- Home
- »
- Pharmaceuticals
- »
-
Antifungal Drugs Market Size & Share, Industry Report, 2033GVR Report cover
![Antifungal Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Antifungal Drugs Market (2026 - 2033) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Drug Class (Azoles, Polyenes, Allylamines, Echinocandins), By Indication, By Dosage Form, By Distribution Channel, By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-1-68038-293-8
- Number of Report Pages: 150
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2021 - 2024
- Forecast Period: 2026 - 2033
- Industry: Healthcare
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Antifungal Drugs Market Summary
The global antifungal drugs market size was estimated at USD 16.93 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 23.39 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.19% from 2026 to 2033. The market is driven by the increasing prevalence of fungal infections, particularly among immunocompromised patients, and the rising demand for effective treatment options.
Key Market Trends & Insights
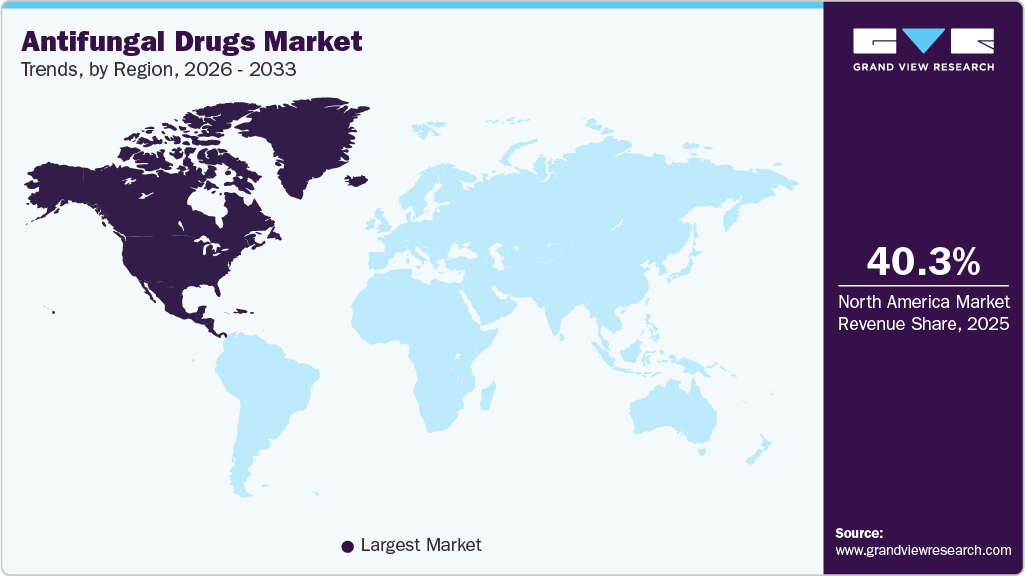
- North America dominated the global market with a share of 40.32% in 2025.
- Based on drug class, azoles segment held the largest market share of 47.83% in 2025.
- Based on the indication, candidiasis held the largest market share of 40.61% in 2025.
- Based on the dosage form, oral drugs dominated the market with a share of 48.93% in 2025.
