- Home
- »
- Reports
- »
-
Connected Devices and Wearables Category Report, 2030
![Connected Devices and Wearables Category Report, 2030]()
Connected Devices and Wearables Procurement Intelligence Report, 2023 - 2030 (Revenue Forecast, Supplier Ranking & Matrix, Emerging Technologies, Pricing Models, Cost Structure, Engagement & Operating Model, Competitive Landscape)
- Published Date: Sep, 2023
- Base Year for Estimate: 2022
- Report ID: GVR-P-10534
- Format: Electronic (PDF)
- Historical Data: 2020 - 2021
- Number of Pages: 60
Connected Devices and Wearables Category Overview
“The connected devices and wearables category’s growth is driven by the significant increase in demand for smartphones and multimedia devices.”
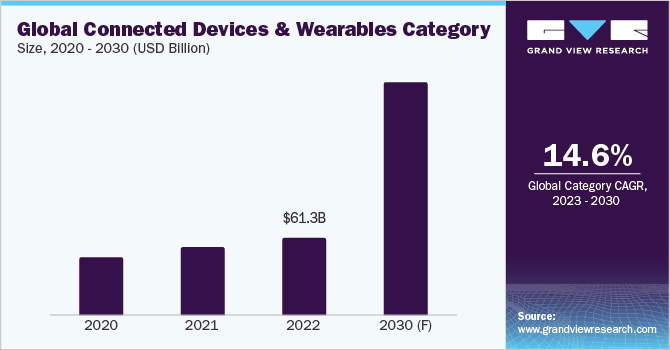
The connected devices and wearables category is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% from 2023 to 2030. Consumer adoption of smart wearable technology items is propelling industry growth. Furthermore, many manufacturers are focusing on providing products with different sports options, a huge display, a stronger battery, and a durable metal casing that will appeal to sportsmen. This is likely to propel the sector forward. Manufacturers can add new advanced features to their products by integrating AI and AR technologies. Major shifts in consumer demographics, such as altering habits and choices, are likely to improve product demand, driving industry growth. Also, increasing consumer expenditure on personal care products is expected to stimulate demand for wearable devices. Smartwatches are popular among swimmers, bicyclists, athletes, and members of the gym because they help in tracking the number of calories consumed, hourly activity, and idle time. For instance, the Adaptive EQ technology introduced by Apple, Inc. with the launch of their AirPods in 2021 tunes the sound in real-time based on the profile and fit of the user’s ear.
The usage of these electronic devices has been beneficial in doing simple health checks daily. In the case of obesity, they play an incredibly significant role in monitoring numerous vitals of the body. It aids in the generation of data related to the number of calories consumed and expended during the day. Constant research and development procedures have resulted in improved hardware and software. These devices are also employed in the defense industry to aid in the performance of various activities. Digital screens that have been put on the market are both versatile and practical, leading to a growth in the use of wearable gadgets. Consumers are increasingly favoring these devices for monitoring and computing multiple tasks. This factor increases the likelihood of growth in the next years. Another aspect that will contribute to the category’s growth in the coming years is the 5G connectivity given by these devices with cellphones.
One of the issues for wearable devices is comfort and ergonomics, especially with wearable devices designed to be worn for extended periods. The device's comfort level should please the user. For example, wearing for an extended amount of time may create heat to the device, causing discomfort for the user, and posing issues for the connected devices and wearables category. Another problem for wearable gadgets is battery life, which is now the most difficult challenge in technology. Wearable gadgets necessitate effective power, but battery life is restricted. To solve this, the gadgets should run for a decent amount of time while retaining maximum battery life. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, can be toxic if mishandled, and worn gadgets that contain these batteries, which will be so close to the body every time, may provide a significant safety issue.
Supplier Intelligence
“How can the nature of the connected devices and wearables category be best described? Who are some of the key players?”
