- Home
- »
- Reports
- »
-
ERP Software Procurement & Cost Intelligence Report, 2030
![ERP Software Procurement & Cost Intelligence Report, 2030]()
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software Procurement Intelligence Report, 2023 - 2030 (Revenue Forecast, Supplier Ranking & Matrix, Emerging Technologies, Pricing Models, Cost Structure, Engagement & Operating Model, Competitive Landscape)
- Published Date: Sep, 2023
- Base Year for Estimate: 2022
- Report ID: GVR-P-10544
- Format: Electronic (PDF)
- Historical Data: 2020 - 2021
- Number of Pages: 60
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software Category Overview
“The ERP software category’s growth is driven by the increasing adoption of mobile and cloud applications in addition to the growing demand for operational efficiency in business operations.”
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software category is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11% from 2023 to 2030. The growing demand for data-driven choices, the rise in the adoption of mobile and cloud applications, and the increasing demand for operational efficiency and transparency in business operations are the main drivers of the expansion of this category. Over the next few years, it is anticipated that the growth of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in emerging markets, particularly in China, India, and Brazil, will increase product demand. Global businesses invest in advanced ERP systems for the following main reasons: to unify regional and international manufacturing data and workflows into one centralized system, to efficiently manage costs in a complex manufacturing supply chain, use ERP systems as a powerful facilitator for currency conversions across international borders or project implementations or structural management, and to foster flexibility and development.
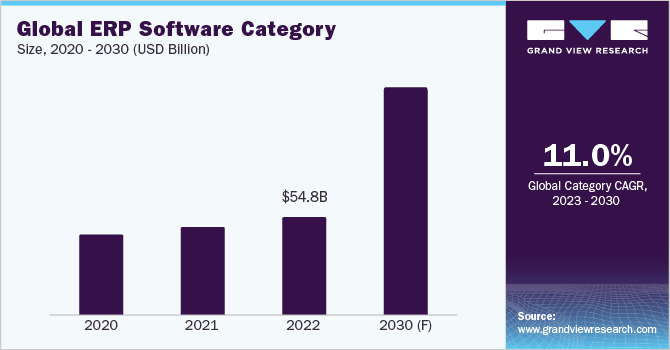
The global ERP software category size was estimated at USD 54.76 billion in 2022. Two of the key trends are the shifting preference of SMEs to cloud-based systems and the gaining popularity of two-tier ERP systems. According to a study in 2022, it was found that more than 70% of SMEs are willing to purchase a cloud solution next time they need a new application. Small businesses with just one or two IT professionals benefit from cloud-based ERP systems that they otherwise wouldn't be able to afford to operate thanks to these software types. The cloud ERP market has offered users intuitive apps and cross-platform or mobile-native features over the last few years. On the other hand, a rising IoT presence in the business world has been necessitated by customer demand. As a result, IoT integration with AI is expected to become an asset for ERP software buyers throughout the industry. Factors such as remote work and automation have in turn accelerated the demand for these technologies which enable companies to make smart decisions.
ERP combined with AI and IoT provides multiple benefits to organizations. For instance, to track items inside a warehouse, data from mobile scanners and intelligent conveyor belts can be used. Vehicles can send manufacturers real-time data so they can spot and address issues before they arise. When inventory levels drop, smart shelves at retail establishments can automatically arrange orders. In the current ERP environment, powerful analytics, and technologies in addition to providing the data also guide the user through their tasks, provide context-rich insights, and flag anomalous events, thereby alerting the user. According to Gartner in 2022, organizations can save expenses by up to 30% over the next three years by utilizing AI, machine learning, and RPA with their ERP systems.
Two distinct ERP systems are used by businesses with two-tier ERP models to meet their demands. At the corporate level, a Tier 1 ERP is utilized that has the capability needed to manage a sizable international business. While divisions and subsidiaries operate a more adaptable Tier 2 ERP that serves their unique requirements, typically in the cloud. Tier 1 examples include SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, Oracle, and Infor. Tier 2 examples include Epicor, Syspro, Plex, Sage, and NetSuite. For instance, Amazon uses SAP, Starbucks uses Oracle, TD Bank Group uses Microsoft Azure ERP, and Toyota uses Microsoft Dynamics.