- Based on the distribution channel, hospital pharmacies segment dominated the market in 2025
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 16.93 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 23.39 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 4.19%
- North America: Largest market in 2025
In addition, advancements in antifungal drug development and growing awareness contribute to market expansion. The global market is witnessing substantial growth, driven by the increasing incidence of fungal infections across both developed and developing regions. Hospital-associated infections (HAIs), particularly candidemia, are a major contributor to the rising demand for antifungal treatments. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2024, fungal infections are responsible for a significant number of hospital-related infections worldwide, exacerbated by the increasing number of immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing cancer treatments, organ transplants, or immunosuppressive therapies.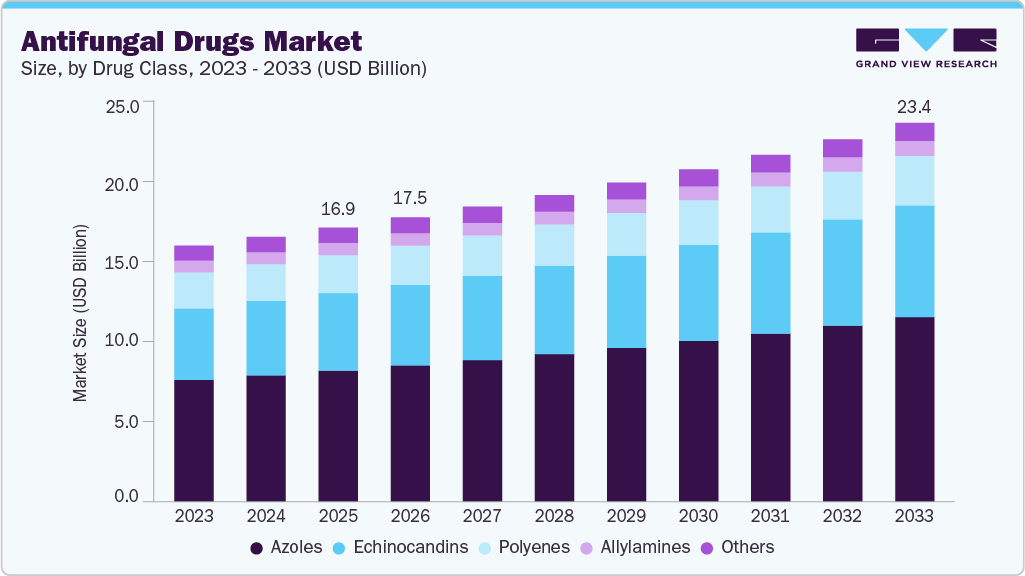
The growing global burden of such infections, especially in regions with expanding healthcare infrastructure, contributes to sustained demand for antifungal therapies. Furthermore, the spread of multidrug-resistant pathogens like Candida auris, identified as an urgent global health threat by the CDC in 2024, has heightened concerns and prompted efforts to develop new and more effective antifungal drugs. The persistent prevalence of superficial fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, onychomycosis, and vaginal candidiasis, also ensures a steady demand for both prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal treatments globally.
Technological advancements in antifungal drug development are a key factor shaping the market landscape. The approval of novel antifungal agents, such as rezafungin in 2023, is expected to expand the treatment options available for invasive fungal infections. This systemic antifungal, which allows for once-weekly dosing, has gained attention for its clinical and economic advantages, particularly in outpatient settings. In addition, the development of new therapeutic classes and agents, such as fosmanogepix, a novel Gwt1 inhibitor, and olorofim, an orotomide targeting resistant Aspergillus species, is addressing critical gaps in treatment, particularly for immunocompromised populations. These innovations, alongside the ongoing advancements in diagnostic technologies like molecular diagnostics, are improving pathogen identification and enabling more targeted treatments. As a result, the market is expanding as new therapies are introduced and integrated into clinical practice, offering greater efficacy and convenience for patients and healthcare systems alike.
Despite these advancements, the market faces significant challenges, primarily stemming from antifungal resistance and the high costs of treatment. Resistance to commonly used antifungal agents, such as azoles and echinocandins, is becoming increasingly prevalent. The CDC’s 2024 report highlights the rapid rise of Candida auris infections, with resistance rates to fluconazole exceeding 90% in some regions, making it one of the most difficult pathogens to treat. This growing resistance undermines the effectiveness of established treatments and creates a demand for newer, more expensive antifungal agents. The high cost of novel therapies, such as rezafungin, and their limited accessibility in many regions, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, presents a significant barrier to market growth. Furthermore, diagnostic delays and limited access to advanced antifungal treatments in resource-constrained settings exacerbate the public health burden of fungal infections. While advancements in drug development offer hope, the ability to make these therapies accessible and affordable, especially in underserved markets, will be crucial for realizing the full market potential.