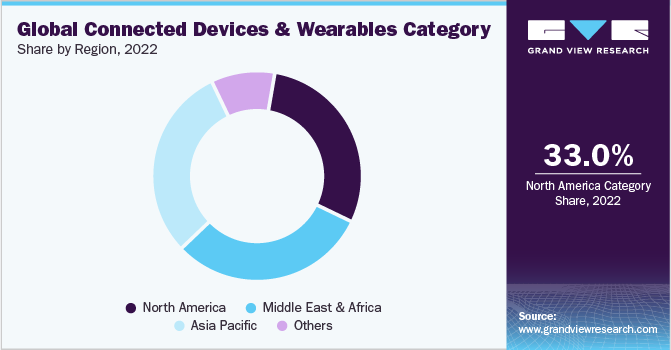
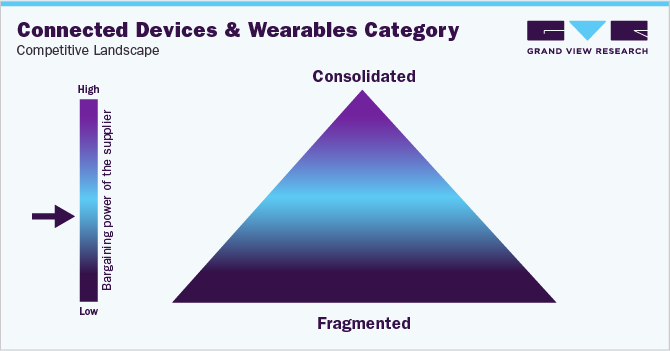
The global market for connected devices and wearables is fragmented, with numerous large and medium-sized businesses accounting for the majority of category revenue. This category is also drawing a large number of startups, which further intensifies the rivalry. Major businesses are implementing numerous tactics, such as mergers and acquisitions, strategic alliances and agreements, and the development, evaluation, and release of new products. For instance, In September 2022, Fitbit upgraded its smartwatch range which has the latest aesthetics and functionality. In October 2021, Amazfit, a Chinese smart wearable company, released three new smartwatches-the GTR 3 Pro, GTR 3, and GTS 3-with revolutionary haptic technology.
Connected devices and wearables provide considerable opportunity for product differentiation by allowing businesses to segment users, design products, establish prices, and provide value-added services. They also aid in the development of deeper client ties, the increase of buyer costs, the reduction of buyer reliance on distribution or service partners, and the reduction of the bargaining power of buyers. Furthermore, these devices introduce powerful providers such as Google and Apple, which provide sensors, software, networking, embedded operating systems, data storage, analytics, and other technological components. These companies have the talent and capabilities required for product differentiation and cost reduction, strengthening suppliers' bargaining power.
Key suppliers covered in this category:
-
Alphabet Inc.
-
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
-
Sony Corp.
-
Huawei Technologies Group Co., Ltd.
-
Apple Inc.
-
Xiaomi Corp.
-
Adidas AG
-
Nike, Inc.
-
Fitbit, Inc.
-
Garmin Ltd.
Pricing and Cost Intelligence
“What are some of the major cost components in connected devices and wearables? Which factors impact the cost of connected devices and wearables?”
The cost of connected devices and wearables can be broken down into seven main categories: hardware, software, connectivity, manufacturing, marketing, support, and other costs. The three largest cost components in this category are hardware, software, and connectivity. Together, they account for roughly 80% of total costs. The largest cost component of a device is hardware, which includes physical components like processor, memory, sensors, display, and battery. Software includes operating systems, firmware, and applications, while connectivity costs include wireless technology for the internet or other devices.
It is important to note that these cost contributions can vary depending on the specific device and the manufacturer. A high-end smartwatch with a lot of features will have a higher hardware cost than a basic fitness tracker. Similarly, a device that uses cellular connectivity will have a higher connectivity cost than a device that uses Wi-Fi only. The price of a connected device or wearable can vary significantly depending on the specific features and capabilities of the device. For example, a high-end smartwatch with a heart rate monitor, GPS, and cellular connectivity can cost upwards of USD 500, while a basic fitness tracker with only step-tracking capabilities can cost as little as USD 50.