Supplier Intelligence
“What is the nature of the ERP software category? Who are some of the leading players?”
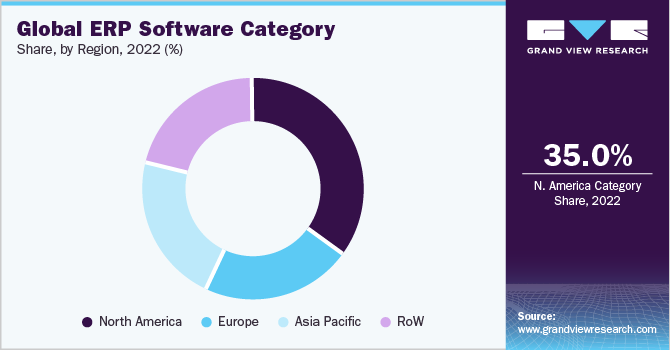
The global ERP software category features a fragmented landscape with the presence of many leading international and regional companies. There is a strong push toward ERP software fragmentation due to the increasing use of cloud and SaaS-based pricing structures. There is intense competition between the product providers as there is a huge demand for alternatives to dominant large-scale vendors (such as Oracle, SAP, Infor, etc.). The top fifteen to twenty players account for only 30% - 35% of the market share. As new vendors focus on developing markets such as employee engagement and financial planning, the variety of providers in this category is continuing to expand. These are the areas where small providers frequently outperform large vendors in terms of agility.
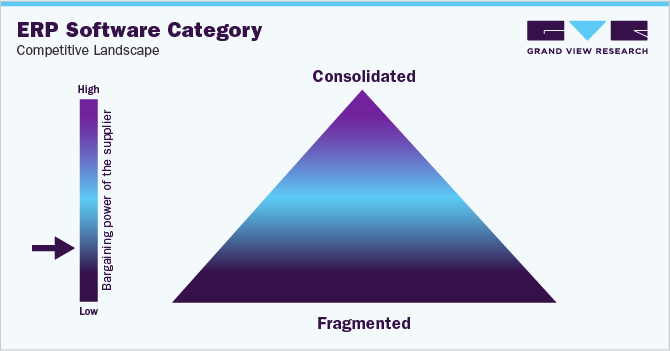
The bargaining power of the suppliers is low due to increased fragmentation. In addition to numerous smaller strategic mergers in industries crucial to business IT, 2021 saw numerous acquisitions in the hardware, software, and service sectors valued at USD 1 billion or more. Dealmaking was active throughout 2021, with smaller businesses combining or being absorbed to expand the capabilities provided by the industry's largest providers of enterprise software and services. For instance:
-
In May 2022, Aptean, an enterprise solutions company acquired RLM Apparel Software Systems, which specializes in providing software solutions for the fashion and apparel sector
-
In March 2022, Microsoft acquired Nuance Communications, one of the leading companies in AI and ambient intelligence. Nuance serves companies across healthcare, retail, financial services, and telecommunications. With security-focused, cloud-based solutions infused with powerful, vertically optimized artificial intelligence, Microsoft and Nuance collaborated with the intent of developing an outcomes-based AI.
Key suppliers covered in the category:
-
Infor Inc.
-
Epicor Software Corporation
-
IBM
-
HP Enterprise
-
Microsoft Corporation
-
NetSuite Inc.
-
Oracle Corporation
-
Sage Group, plc
-
SAP SE
-
Unit4
-
Workday
-
ServiceNow, Inc.
-
QAD Inc.
Pricing and Cost Intelligence
“What are some of the major cost components involved in the ERP Software category? Which factors impact the cost of this category?”
