, and ALS. The growing need for precision medicine and early disease detection further accelerates their market dominance.
ADx NeuroSciences, a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujirebio, and Alamar Biosciences exemplify this trend through their partnership in developing customized biomarker assay solutions. By integrating Alamar’s NULISA™ (Nucleic Acid Linked Immuno-Sandwich Assay) immunoassay platform and ARGO™ HT System, they aim to enhance biomarker detection and quantification. These innovations provide pharmaceutical companies with tools for early diagnosis and monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases, which are essential for effective drug development.
Moreover, the expansion of biopharma collaborations and regulatory support for biomarker-driven clinical trials have strengthened pharma and biotech companies' market share. With the increasing global prevalence of neurological disorders, companies focus on developing more accessible and scalable biomarker technologies. The integration of next-generation immunoassays and high-throughput screening platforms is expected to sustain the sector’s leadership in driving advancements in neurological biomarker research and drug discovery.
Regional Insights
North America region commanded the highest share of around 41.47% of the neurological biomarkers market in 2024 and is expected to witness a significant growth rate over the forecast period. Growth of the region can also be attributed to the increasing understanding of significant potential of biomarkers in drug development. The local presence of regulatory entities in the region is also expected to fuel the growth of biomarker-based drug development in the near future. This is mainly because these entities are pivotal in creating awareness among the population about the potential of biomarker-based therapies in disease management.
U.S. Neurological Biomarkers Market Trends
The neurological biomarkers market in the U.S. is expanding rapidly due to growing research funding, increasing neurodegenerative disease prevalence, and technological advancements. One major trend is the development of multiplex biomarker panels, allowing simultaneous detection of multiple disease markers. For example, Quanterix’s Simoa technology enables ultra-sensitive measurement of neurofilament light chain (NfL), a key biomarker for multiple sclerosis and traumatic brain injuries.
Another emerging trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in biomarker analysis, improving diagnostic accuracy. Companies like C2N Diagnostics have developed AI-driven blood tests, such as the PrecivityAD test, which measures amyloid-beta levels to support Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Moreover, the increasing role of biomarkers in clinical trials is driving market growth. The FDA’s Biomarker Qualification Program has facilitated the acceptance of biomarkers as surrogate endpoints in drug development, accelerating the approval of new neurological therapies. These trends are shaping a dynamic and innovation-driven market landscape.
Europe Neurological Biomarkers Market Trends
The neurological biomarkers market in Europe is witnessing strong growth due to rising neurodegenerative disease cases, supportive regulatory frameworks, and advancements in biomarker-based diagnostics. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has promoted biomarker integration in drug development, accelerating research efforts. Companies like Roche and Fujirebio are expanding biomarker-based tests for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, leveraging CSF and blood-based assays. Furthermore, collaborative initiatives, such as the European Platform for Neurodegenerative Diseases (EPND), are fostering biomarker discovery. The increasing adoption of digital biomarker technologies, such as EEG and wearable devices for real-time neurological monitoring, is further shaping the market’s evolution.
France neurological biomarkers market is expanding due to government-backed research initiatives, increasing Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease prevalence, and advancements in biomarker-based diagnostics. The French National Plan for Neurodegenerative Diseases has prioritized biomarker research, fostering collaborations between institutions like Inserm and biotech firms. Companies such as BioMérieux and Cellectis are developing innovative biomarker-based diagnostic solutions. In addition, the growing integration of artificial intelligence in neurological biomarker analysis is enhancing early disease detection. France’s strong clinical trial ecosystem and partnerships with global pharma companies are further driving the adoption of neurological biomarkers for precision medicine applications.
The neurological biomarkers market in Germany is driven by strong government funding, cutting-edge research institutions, and a growing aging population. The German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) collaborates with universities and biotech firms to advance biomarker research for conditions like Alzheimer's and multiple sclerosis. Companies such as Roche and Siemens Healthineers are investing in biomarker-based diagnostics, integrating AI and precision medicine. Moreover, Germany’s emphasis on clinical trials and regulatory support for innovative neurological diagnostics is fostering market growth. With increasing demand for early disease detection and personalized treatments, the adoption of neurological biomarkers continues to rise across the country.
Asia Pacific Neurological Biomarkers Market Trends
The neurological biomarkers market in Asia Pacific is expanding rapidly due to increasing investments in research, a rising geriatric population, and growing awareness of neurodegenerative diseases. Countries like China and Japan are leading in biomarker research, with government-backed initiatives supporting early diagnosis and precision medicine. South Korea’s biotech sector is advancing blood-based biomarker tests, while India’s healthcare industry is witnessing increased adoption of biomarker-based diagnostics. Companies like Fujirebio and Sysmex are driving innovation, particularly in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease biomarkers. The region’s improving healthcare infrastructure and expanding clinical trials are further accelerating market growth.
Japan neurological biomarkers market is expanding due to its rapidly aging population and rising cases of neurodegenerative diseases. Japanese biotech firms like Takara Bio and Shionogi are investing in cutting-edge biomarker research, focusing on RNA-based and metabolic biomarkers for early disease detection. The country’s regulatory body, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), has accelerated approvals for innovative biomarker-driven diagnostics. Furthermore, institutions like RIKEN and Kyoto University are pioneering AI-driven biomarker analysis to enhance predictive accuracy in neurological disorders. Japan’s focus on integrating biomarkers into digital health platforms is further fueling market growth.
