- Home
- »
- Market Trend Reports
- »
-
Rapid Point-Of-Care Testing For Sickle Cell Anemia Market Trends And Competitive Market
Report Overview
The rapid point-of-care testing market for sickle cell anemia is experiencing robust growth, fueled by advancements in diagnostic technologies and increasing awareness of sickle cell disease (SCD), especially in high-prevalence regions such as India and sub-Saharan Africa. SCD is a hereditary blood disorder marked by the production of sickle-shaped red blood cells that obstruct normal blood flow, leading to complications such as severe pain, anemia, and potential organ damage. According to the Journal of Hematology and Allied Science (JHAS), India has one of the highest frequencies of the sickle β-globin allele globally, with an estimated 30 million carriers and regional prevalence ranging from 1% to 44%. These figures highlight the urgent need for widespread, efficient screening methods.
The evolution of point-of-care (POC) testing technologies is addressing this need by offering rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostics that significantly reduce the time between testing and results. Traditional laboratory testing often involves logistical hurdles and delays, particularly in remote or underserved areas. In contrast, modern POC devices such as Sickle SCAN-EZ, a multiplexed, qualitative immunoassay-deliver results in as little as five minutes and can differentiate between sickle cell trait, sickle cell anemia, and HbSC disease. Their compact design, ease of use, and minimal infrastructure requirements make these tools ideal for community health programs, mobile clinics, and rural healthcare settings.
Growth in this market is also driven by rising public health initiatives and policy focus on early diagnosis and management of hemoglobinopathies. Organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasize the importance of screening programs, particularly in countries with high carrier rates. The combination of technological innovation, increased funding for genetic disorder screening, and broader integration of POC solutions into national health strategies is expected to sustain the upward trajectory of this market. Moving forward, partnerships between device manufacturers, NGOs, and government health departments will be key to expanding access and ensuring early intervention for individuals affected by SCD.
Rapid Point-Of-Care Testing For Sickle Cell Anemia Market: Trends And Competitive Analysis Report Scope
Report Attributes
Details
Areas of Research
Industry trends, market opportunity, ease of doing business across countries, competitive analysis
Report Representation
Consolidated report in PDF format
Country Coverage
20+ Countries
Highlights of Report (Competitive Landscape, by country)
- Current & Future Market Opportunity Analysis
- Target Population Analysis
- Pricing Analysis
- Consumer Behavior Analysis
- Market Entry Strategies
- Barriers to Entry and Risks
- Potential Partnerships and Collaborations
- Company Strategy Mapping And Recent Developments
Rapid Point-Of-Care Testing For Sickle Cell Anemia Market: Trends And Competitive Analysis Coverage
Current & Future Market Opportunity Analysis
Strategic collaborations and partnerships are becoming increasingly essential in driving the growth of the rapid point-of-care testing market for sickle cell anemia. These alliances bring together technological, financial, and clinical expertise from diagnostic companies, healthcare institutions, research organizations, and governments. Such synergy plays a critical role in overcoming diagnostic challenges in low-resource settings, where conventional laboratory testing may be unavailable, expensive, or logistically impractical. By leveraging shared resources and innovation, these partnerships help develop and deploy efficient, decentralized diagnostic solutions tailored to the needs of underserved communities.
A notable example is the August 2021 collaboration between Mylab Discovery Solutions (India) and Hemex Health (USA). This partnership focuses on co-developing advanced POC diagnostics for various diseases, including SCA. Mylab contributes its expertise in assay development, while Hemex provides its Gazelle platform, a compact diagnostic device that delivers lab-quality results in minutes. Designed to function effectively in diverse and resource-limited environments, this combined technology offers a powerful tool for early and accessible disease detection. Such initiatives are streamlining diagnostics, enabling immediate clinical interventions, and ultimately improving patient outcomes in areas where timely testing was previously out of reach.
Investment and awareness are further propelling the POC testing market forward. In March 2023, Hemex Health received a USD 3 million grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) to bring the Gazelle device to the U.S. market. With successful deployments in 27 countries across Africa, Asia, and the Middle East, this funding supports Hemex's regulatory efforts and broader access in high-need areas. Similarly, BioMedomics, maker of Sickle SCAN, has launched a three-year Independent Research Grant Program beginning June 19, 2024-World Sickle Cell Disease Day. Focused on Sub-Saharan Africa, this initiative aims to enhance awareness, testing availability, and affordability through partnerships with local distributors, ensuring that life-saving diagnostics reach the populations that need them most.