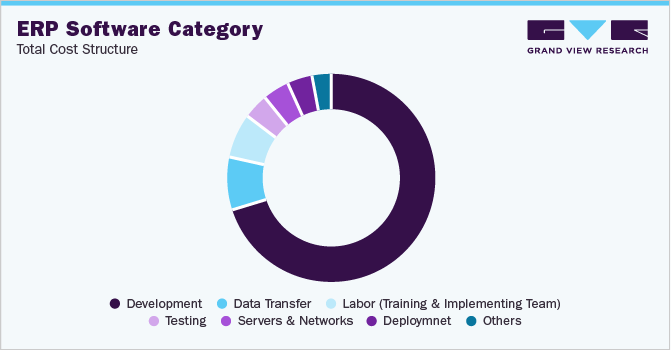
The major cost components associated with ERP software include the cost of development, data transfer, labor, servers and network, and deployment. Development forms the largest cost component accounting for between 50% to 60% of the total costs. The main objective of ERP product development is to increase operational efficiency and enhance firm profitability by automating repetitive jobs and eliminating redundant processes. Depending on the business needs and complexity, the estimated cost of developing ERP software could range from USD 25,000 to USD 350,000. The total cost of developing an ERP system is directly influenced by a wide range of various variables. Some of the major factors impacting the cost are the number of users and features, add-ons, customization, implementation, maintenance, upgrades, process redesign, technology additions, the number of hours required for the development, and the location of the developers.
Perpetual licensing and subscription plans are the two primary pricing structures that ERP software suppliers typically operate around. The following chart below illustrates the major cost components associated with the category.
Many product vendors charged by the user. As a result, the price of products increases together with the number of users. The distinctive characteristics of ERP software set it apart from other kinds of software. These consist of widely used databases, automation, communication, information gathering, and more. The cost of developing an entire system would increase as more functions are added. On the other hand, compared to cloud-based solutions, the on-premise system will require frequent and scheduled maintenance to make sure it is up and functioning as planned. In general, maintenance costs range from 15% to 20% of the cost of initial setup and acquisition. On-premise systems are therefore typically regarded as a capital expenditure as they require one significant upfront investment. A cloud ERP solution is typically regarded as an operating expense.
The duration of time it takes developers to complete an entire system also has a significant impact on the overall cost of developing the systems. The team needs additional specialists to complete the tasks more quickly and effectively if the application is complex and the company wants to reduce the number of hours spent on development. This in turn increases the total cost.
Phase
Leaders & experts
Front end developer
Backend developer
Quality control
Concept/design
10%
-
-
-
Development
6%
12%
20%
-
Testing
2%
-
-
-
Support Device
-
-
-
5%
Total
20%
25%
The chart illustrated above as an example, shows a timeline estimate (in %) of how much time professionals spend on each phase of the product development process. Depending on the size of the business and the scope of the implementation, the whole process can take a number of months. The timeframe for small businesses usually ranges between one to three months and for medium businesses three to six months.
The report provides a detailed analysis of the cost structure of ERP Software and the pricing models adopted by prominent suppliers in this category.
Sourcing Intelligence
“Which countries are preferred for sourcing ERP software solutions? What kinds of models do companies engage in?”
Most B2B companies opt for a full outsourcing model for their ERP software development requirements. 78% of companies regard outsourcing favorably for this category. The prices are substantial when the companies have an in-house software development staff. They are responsible for paying their salary as well as their perks, holidays, and other expenses. In fact, according to a study in 2022, it was found that, when all benefits, taxes, meetings, and other expenses are taken into account, the true cost of a new in-house developer for a business might be as high as 2.7 times the base pay in the U.S. A company may have to pay between USD 280 - USD 350 for an in-house developer compared to an outsourced developer, which can cost between USD 100 - USD 200.
It was also found in the study in 2022, that the time it takes to hire one developer for a company's in-house setup may be equal to or less than the time it takes to hire an entire software outsourcing team. Hence, by outsourcing the development, the company can reduce its expenses significantly, get access to specialized teams with a wide range of skills and an advanced stack of technology, bring in fresh talent on an ad-hoc basis, and increase the flexibility and scalability of the project.

In the full services outsourcing model, the client outsources the complete operation/manufacturing to single or multiple companies.