The most deployed pricing model by vendors of connected devices and wearables is the subscription model. This model is based on the idea that users pay a recurring fee to access the device or service. The subscription fee can be based on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis. There are several advantages of using a subscription model for vendors. First, it can ensure they have a regular and predictable income stream. Second, it can help them to reduce the risk, as they are only paid for the services that they provide. Third, it can help to promote customer loyalty, as users have already invested time and money into the service, and they are less likely to want to start over with a new service. This can further encourage customers to stay subscribed.
The chart below shows a breakdown of the cost structure associated with connected devices and wearables along with major cost components, as demonstrated below.
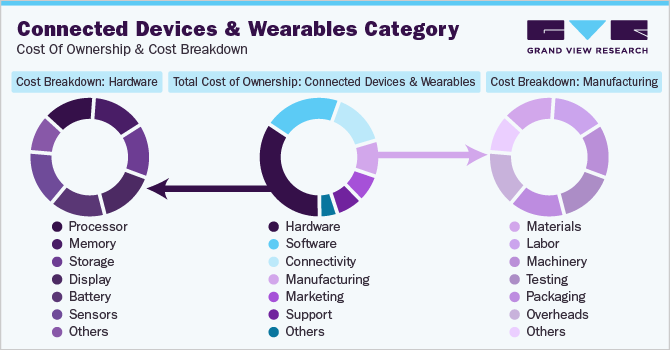
The Connected Devices and Wearables Procurement Intelligence Report provides a detailed analysis of the cost structure and the pricing models adopted by prominent suppliers in this category.
Sourcing Intelligence
“Which countries are the leading sourcing destination for Connected Devices and Wearables? What is the type of engagement model?”
China, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, and the U.S. are some of the top sourcing destinations for connected devices and wearables. Access to a skilled workforce, and large manufacturing capacity, complemented by high-quality production and focus on research and development make these countries the preferred location for procuring connected devices and wearables. However, the semiconductor chip shortage has had a significant impact on the supply chain of electronic products essential for manufacturing connected devices and wearables. The shortage has led to delays in production, increased prices, and shortages of specific products. According to a report by Gartner, the global semiconductor shortage is expected to cost the electronics industry USD 110 billion in lost revenue in 2022. The report also states that the shortage is expected to delay the production of electronic products by an average of 3 months. The average price of a smartphone increased by 16-18% in the first quarter of 2023 compared to the first quarter of 2022 due to the semiconductor chip shortage. The semiconductor chip shortage pushed up prices for electronic products by roughly 3.6% throughout 2022.
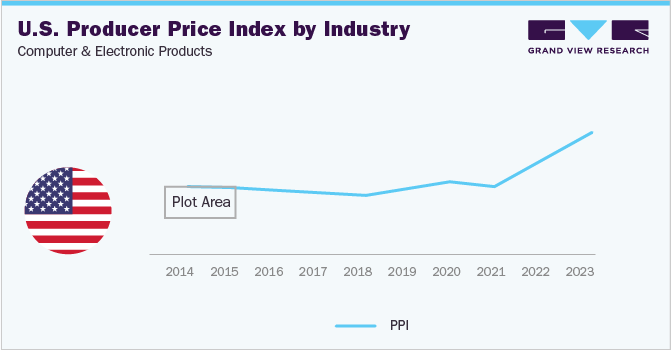
This can be observed through the rising producer price index for electronic products. The data shows that the PPI for electronic products has been increasing in recent years. In 2013, the PPI for electronic products was 89.4. In 2022, the PPI for electronic products was 96.35. This represents an increase of 7.4% over a period of 9 years. The rising producer price index for electronic products is causing due to increased sourcing costs for procurement professionals, leading to increased competition among suppliers. This competition is driven by procurement professionals seeking lower-cost electronic products. As a result, there is a demand for alternative sourcing strategies, such as sourcing from alternative suppliers, negotiating better prices with suppliers, using e-procurement tools, and outsourcing procurement activities to third-party providers. These strategies aim to provide procurement professionals with more cost-effective and efficient options for their electronic product needs.