Target Population Analysis
Rapid point-of-care (POC) diagnostic devices are vital in modern healthcare, particularly for conditions like sickle cell disease (SCD), which require swift diagnosis and long-term monitoring. These tools are especially valuable for populations that are medically underserved or face logistical barriers to traditional laboratory testing. SCD, a hereditary blood disorder that can cause severe health complications, presents a compelling case for targeted deployment of POC devices. By enabling early diagnosis and routine monitoring outside of advanced healthcare settings, POC diagnostics can bridge critical access gaps and improve disease management outcomes.
Globally, the burden of SCD has grown substantially. According to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), the number of individuals living with SCD increased by 41.4%-from 5.46 million in 2000 to 7.74 million in 2021. This rise is largely driven by population growth in western and central sub-Saharan Africa and the Caribbean. In 2021, 515,000 babies were born with SCD worldwide, a 13.7% increase since 2000. Tragically, SCD-related complications led to the deaths of 81,100 children under five, making it the 12th leading cause of all-age mortality globally, as reported by the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. These figures underscore the urgent need for accessible diagnostic tools that can detect and manage the disease early, especially in high-burden regions.
In the U.S., SCD impacts an estimated 100,000 individuals as of May 2024, with over 90% of cases among non-Hispanic Black or African American populations. Life expectancy for individuals with SCD in the U.S. is over two decades shorter than the national average, and many do not receive adequate screening or treatment. A 2023 study from the American Society of Hematology (ASH) reported 120,156 SCD cases in 2020, with 13% from immigrant populations-primarily from the Caribbean and African nations. States like Florida, New York, Texas, Georgia, and Maryland carry the highest disease burdens, and when migration is factored in, national prevalence estimates rise to approximately 167,484 cases. Globally, the burden is most concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa, which had 405,000 SCD births and 5.68 million prevalent cases in 2021-a 67.4% increase since 2000. Nigeria, India, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo account for 90% of the global SCD population, with Nigeria alone recording 150,000 affected births annually. These numbers reflect an urgent need for scalable, cost-effective diagnostic solutions in both domestic and international healthcare systems.
Pricing Analysis
Product
Price (in USD)
Sickle SCAN
4.50
HemoTypeSC
2.0
Variant nbs Sickle Cell Program, 1000 test kit
1,720.00
Sickle Cell Short Reorder Packs
1,356.00/kit
CellaVision DC-1
33,642
Hemo Control
829.91–1,286.03
HemataStat II
3,928
HemoCue Hb 201+ System
1,787.00
HemoCue Hb 301 System
450
Consumer Behavior Analysis
Multifaceted Influences on POC Test Adoption
The decision to implement rapid point-of-care (POC) testing for sickle cell anemia is shaped by a mix of medical, economic, social, and logistical factors. These considerations are crucial for a wide range of stakeholders, including governments, healthcare providers, community health workers, and families, especially in determining the viability of deploying these tests in clinical or outreach settings.
Clinical Accuracy and Diagnostic Confidence
A key factor influencing adoption is the test’s clinical accuracy. POC diagnostics must exhibit high sensitivity (accurately detecting those with the disease) and high specificity (correctly identifying those without it). Tests like HemoTypeSC and PathoCatch, which have both shown sensitivity and specificity rates exceeding 99%, are strong candidates for widespread use. Inaccurate tests could lead to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, or unnecessary distress, making reliability essential.
Affordability and Economic Feasibility
In resource-constrained environments, affordability plays a central role. Traditional lab-based methods like hemoglobin electrophoresis or HPLC, while reliable, are expensive and require significant infrastructure. By contrast, rapid POC tests such as HemoTypeSC, which can cost under USD 2, are more accessible for government-led or NGO-supported screening programs. Lower costs also make testing more feasible for families in underserved areas who might otherwise forgo it due to financial limitations.
Logistics, Infrastructure, And Accessibility
Traditional diagnostics often demand electricity, refrigeration, and skilled personnel-resources not always available in rural or tribal areas. In contrast, POC tests that are portable, stable at room temperature, and operable without electricity or specialized equipment are better suited to these environments. In India, for instance, PathoCatch is being effectively used in rural camps and mobile clinics, offering practical solutions where laboratory infrastructure is absent.