In terms of ERP software sourcing intelligence, the most preferred countries for software development are India, China, Germany, the UK, Canada, Singapore, and the U.S. India is the most preferred option for the U.S. or the UK. firms interested in outsourcing because it is the second-largest English-speaking nation in the world. India's educational system places a strong emphasis on mathematics as well and can create up to 2.6 million STEM graduates each year. In addition to being a low-cost country, India also has a highly developed IT market. Compared to the U.S., according to PayScale in 2022, the average annual salary for a software developer in India can start from as low as USD 15,000 - USD 20,000. Salaries can, however, increase based on technical skills, and years of experience, among other factors.
The report also provides details regarding day one, quick wins, portfolio analysis, key negotiation strategies of key suppliers, and low-cost/best-cost sourcing analysis.
ERP Software Procurement Intelligence Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
ERP Software Category Growth Rate
CAGR of 11% from 2023 to 2030
Base Year for Estimation
2022
Pricing Growth Outlook
8% - 12% (Annually)
Pricing Models
Licensing-based, subscription-based, usage-based, and tier-based pricing model
Supplier Selection Scope
Cost and pricing, past engagements, productivity, geographical presence
Supplier Selection Criteria
By cloud deployment type, features (financial management, reporting and dashboards, supply chain management, customer relationship management, and others), operational capabilities, quality measures, technology, certifications, data privacy regulations, and others
Report Coverage
Revenue forecast, supplier ranking, supplier positioning matrix, emerging technology, pricing models, cost structure, competitive landscape, growth factors, trends, engagement, and operating model
Key Companies Profiled
Infor Inc., Epicor Software Corporation, IBM, HP Enterprise, Microsoft Corporation, NetSuite Inc., Oracle Corporation, Sage Group plc, SAP SE, Unit4, Workday, ServiceNow, Inc., and QAD Inc.
Regional Scope
Global
Historical Data
2020 - 2021
Revenue Forecast in 2030
USD 126.20 billion
Quantitative Units
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2023 to 2030
Customization Scope
Up to 48 hours of customization free with every report.
Pricing and Purchase Options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global ERP software category size was valued at approximately USD 54.76 billion in 2022 and is estimated to witness a CAGR of 11% from 2023 to 2030.
b. The growing demand for data-driven choices, the rise in the adoption of mobile and cloud applications, and the increasing demand for operational efficiency and transparency in business operations are the main drivers of the expansion of the ERP software category.
b. According to the LCC/BCC sourcing analysis, India, China, Singapore, Germany, and Canada are the preferred countries for sourcing ERP software development solutions.
b. The global ERP software category features a fragmented landscape with the presence of many leading international and regional companies. Some of the key players are Infor Inc., Epicor Software Corporation, IBM, HP Enterprise, Microsoft Corporation, NetSuite Inc., SAP SE, Oracle Corporation, Sage Group Plc, Unit4, Workday, ServiceNow, Inc., and QAD Inc.
b. The major cost components associated with the category include the cost of development, data transfer, labor, servers and network, and deployment. Development forms the largest cost component accounting for between 50 to 60% of the total costs.
b. Negotiating with more than two vendors, acquiring or partnering with technological firms to expand their service offerings, sourcing from low-cost and high-tech talent pool countries, and choosing suppliers that can provide enhanced customizations, following regulatory compliance and data privacy standards, and quality certifications are some of the best practices that are considered while sourcing this category.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself...
Add-on Services
Should Cost Analysis
Component wise cost break down for better negotiation for the client, highlights the key cost drivers in the market with future price fluctuation for different materials (e.g.: steel, aluminum, etc.) used in the production process
Rate Benchmarking
Offering cost transparency for different products / services procured by the client. A typical report involves 2-3 case scenarios helping clients to select the best suited engagement with the supplier
Salary Benchmarking
Determining and forecasting salaries for specific skill set labor to make decision on outsourcing vs in-house.
Supplier Newsletter
A typical newsletter study by capturing latest information for specific suppliers related to: M&As, technological innovations, expansion, litigations, bankruptcy etc.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