Opportunity Analysis
The global antifungal drugs industry offers considerable growth opportunities, particularly through innovations aimed at tackling the increasing prevalence of drug-resistant fungal infections. The rise of multidrug-resistant pathogens like Candida auris and resistant strains of Aspergillus continues to pose significant treatment challenges, creating a pressing need for new antifungal therapies. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in its 2024 report on antimicrobial resistance, Candida auris infections have shown a concerning rise, with cases of resistance to commonly used antifungal agents such as fluconazole growing rapidly, making it a critical global health threat. This creates a substantial opportunity for pharmaceutical companies to invest in the development of novel antifungal agents to address these resistant strains. In particular, novel agents like rezafungin and fosman ogepix are in advanced stages of development and have the potential to address these clinical gaps. According to the WHO, C. auris is now classified as one of the highest priorities in the global antimicrobial resistance threat list.
Furthermore, the growing global accessibility of over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal treatments represents another opportunity for market expansion. OTC antifungals, such as clotrimazole, terbinafine, and miconazole, are widely used to treat superficial fungal infections like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and onychomycosis. These infections are prevalent globally, especially in regions with warm climates and high humidity. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has estimated that nearly 70% of Americans will experience athlete’s foot at some point in their lifetime, highlighting the scale of demand for such treatments. According to the CDC, the availability of OTC antifungal products has provided an accessible and cost-effective solution for consumers, driving higher product adoption. This increase in consumer access, coupled with the regulatory affirmation by the FDA in 2024 to allow OTC sales of certain antifungal treatments, is expected to further boost market growth for these products.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The global antifungal drugs industry remains moderately concentrated, with a few major players holding significant shares while numerous smaller and specialized companies contribute to innovation in niche areas such as antifungal resistance and rare fungal diseases. Larger multinational companies dominate key therapeutic classes such as azoles, echinocandins, and polyenes, leveraging their established market presence and distribution networks. However, emerging biotech firms are driving innovations, particularly in the development of new antifungal agents targeting resistant fungal pathogens and rare fungal infections. This results in a dynamic and competitive market environment, where established companies and emerging players coexist, with innovation continuing to fuel market growth.
Innovation in the global antifungal drugs industry is driven by the need to address antifungal resistance and limited treatment options for invasive fungal infections. In March 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved rezafungin (Rezzayo) for the treatment of candidemia and invasive candidiasis in adults with limited or no alternative treatment options, following evaluation of Phase 3 clinical trial data. In parallel, fosmanogepix is in Phase 3 clinical development for the treatment of invasive fungal infections, including infections caused by resistant pathogens. Its clinical status is documented in the U.S. National Library of Medicine’s registry. The need for new antifungal therapies is supported by data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which reports increasing resistance to commonly used antifungal agents such as fluconazole, particularly in healthcare settings. These developments indicate ongoing innovation focused on unmet clinical needs, especially among immunocompromised patient populations.