Ease of Use and Training Simplicity
POC tests that are easy to administer and interpret-with simple procedures involving just a drop of blood and a visual result-are especially valuable in low-resource settings. Their simplicity allows them to be used by community health workers or trained field staff without laboratory training. This user-friendliness has been demonstrated in India’s tribal regions, where PathoCatch was used effectively by field workers during national screening efforts.
Rapid Turnaround and On-the-Spot Results
The speed at which results are available is another major advantage. While traditional diagnostics can take days or even weeks, rapid POC tests deliver results in under 15 minutes. This immediacy facilitates prompt counseling, referrals, and treatment-critical for newborns, pregnant women, and mobile populations. Faster results also help reduce the risk of patients being lost to follow-up, ensuring that more individuals receive timely care.
Government Support and Policy Alignment
National health policy plays a pivotal role in the scale-up of POC testing. For example, India’s 2023 launch of the National Sickle Cell Elimination Mission prioritized the use of rapid diagnostic tests for mass screening. When governments provide strong backing, it helps streamline funding, training, supply chains, and awareness campaigns, making broad adoption more achievable.
Community Engagement and Cultural Acceptance
Social and cultural perceptions of sickle cell disease also influence testing decisions. In communities where stigma exists, individuals may be reluctant to undergo screening. Therefore, public health campaigns that educate communities about the genetic nature of the disease, its health implications, and the benefits of early detection are vital in fostering trust and encouraging participation in testing programs.
Integration with Existing Health Services
Ease of integration into existing healthcare frameworks is another important consideration. POC testing becomes more scalable when linked with maternal and child health services, school screenings, or immunization campaigns. These existing platforms provide practical touchpoints for testing, increasing efficiency and ensuring wider coverage without requiring entirely new infrastructure.
Data Collection and Health System Monitoring
Finally, the ability to record and track testing data is essential for effective health system planning and disease surveillance. Decision-makers often favor diagnostic tools that allow for easy reporting, whether through digital systems or simple paper formats. Reliable data collection supports program evaluation, informs future strategies, and contributes to national and regional public health goals.
Market Entry Strategies
-
Leverage Government Programs: Engage with initiatives like India’s National Sickle Cell Anemia Elimination Mission and Africa’s CONSA to gain access to mass screening efforts, public health funding, and distribution networks.
-
Focus on High-Prevalence Regions: Target regions with the highest SCA burden, such as Sub-Saharan Africa and Indian tribal states, to address urgent healthcare needs and establish early market traction.
-
Conduct Clinical Validation: Partner with local healthcare institutions to validate POCT devices in real-world settings, ensuring credibility, trust, and readiness for local use.
-
Secure Regulatory Compliance: Obtain certifications from relevant national authorities (e.g., CDSCO in India, NAFDAC in Nigeria) to access public tenders and official health programs.
-
Build Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with governments, NGOs, diagnostic labs, and academic institutions to support implementation, training, and scalability of POCT solutions.
-
Integrate Digital & Mobile Tools: Develop POCT systems with mobile connectivity, cloud dashboards, and telehealth features for real-time data sharing, remote monitoring, and policy planning.
-
Adopt Tiered & Volume-Based Pricing: Offer flexible pricing strategies to accommodate varying economic capabilities, ensuring affordability and wide adoption in low-resource markets.
-
Invest in Community Engagement: Raise awareness through localized outreach via schools, health camps, and trusted community leaders to boost screening participation and reduce stigma.
-
Align with National Digital Health Goals: Ensure your solutions are compatible with national digital health infrastructures, enabling smoother integration and long-term sustainability.
-
Leverage Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Work with donor organizations and private sector partners to expand reach, reduce cost barriers, and deliver coordinated care to underserved populations.