Latin America Neurological Biomarkers Market Trends
The neurological biomarkers market in Latin America is growing due to increasing awareness of neurodegenerative diseases and improved healthcare infrastructure. Countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are investing in biomarker research, driven by rising Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease cases. Brazilian institutions, such as Fiocruz and Butantan Institute, are developing biomarker-based diagnostic tools. Mexico is seeing increased collaborations between universities and global biotech firms for early biomarker detection in dementia. In addition, Argentina's National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) is advancing proteomic and genomic biomarker studies. Expanding clinical trials and government initiatives are further driving market development.
Brazil neurological biomarkers market is expanding due to a rising prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases and increasing investments in precision medicine. Institutions like Fiocruz and the University of São Paulo are actively developing biomarker-based diagnostic tools for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. The Brazilian government is also supporting biomarker research through funding programs such as FAPESP and CAPES, encouraging local innovation. Moreover, partnerships between public hospitals and global biotech firms are facilitating clinical trials for novel biomarker-based therapies. The growing adoption of AI-driven diagnostics and liquid biopsy techniques further accelerates market development in Brazil.
Middle East & Africa Neurological Biomarkers Market Trends
The neurological biomarkers market in the Middle East & Africa is witnessing growth due to increasing awareness of neurodegenerative diseases, improving healthcare infrastructure, and rising investments in medical research. Countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are driving advancements through government initiatives and collaborations with international biotech firms. For instance, Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 supports precision medicine, fostering research on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s biomarkers. South Africa is also emerging as a key player, with institutions like the University of Cape Town conducting biomarker-based studies. However, challenges such as limited funding and accessibility to advanced diagnostic technologies remain barriers to market expansion.
Saudi Arabia neurological biomarkers market is expanding due to government-backed healthcare initiatives, increasing R&D investments, and collaborations with global biotech firms. Under Vision 2030, the country is advancing precision medicine and neurodegenerative disease research, fostering biomarker development for conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Institutions such as King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre are actively conducting biomarker studies, integrating AI-driven diagnostics and genomic research. Furthermore, rising awareness and a growing elderly population are fueling demand for early disease detection. However, challenges like limited specialized neurology centers and high costs of advanced biomarker testing still hinder widespread adoption.
Key Neurological Biomarkers Company Insights
Companies are adopting strategies that allow them to use their resources to aid in the development of new products and enhance their supply chain. For instance, in March 2023, Abbott Laboratories announced the FDA clearance of the Alinity I laboratory traumatic brain injury (TBI) blood test, the first of its kind, which would assist medical professionals in evaluating individuals with mild TBIs. Furthermore, in July 2023 , Quanterix announced the launch of LucentAD, a biomarker blood test to assist in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease in individuals. Moreover, in Jan 2025, Beckman Coulter Diagnostics' latest breakthrough represents a major advancement in Alzheimer's disease diagnostics. The FDA's Breakthrough Device Designation for the Access p-Tau217/β-Amyloid 1-42 plasma ratio test underscores its potential to enhance early detection of amyloid pathology, a key characteristic of Alzheimer’s. Traditional methods, such as cerebrospinal fluid analysis and PET imaging, are often invasive and expensive. In contrast, this blood-based biomarker test provides a more accessible and efficient alternative, facilitating earlier and more accurate diagnosis. This innovation aligns with the increasing demand for non-invasive diagnostic tools in neurology, supporting precision medicine in managing neurodegenerative diseases.
Key Neurological Biomarkers Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the neurological biomarkers market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Abbott
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- DiaGenic ASA
- BANYAN BIOMARKERS, INC.
- Quanterix
- Alseres Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Rules-Based Medicine
- C2N Diagnostics
Neurological Biomarkers Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 10.21 billion
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 18.75 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 12.9% from 2025 to 2030
Actual data
2018 - 2024
Forecast period
2025 - 2030
Report updated
April 2025
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million/billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Type, application, end use, region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; UK; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; India; China; Japan; Australia; Thailand; South Korea; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; UAE; South Africa; Kuwait
Key companies profiled
Abbott; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Merck & Co., Inc.; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; BANYAN BIOMARKERS, INC.; DiaGenic ASA; Banyan Biomarkers, Inc.; Rules-Based Medicine; Quanterix
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Global Neurological Biomarkers Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth and provides an analysis of the market trends in each of the sub-markets from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global neurological biomarkers market based on type, application, end use, and region:
-
Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Genomic
-
Proteomic
-
Metabolomic
-
Imaging
-
Others
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Alzheimer's Disease
-
Parkinson's Disease
-
Multiple Sclerosis
-
Autism Spectrum Disorder
-
Others
-
-
End Use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Research Organizations
-
Pharma & Biotech Companies
-
Clinical Diagnostics
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
UK
-
Germany
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Denmark
-
Sweden
-
Norway
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
India
-
China
-
Japan
-
Australia
-
South Korea
-
Thailand
-
-
Latin America
-
Argentina
-
Brazil
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
UAE
-
South Africa
-
Kuwait
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global neurological biomarkers market size was estimated at USD 9.1 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 10.21 billion in 2025.
b. The global neurological biomarkers market is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate of 12.9% from 2025 to 2030 to reach USD 18.75 billion in 2030.
b. Based on application, Alzheimer's Disease segment held the largest share of 34.80% in 2024, owing to high prevalence of the disease and availability of a higher number of products for clinical use.
b. Some key players operating in the neurological biomarkers market include Abbott; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Merck & Co., Inc.; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; BANYAN BIOMARKERS, INC.; DiaGenic ASA; Banyan Biomarkers, Inc.; Rules-Based Medicine; Quanterix
b. The major factors driving neurological biomarkers market growth are the increasing prevalence of neurological diseases, technological advancements, and the need for early diagnosis of neurological disorders.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.