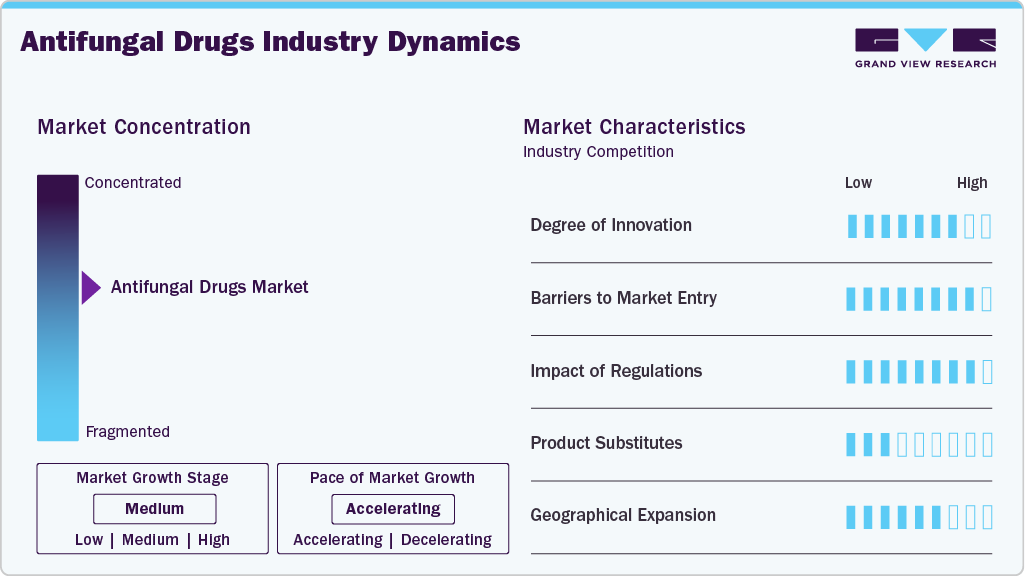
Barriers to entry in the antifungal drugs industry include regulatory requirements and high development costs. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) require extensive clinical evidence to demonstrate safety and efficacy due to the complexity of fungal diseases. The FDA outlines general expectations for clinical development and regulatory submission through its drug guidance framework. Similarly, the EMA requires comprehensive clinical evaluation for antifungal agents, as described in its guideline for the treatment of fungal infections, which addresses study design, endpoints, and patient populations.
Regulatory frameworks play a central role in shaping development timelines and approval outcomes in the antifungal drugs industry. Regulatory authorities such as the FDA apply stringent review standards, particularly for drugs targeting invasive or resistant fungal infections. The FDA approval of rezafungin was supported by a detailed multidisciplinary review and formal approval documentation, which outlines clinical efficacy and safety considerations. Differences in regulatory requirements and review timelines across regions add complexity for companies pursuing multi-regional product launches. The World Health Organization (WHO) has highlighted the need for regulatory convergence to improve access to essential medicines, including antifungal therapies.
The antifungal drugs industry includes competition from generic medicines, off-label use of existing therapies, and non-pharmaceutical alternatives. Generic antifungal agents such as fluconazole and itraconazole are widely used for common fungal infections and are listed in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, reflecting their established clinical role. In some regions, non-pharmaceutical approaches such as herbal treatments are used for superficial fungal infections. Clinical literature has documented antifungal activity of substances such as tea tree oil; however, these findings are primarily limited to laboratory or small clinical studies and are not recommended for invasive infections. As a result, prescription antifungal drugs remain the standard of care for systemic and severe infections.
Geographical expansion opportunities exist in regions experiencing a higher reported incidence of fungal infections and improving access to healthcare services. In 2024, the WHO published its Fungal Priority Pathogens List, identifying regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia as areas with significant unmet needs in fungal disease diagnosis and treatment. The WHO has also documented gaps in the availability of antifungal medicines and diagnostic capacity in these regions, particularly among vulnerable populations. To address these gaps, international health organizations and national governments have initiated programs aimed at improving access to antifungal treatments, including regional efforts coordinated by WHO offices in Southeast Asia.
Drug Class Insights
The azole drug class segment dominated the market with a share of 47.83% in 2025, supported by its broad-spectrum activity, long-standing clinical familiarity, and extensive use across both hospital and outpatient settings. This class remains a first-line option for treating a wide range of superficial and systemic fungal infections, including candidiasis, dermatophytosis, and certain forms of aspergillosis. Their dominance is reinforced by widespread inclusion in international treatment guidelines and essential medicines lists. According to the World Health Organization, in its WHO Model List of Essential Medicines updated in 2023, key azoles such as fluconazole and itraconazole are classified as essential for managing common and invasive fungal infections, underscoring their continued global relevance. In addition, azoles benefit from broad geographic availability, established generic manufacturing, and use in both prescription and OTC formulations in several markets, which collectively sustain high consumption volumes across mature and emerging healthcare systems.
