- Home
- »
- Market Trend Reports
- »
-
Rare Diseases Clinical Trials: Emerging Trends And Pipeline Outlook
Report Overview
Emerging trends in rare disease clinical trials have accelerated the adoption of adaptive and decentralized trial designs. These innovative approaches have improved patient recruitment and retention rate by accommodating the challenges posed by small and geographically dispersed population. In addition, the integration of real-world data (RWD) and real-world evidence (RWE) is gaining significant traction in the market, which is offering insights into disease progression and treatment outcomes, thereby guiding the determination of trial endpoints and regulatory decisions.
Rare diseases affect less than 200,000 people in the U.S and less than 1 in 2,000 individuals in Europe, collectively imposing a global health burden of more than 300 million individuals. The lower prevalence rate, diverse clinical presentations, and the scarcity of established therapies is making the studying challenging for rare diseases. According to the data published by Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology in March 2023, there are more than 7,000 distinct rare diseases, with only a small fraction having effective treatments available, further diving the urgent need for innovative clinical trials and a robust development pipeline. Similarly, according to the data published by NCBI in March 2025, approximately 80% of rare diseases are genetic in origin, which will further create the significant demand for advanced genetic research, targeted therapies, and precision medicine platforms.
Rare Disease Clinical Trials: Emerging Trends and Pipeline Outlook Report Coverage
Rare Disease Clinical Trials: Emerging Trends and Pipeline Outlook Report Coverage
Market Outlook
Prevalence Trends Analysis
R&D Investment Analysis
Industry Ecosystem Analysis
Market Dynamics
Regulatory Framework
List of Top 50 Active Trials by Phase, Sponsor, and Indication
Emerging Clinical Trial Model Analysis
Global Rare Disease Clinical Trials, by Phase & Study Design
Global Rare Disease Clinical Trials, by key Indications, By Region
Furthermore, the evolving landscape of rare disease clinical trials is further accelerating the collaboration agreement among several pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and patient advocacy groups. Moreover, increasing government support such as the launch of several innovative initiatives focused on rare disease clinical trials is projected to drive the market growth. For instance, in September 2023, the U.S. FDA announced the launch of pilot program, which aims to accelerate the development of rare disease therapies. This initiative facilitates more frequent interactions among sponsors and FDA staff, which will further address specific clinical development challenges including study design, control group selection, and patient population considerations. Thus, the aforementioned factors would accelerate the availability of treatments thereby improving the outcomes for patients with unmet medical needs.
In addition, increasing number of approved rare disease drugs is also one of the factors fueling the growth in the rare disease clinical trials market. The growing trend towards the increasing number of approved therapies signifies the stronger regulatory support further encouraging pharmaceutical companies to invest significantly in the research and development activities of rare diseases. Thus, these factors would further increase the volume of clinical trials and drive the opportunity to bring innovative treatments to the market with faster approval timelines. Below figure depicts the upward trajectory in the number and percentage of drugs approved to treat rare diseases.
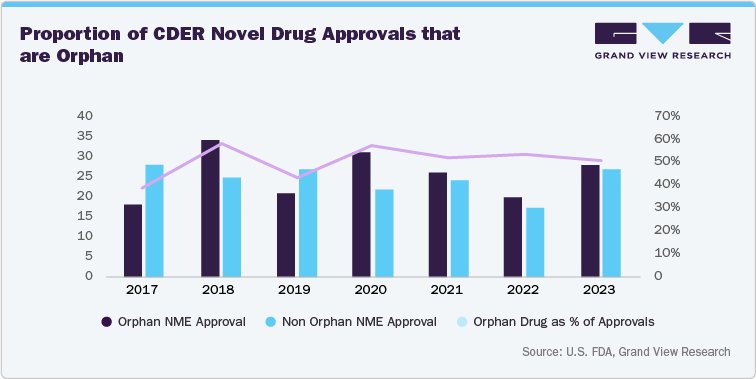
R&D Investment And Funding Analysis
The research and development funding in rare disease clinical trials is witnessing significant transformation due to various regulatory incentives, technological advancements, and evolving market dynamics. Regulatory frameworks such as the Orphan Drug Act have played a significant role in boosting the investments in this field. These initiatives have led to an increasing number of orphan drug approvals, with FDA approving approximately 57 novel drugs in 2024. These approvals include several gene therapies and is projected to generate an annual revenue of USD 60 billion.
Furthermore, increasing government support such has growing funding initiatives is also contributing to the market growth. For instance, in December 2024, the government of India established the National Fund for Rare Diseases (NFRD) and allocated the funding of USD 113.3 million for the financial years 2024–25 and 2025–26. Similarly, the collaboration between Horizon Europe and ERDERA: European Rare Diseases Research Alliance has further accelerated the research and development activities in the rare disease sector. The research entity has allocated USD 429.36 million funding to support rare disease research and implement a broad range of integrative activities aimed at strengthening and advancing the entire rare disease research ecosystem.
Furthermore, the growing pipeline of rare disease therapies with several candidates progressing through clinical phases would further contribute to the market growth. This will further enhance public-private partnerships and regulatory adaptations to streamline trial processes. Moreover, the integration of precision medicine tools such as genomic profiling and biomarker-driven patient selection would further enhance the trial efficiency and success rates.
However, despite these advancements, funding remains a significant challenge owing to high cost and complexities of rare disease clinical trials. Rare disease companies majorly rely on venture capital and public funding. In addition, the evolving policy landscape, such as Medicare’s Drug Price Negotiation provisions which include only limited exceptions for orphan drugs, have introduced new uncertainties that could impact investment decisions in the sector.