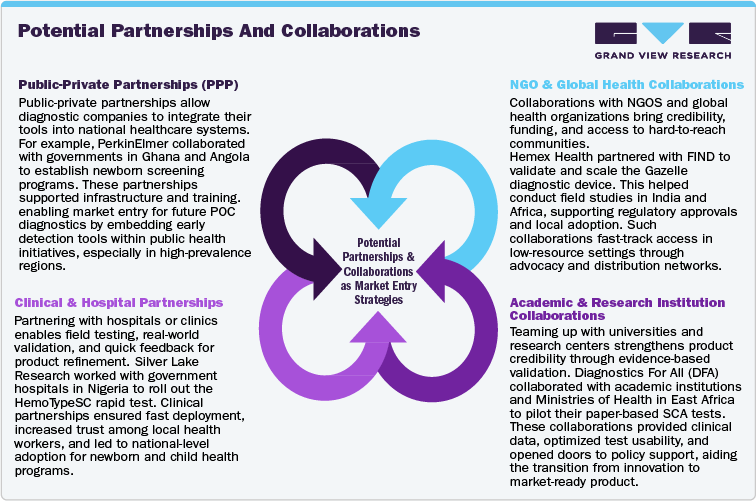
Barriers To Entry And Risks
1. Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure
Barrier: In remote and underserved regions, lack of basic healthcare infrastructure poses a major challenge for implementing POCT. Issues such as unreliable electricity, poor internet connectivity, shortage of trained health professionals, and weak supply chain systems make traditional diagnostic rollouts unfeasible.
Mitigation: To address this, companies should design battery-operated or solar-powered POCT kits that are rugged, portable, and user-friendly. Empowering local frontline health workers-like India’s ASHAs or Africa’s CHWs-through tailored training allows for decentralized, community-level screening. Mobile health units equipped with POCT tools can bridge geographic gaps and enable outreach in hard-to-reach villages. Devices should also support offline data capture, syncing test results when connectivity becomes available.
2. Low Awareness and Cultural Stigma
Barrier: Low awareness about SCA and deeply rooted stigma hinder testing uptake. Misconceptions-such as the belief that SCA is a curse-combined with fears of social discrimination in marriage or employment, often deter individuals from participating in screening programs.
Mitigation: Building trust through partnerships with local NGOs, tribal elders, and community influencers is essential. Awareness campaigns should use culturally appropriate messaging delivered via community radio, storytelling, and mobile theatre. School-based drives and youth engagement can foster generational change. According to a 2024 survey, nearly 78% of parents supported awareness efforts targeting young children, suggesting a high-impact strategy for early intervention.
3. High Upfront Investment and Financial Risk
Barrier: Significant capital is needed for R&D, clinical validation, regulatory approvals, and market entry, especially in emerging markets where reimbursement models remain uncertain.
Mitigation: To offset this, companies can seek funding from global health organizations like Gavi, Unitaid, and the Wellcome Trust. Strategic public-private partnerships (PPPs) with governments or NGOs can help share operational risk and improve access to mass screening initiatives. Launching pilot projects in high-burden zones can provide proof-of-concept, generate impact data, and attract further investment.
4. Intense Market Competition
Barrier: Established players in India and Africa often dominate due to early entry, strong government ties, and well-developed distribution networks. This entrenched presence makes it hard for new entrants to gain traction.
Mitigation: Newcomers should focus on product innovation-offering faster, cheaper, or more portable diagnostics-and build brand credibility through local clinical validation. Rather than competing head-on in saturated regions, targeting underserved or niche markets can enable faster adoption and loyalty building.
5. Regulatory Complexity and Delays
Barrier: Navigating country-specific regulations can delay launches and restrict access to public health tenders. Approvals may require in-country validation, extensive documentation, or alignment with WHO standards.
Mitigation: Working with local regulatory experts or CROs ensures faster and more accurate submissions. Companies should engage early with regulatory bodies and leverage existing certifications (e.g., CE mark, US FDA) to streamline approval via international harmonization agreements.
6. Pricing Pressures and Procurement Risks
Barrier: Cost sensitivity in public tenders and donor-funded programs often leads to aggressive price negotiations, contract uncertainties, and sustainability challenges.
Mitigation: Tiered pricing models tailored to buyer capacity and bundled value-added services-such as analytics dashboards, digital health tools, or on-site training-can improve cost justification. Participating in pooled procurement platforms like UNICEF or AMSP and building local manufacturing bases can also reduce costs and secure larger, long-term contracts.