Echinocandins represent the fastest-growing segment within the global market, primarily driven by their increasing use in the treatment of invasive fungal infections and their favorable resistance profile. This growth is closely associated with the rising global incidence of invasive candidiasis and the spread of multidrug-resistant Candida species, particularly Candida auris. Echinocandins are recommended as first-line therapy for candidemia in hospitalized patients due to their effectiveness and safety profile. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in its Clinical Overview of Candida auris updated in December 2024, echinocandins are the preferred initial treatment for C. auris infections, as most isolates remain susceptible to this drug class. This clinical preference, combined with increasing ICU admissions and stewardship-driven prescribing practices, continues to support accelerated adoption of echinocandins across global healthcare systems.
Indication Insights
Candidiasis dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 40.61% in 2025, driven by its high prevalence across both hospital and community settings and its broad clinical spectrum ranging from superficial infections to life-threatening invasive disease. The condition disproportionately affects immunocompromised populations, including patients undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplantation, intensive care treatment, and long-term catheterization, which sustains consistent demand for antifungal therapies worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, in October 2022, candidiasis-particularly invasive candidiasis-was identified as a major contributor to fungal-related morbidity and mortality globally, leading to its inclusion in the WHO Fungal Priority Pathogens List. This classification reflects the high clinical burden and healthcare resource utilization associated with Candida infections, reinforcing their central role in antifungal treatment demand across developed and emerging healthcare systems.
Candidiasis is also the fastest-growing indication segment, supported by the increasing incidence of invasive infections and the rapid global spread of drug-resistant Candida species. Rising ICU admissions, greater use of immunosuppressive therapies, and an expanding elderly population have contributed to higher rates of candidemia and deep-seated Candida infections across regions. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in December 2024, reported clinical cases of Candida auris continued to increase globally, with the pathogen classified as an urgent antimicrobial resistance threat due to its rapid transmission and limited treatment options. This trend is accelerating the use of systemic antifungals, particularly in hospital settings, and driving sustained growth in the candidiasis treatment segment as healthcare systems prioritize early and effective antifungal intervention.
Dosage Form Insights
Oral antifungal drugs dominated the market with a share of 48.93% in 2025, due to their broad clinical utility, ease of administration, and central role in the treatment of both superficial and systemic fungal infections. Oral formulations are widely prescribed for conditions such as candidiasis, dermatophytosis, and onychomycosis, particularly when long-term therapy or systemic exposure is required. According to the World Health Organization, in July 2023, oral antifungals, including fluconazole and itraconazole, were reaffirmed in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for the treatment of a wide range of fungal infections, underscoring their importance in standard treatment protocols across global healthcare systems. This essential-medicine status supports consistent procurement by public health programs and reinforces sustained global utilization of oral antifungal therapies in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Antifungal ointments represent the fastest-growing dosage-form segment, driven by the high global prevalence of superficial fungal infections and increasing preference for topical, self-administered treatments. Ointments are commonly used for dermatophytosis, cutaneous candidiasis, and other skin-related fungal conditions, particularly in outpatient and retail settings. According to published data in April 2025, superficial fungal infections were identified as among the most common fungal diseases worldwide, affecting hundreds of billions of people annually and predominantly managed with topical antifungal therapies. The growing emphasis on early intervention, improved skin-targeted formulations, and expanded OTC availability in multiple regions is accelerating the adoption of antifungal ointments, supporting their faster growth relative to other dosage forms.