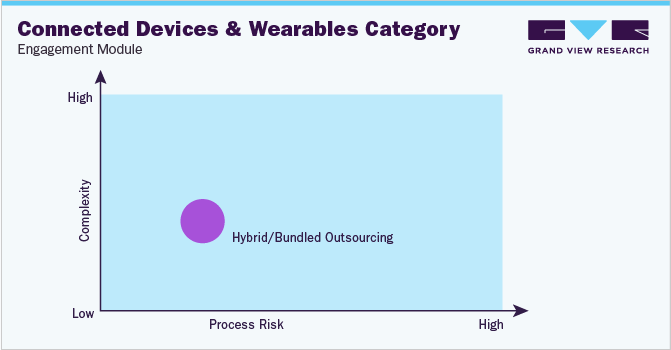
In terms of connected devices and wearables sourcing intelligence, Vendors of connected devices and wearables typically use a hybrid/bundled outsourcing model. This model allows them to retain control of some of the key functions of their business, such as product development and marketing, while outsourcing other functions, such as manufacturing and logistics, to third-party providers. The hybrid outsourcing model offers a number of advantages for vendors of connected devices and wearables. First, it allows them to focus on their core competencies and outsource non-core functions to experts. Second, it helps them to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Third, it gives them access to the latest technologies and expertise.
The Connected Devices and Wearables Procurement Intelligence report also provides details regarding day one, quick wins, portfolio analysis, key negotiation strategies of key suppliers, and low-cost/best-cost sourcing analysis.
Connected Devices and Wearables Procurement Intelligence Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Connected Devices and Wearables Category Growth Rate
CAGR of 14.6% from 2023 to 2030
Base Year for Estimation
2022
Pricing Growth Outlook
10% - 15% (annual)
Pricing Models
Subscription-based pricing model, tier-based pricing model, fixed-fee pricing model
Supplier Selection Scope
Cost and pricing, past engagements, productivity, geographical presence
Supplier Selection Criteria
Technology, service, quality, service, reliability, technical expertise, security measures, cost and value, support and maintenance, regulatory compliance, and others
Report Coverage
Revenue forecast, supplier ranking, supplier positioning matrix, emerging technology, pricing models, cost structure, competitive landscape, growth factors, trends, engagement, and operating model
Key Companies Profiled
Alphabet Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Sony Corp., Huawei Technologies Group Co., Ltd., Apple Inc., Xiaomi Corp., Adidas AG, Nike, Inc., Fitbit, Inc., Garmin Ltd.
Regional Scope
Global
Historical Data
2020 - 2021
Revenue Forecast in 2030
USD 186.14 billion
Quantitative Units
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2023 to 2030
Customization Scope
Up to 48 hours of customization free with every report.
Pricing and Purchase Options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global connected devices and wearables category size was valued at approximately USD 61.30 billion in 2022 and is estimated to witness a CAGR of 14.6% from 2023 to 2030.
b. The increasing consumer expenditure on personal care, as well as the growing acceptance of wearable technology along with rising demand for smartphones and multimedia devices is driving the growth of this category.
b. According to the LCC/BCC sourcing analysis, China, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, and the US are the ideal destinations for sourcing connected devices and wearables.
b. This category is fragmented with the presence of many large players competing for the market share. Some of the key players are Alphabet Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Sony Corp., Huawei Technologies Group Co., Ltd., Apple Inc., Xiaomi Corp., Adidas AG, Nike, Inc., Fitbit, Inc., Garmin Ltd.
b. Hardware, software, and connectivity are the major cost components of this category. Other key costs include manufacturing, marketing, and support.
b. Considering the cost and the quality of products, evaluating the lead times for various products, and the warranty & return policy of multiple suppliers are some of the best sourcing practices in this category.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself...
Add-on Services
Should Cost Analysis
Component wise cost break down for better negotiation for the client, highlights the key cost drivers in the market with future price fluctuation for different materials (e.g.: steel, aluminum, etc.) used in the production process
Rate Benchmarking
Offering cost transparency for different products / services procured by the client. A typical report involves 2-3 case scenarios helping clients to select the best suited engagement with the supplier
Salary Benchmarking
Determining and forecasting salaries for specific skill set labor to make decision on outsourcing vs in-house.
Supplier Newsletter
A typical newsletter study by capturing latest information for specific suppliers related to: M&As, technological innovations, expansion, litigations, bankruptcy etc.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