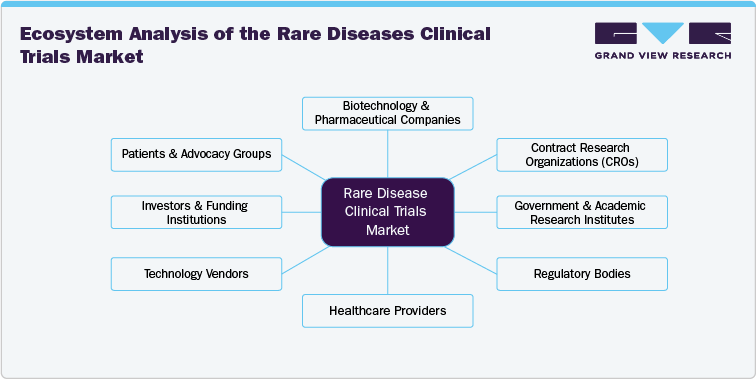
The rare disease clinical trials ecosystem comprises numerous stakeholders, including pharmaceutical & biotechnological companies, CROs, regulatory bodies, research institutions, healthcare providers, technology vendors, investors & funding institutions, and patients & advocacy groups. Pharmaceutical organizations and biotech firms are at the forefront of clinical trial sponsorship, investing heavily in research to develop innovative therapies for age-related eye diseases, retinal disorders, and gene therapies.
CROs, acting as intermediaries between sponsors and clinical trial sites, play a critical role in ensuring trial efficiency, regulatory compliance, and data management. Research institutions and universities often collaborate with industry players to advance novel treatment approaches, particularly in niche areas like gene editing and stem cell therapy.
Regulatory bodies like the U.S. FDA and EMA establish the framework within which clinical trials operate, influencing study design, recruitment strategies, and approval processes. The ecosystem also includes technology vendors providing clinical trial management solutions, data analytics tools, and advanced diagnostic technologies like OCT and AI-driven imaging. The convergence of these entities is fostering innovation, making the Rare Diseases clinical trials market highly collaborative and competitive.
Emerging Clinical Trial Models
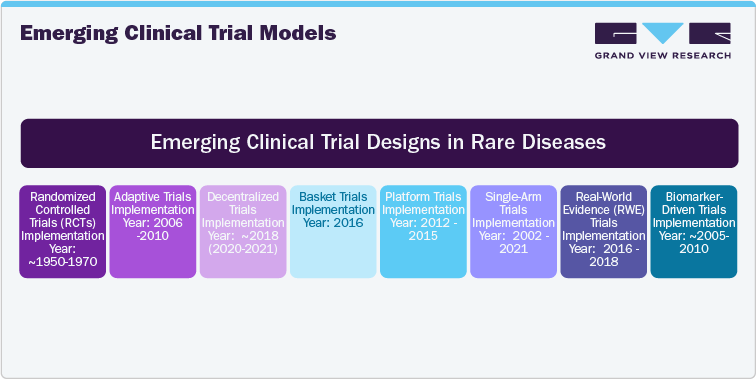
Emerging clinical trial models are transforming the way rare disease trials are designed and conducted. With the advent of decentralized trials, remote patient monitoring, and telemedicine, clinical trials are becoming more patient-centric, reducing geographic and logistical barriers. Virtual visits, wearables, and mobile health apps enable real-time data collection, making it easier for patients to participate from their homes, especially in rare or geographically dispersed conditions. Adaptive trial designs are also gaining traction, allowing modifications to the trial protocol based on interim results, thereby improving efficiency and reducing costs. Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are enhancing recruitment, predictive modeling, and the identification of patient population that are most likely to benefit from specific therapies. These advancements are making clinical trials more efficient and allowing the collection of more granular data, thus providing deeper insights into treatment efficacy and safety. This report explores these emerging trial models, offering key insights into how these innovative approaches are reshaping rare disease research.
U.S. Rare Disease Active Clinical Trials, by Phase (2024)
Phase
Number of Trials
Key Sponsors
Top Indications
Phase I
8
Massachusetts General Hospital
Hypophosphatemic Rickets
Phase II
50
AstraZeneca, Takeda
Epilepsy
Phase III
11
Cancer Research UK, Zogenix, Inc.
Dravet Syndrome, Rare Cancers
Phase IV
2
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Rare Cancers
Source: Clinicaltrials.gov, Grand View Research
This report’s detailed analysis of active clinical trials across phases provides stakeholders with a global view of ongoing research, helping identify trends, key players, and the most promising areas for investment. By offering insights into the number of trials, sponsors, and indications at each phase, this table serves as a vital resource for those looking to track the progress of the rare diseases pipeline and make informed decisions about future investments and trial strategies.
List Of Major Active Trials By Phase, Sponsor, And Indication, A Key Example:
Clinical Trial Study Title
Calcitriol Monotherapy for X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Study Status
Recruiting
Phase
Early Phase 1
Study Type
Interventional
Study Design
- Allocation: NON_RANDOMIZED
- Intervention Model: PARALLEL
- Masking: NONE
- Primary Purpose: TREATMENT
Conditions
- X-linked Hypophosphatemia
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- X-Linked Dominant
Interventions
DRUG: Calcitriol
Sponsor
Massachusetts General Hospital
Number of Patients (Enrollment)
20
Start Date
28-03-2019
Primary Completion Date
31-03-2025
Completion Date
31-03-2025
Locations
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, 02114, United States
Other aspects that shall be analyzed will include the market overview, clinical trials by study design, by key indications, by region, and list of key clinical trials, sponsors, among several other factors.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