Distribution Channel Insights
The hospital pharmacies segment held a dominant share of 47.14% in 2025. This leadership is primarily due to hospitals administering complex and costly systemic antifungal therapies, such as echinocandins and azoles, requiring specialist supervision. Hospital settings enable close patient monitoring, ensuring the safe use of treatments for severe fungal infections like invasive candidiasis and aspergillosis. The availability of advanced intravenous formulations in hospitals further supports this trend. Moreover, hospital pharmacies facilitate adherence to rigorous treatment protocols and manage potential drug interactions effectively. These factors collectively sustain hospital pharmacies as the primary distribution channel for critical antifungal drugs.
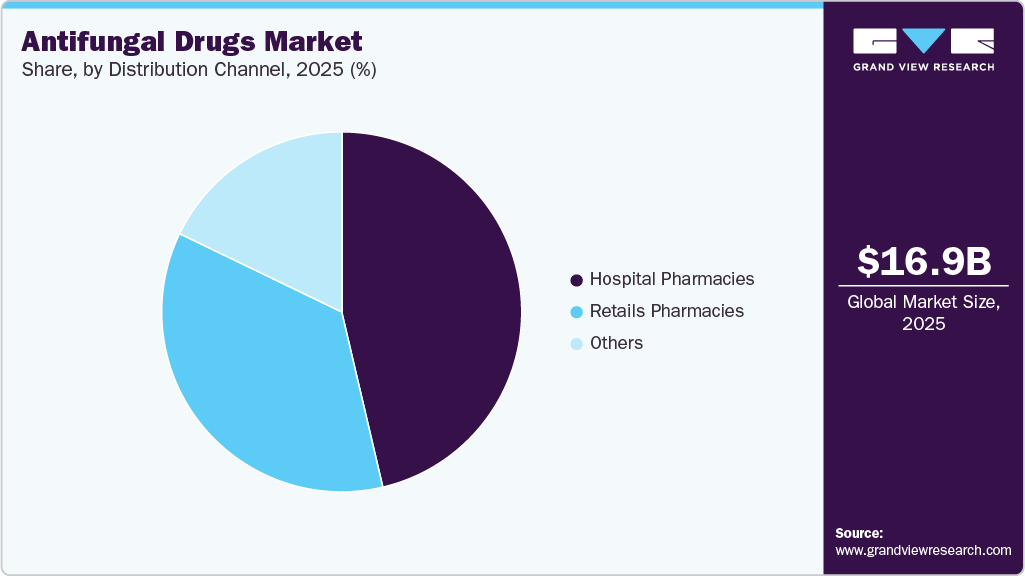
The retail pharmacies segment is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period. This expansion is driven by the increasing availability of topical antifungal agents such as ointments and powders, commonly used for conditions like dermatophytosis. Greater consumer preference for convenient access to oral and topical antifungal medications, supported by pharmacist-led counseling, boosts demand in this channel. Enhanced insurance coverage and rising awareness about fungal infections also contribute to retail pharmacy growth. In addition, integrating digital health platforms and home delivery services improves accessibility and patient adherence. These dynamics position retail pharmacies as a rapidly expanding distribution channel within the antifungal drugs industry.
Regional Insights
North America’s antifungal drugs market is governed by a sustained clinical burden of both superficial and invasive fungal infections, a sizable immunocompromised patient population, and high healthcare utilization that together support consistent demand for systemic and topical antifungal therapies. Treatment needs in hospital settings-driven by factors such as ICU admissions, cancer care, and transplant services-continue to anchor procurement of systemic classes (echinocandins, azoles, polyenes), while retail channels sustain topical and oral outpatient volumes. This dual demand profile creates stable baseline consumption and recurring tendering by large hospital systems and group purchasing organizations across the region.
Surveillance and stewardship are shaping purchasing and adoption patterns, with public health authorities prioritizing early detection and containment of drug-resistant organisms, which in turn drives formulary attention to higher-cost, lower-resistance agents. For example, according to Public Health Ontario, in January 2025, a provincial review covering 2017-2024 reported identified Candida auris cases with high rates of fluconazole resistance and emphasized the need for ongoing surveillance and infection-prevention measures.