Company Strategy Mapping And Recent Developments
Companies
Year
Month
Details
Molbio
2023
May
Molbio Diagnostics collaborated with ShanMukha Innovations to introduced SickleCert, India's first CDSCO-approved point-of-care test for sickle cell anemia. Developed with High-Performance Optical Spectroscopy (HPOS) technology from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), SickleCert delivers accurate results within 15 minutes using a small blood sample. The system includes a portable analyzer, HaemoCube, and a smartphone app for data recording and integration with health records.
BioMedomics, Inc.
2024
December
BioMedomics Inc. developed the Sickle SCAN test, a rapid, point-of-care diagnostic tool for sickle cell disorders. This immunoassay detects hemoglobins A, S, and C using a small blood sample, providing results in under five minutes without the need for electricity or advanced equipment. Clinical studies have demonstrated its high sensitivity and specificity, making it suitable for newborn screening and genetic counseling. The test has received CE Mark approval, indicating compliance with European health, safety, and environmental standards.
Hemex Health
2024
November
Hemex Health unveiled new product offerings for its Gazelle Diagnostic Device. The next-generation Snap Cartridge simplifies sample preparation, enabling minimally trained health workers to perform tests for hemoglobin variants, including sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia. Additionally, the Gazelle Ferritin FIA Test offers accurate measurement of ferritin levels for improved diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia.
BioMedomics, Inc.
2024
June
BioMedomics announced the launch of a three-year grant program aimed at enhancing the testing and management of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in Sub-Saharan African countries. Commencing on June 19, 2024, coinciding with World Sickle Cell Disease Day, this initiative reflects BioMedomics' commitment to improving global health through innovative diagnostics and education. The program seeks to raise SCD awareness and facilitate the availability and affordability of point-of-care testing in the region, with BioMedomics collaborating with local distributors for implementation.
Bhopal Memorial
Hospital and Research Center
2025
March
The Bhopal Memorial Hospital and Research Center (BMHRC) introduced a new DNA sequencer to enhance sickle cell anemia testing. This technology improves diagnostic accuracy and supports the Union Government’s Sickle Cell Anemia Eradication Mission by enabling precise genetic testing to identify the disease’s root causes and guide effective treatment strategies. While traditional tests identify hemoglobin types, the DNA sequencer directly analyzes the HBB gene, allowing for more precise detection of mutations. This breakthrough enables doctors to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s genetic profile.
Company Strategy Mapping And Recent Developments
Sr. No.
Company
Product Category
Features
1
BIOMEDOMICS INC.
Sickle SCAN
A rapid, qualitative point-of-care test for the detection of sickle cell disease and trait, delivering results in minutes from a fingerstick blood sample.
has a combined sensitivity and specificity of >99% time- 5 minutes.
‘BioMedomics Sickle SCAN is not currently available for in vitro diagnostic use in the U.S.’
Sickle SCAN-EZ
It’s a multiplexed, qualitative, point-of-care immunoassay used for the rapid diagnosis of sickle cell disorders. Sickle SCAN-EZ tests for sickle cell trait, sickle cell anemia and HbSC disease.
It is tailored for high-volume screening time- 5 minutes.
‘BioMedomics Sickle SCAN-EZ is not currently available for in vitro diagnostic use in the U.S.’
2
BD
VARIANTnbs Sickle Cell Program (Reagents)
Offers a rapid 3-minute qualitative screen for the presence of hemoglobins F, A, S, D, C, and E in eluates of neonatal blood collected with one step sample preparation.
VARIANTnbs Newborn Screening System
Provides automated newborn screening for sickle cell disease.
VARIANT II Beta-Thal Short
β-thalassemia testing.
used for quantification of HbA2 and HbF and as an aid in the identification of common hemoglobin variants: HbS, HbC, HbD, and HbE.
VARIANT II Hemoglobin Testing System
The multi-analyte system is NGSP-certified and CE-marked to meet the European IVD Directive (EU) 2017/746.
Operating environment
Temperature: 15–35°C
Humidity: 10–90%, non-condensingStorage conditions
Temperature: −20°C to 50°C
Humidity: 10–95%Bio-Rad HbA1c
One-touch Smart HPLC technology gives you an A1c result every 45 seconds.
It is equipped with Gold Standard HPLC technology with an easy-to-use, compact footprint and fast switching between HbA1c and β-thalassemia testing.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