U.S. Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The antifungal drugs market in the U.S. continues to be shaped by the prevalence of fungal infections across acute care and outpatient settings, sustained healthcare spending, and active clinical management of immunocompromised patient groups. High utilization of systemic antifungals-including echinocandins and triazoles-for invasive infections remains a core driver of market value in hospitals, while over-the-counter (OTC) topical formulations maintain steady demand in retail channels for common superficial infections. The presence of established commercial distribution frameworks, robust reimbursement mechanisms, and widespread clinical guideline adoption further supports consistent uptake across diverse care settings.
Resistance management and public health surveillance also influence prescribing patterns and product selection, particularly as emerging resistant pathogens create clinical urgency for newer agents. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in its 2024 Antimicrobial Resistance Threats Report, Candida auris was highlighted as an urgent threat with increasing clinical cases and high levels of resistance to certain azoles, prompting intensified infection control and therapeutic stewardship efforts in U.S. healthcare facilities.
Europe Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The antifungal drugs market in Europe is experiencing heightened clinical and procurement activity driven by rising nosocomial and invasive fungal infections, greater ICU utilization, and strengthened surveillance programs that influence hospital formularies and stewardship policies. Hospital demand continues to favor systemic classes such as echinocandins and newer agents because of their role in treating invasive candidiasis and other severe mycoses, while retail channels sustain topical and oral outpatient volumes for dermatological indications. Payers and national health systems are increasingly prioritizing antifungal stewardship and rapid diagnostic integration, which is shifting procurement toward agents with favorable resistance profiles and clearly demonstrated clinical benefit.
Regional risk is elevated by the emergence and geographic spread of drug-resistant Candidozyma auris, which has prompted public health interventions and tighter infection-control protocols across EU/EEA member states. According to the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), in September 2025, a survey covering cases through 2023 reported 4,012 cases of Candidozyma auris colonization or infection in EU/EEA countries between 2013 and 2023, highlighting accelerating case counts in 2022-2023 and emphasizing urgent gaps in laboratory capacity and preparedness.
The UK antifungal drugs marketis defined by concentrated hospital demand for systemic antifungals and active national stewardship programs that shape prescribing, procurement, and diagnostic investments. NHS trusts and integrated care boards increasingly prioritize rapid laboratory identification, infection-prevention controls, and formulary management to limit outbreaks and preserve effective agents. These dynamics favour drugs with clear efficacy against invasive pathogens and support investment in diagnostics and stewardship initiatives that reduce empirical broad-spectrum use and optimize therapeutic sequencing across acute and community settings.
Surveillance signals and outbreak activity are materially influencing policy and purchasing decisions. For example, according to the UK Health Security Agency, in April 2025, there were 134 new Candidozyma auris cases reported in England during the six months November 2024-April 2025, a 23% increase versus the previous six-month period, with many reporting sites being healthcare providers that had not previously seen cases. This increase has prompted updated guidance on laboratory investigation, screening, and infection prevention, driving demand for targeted systemic antifungals, strengthened IPC measures, and expanded laboratory capacity in the NHS.
The antifungal drugs market in Germany is experiencing heightened hospital demand for systemic antifungals and increased investment in laboratory capacity and infection-control measures. A marked rise in Candida auris detections in 2023 prompted health authorities and acute-care providers to reassess screening protocols, strengthen isolation practices, and prioritize agents with reliable activity against resistant Candida strains. These operational shifts have led to larger hospital formularies for echinocandins and renewed procurement emphasis on validated diagnostic reagents and rapid identification workflows to limit outbreak potential and reduce downstream treatment costs.
Policy and surveillance developments are directly influencing commercial dynamics, with manufacturers and distributors responding to tender specifications that increasingly value diagnostic-drug integration and stewardship support. For example, the Robert Koch-Institut’s Epidemiologisches Bulletin reported a substantial increase in Candida auris cases in Germany in 2023, noting that the rise was driven largely by colonisation detections and underlining the need for enhanced laboratory surveillance and infection-prevention measures. This official assessment is driving demand for point-of-care screening tools and hospital-grade systemic antifungals, while also encouraging investment in training and IPC capacity within German healthcare providers.
Asia Pacific Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The antifungal drugs market in the Asia Pacific is shaped by a high regional burden of both superficial and invasive fungal infections, growing hospital capacity, and expanding cohorts of at-risk patients (oncology, transplant, ICU). These structural factors support sustained demand for systemic antifungals in tertiary centres while topical and oral agents remain widely used in outpatient and retail channels. Clinical practice is increasingly influenced by surveillance reports of rising azole resistance in several countries and by the diagnostic gap that delays targeted therapy, which together drive higher empiric use of broader-spectrum agents and increase pressure on hospital formularies and procurement budgets.
Regional scientific literature documents notable epidemiological shifts that directly inform market dynamics. For example, research assessing changing Candida epidemiology across Asia reports increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant species - including azole-resistant C. tropicalis and the emergence of Candida auris - and highlights the resulting need for improved diagnostics, stewardship, and access to newer antifungal classes.
Japan antifungal drugs market is shaped by an aging population, high standards of hospital care, and strong adherence to clinical guidelines, which together support stable demand for systemic antifungal therapies. Invasive fungal infections are primarily managed within hospital settings, particularly among elderly patients, oncology populations, and individuals with chronic diseases. Oral antifungals are widely used in outpatient care, while topical formulations maintain consistent demand for dermatological indications through retail and prescription channels.
The market is characterized by conservative prescribing behavior, strong pharmacovigilance, and a preference for well-established therapies with proven safety profiles. Cost containment measures and reimbursement controls influence product uptake, favoring agents with clear clinical justification. At the same time, rising awareness of antifungal resistance and hospital-acquired infections is gradually increasing attention toward stewardship programs and diagnostic-driven treatment approaches, shaping future demand patterns.
The antifungal drugs market in China is driven by expanding hospital infrastructure, rising inpatient volumes, and increased diagnosis of fungal infections across urban and secondary healthcare facilities. Systemic antifungal demand is supported by growth in critical care capacity, oncology treatment, and surgical interventions, while topical and oral formulations remain widely used in outpatient and community settings. The market benefits from large patient volumes and improved access to antifungal therapies across public hospitals.
Centralized procurement policies, price controls, and a growing emphasis on domestic manufacturing influence market dynamics. These factors support broad access to essential antifungal drugs while limiting rapid premium product penetration. However, increasing clinical focus on resistant infections and hospital infection control is gradually shifting demand toward higher-efficacy agents and improved diagnostic alignment within tertiary care centers.
Latin America Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The antifungal drugs market in Latin America is shaped by a high prevalence of superficial fungal infections, expanding hospital capacity, and uneven access to healthcare across countries. Topical and oral antifungals dominate outpatient treatment, particularly in tropical and subtropical climates, while systemic antifungal use is concentrated in urban hospitals and referral centers managing severe infections. Public-sector procurement plays a significant role in determining market access and pricing.
Structural challenges such as limited diagnostic capacity, budget constraints, and variable reimbursement influence treatment choices, often favoring established antifungal classes. At the same time, gradual improvements in healthcare coverage and infection surveillance are supporting more consistent use of antifungal therapies, particularly in larger economies within the region, contributing to steady long-term market development.
Brazil antifungal drugs marketrepresents the largest within Latin America, supported by its extensive public healthcare system and high burden of both superficial and invasive fungal infections. Hospital demand for systemic antifungals is driven by ICU utilization, transplant activity, and oncology care, while topical formulations remain widely used in primary care and retail settings. Government procurement and public tenders strongly influence pricing and product availability.
The market is characterized by reliance on established antifungal agents, with gradual adoption of newer therapies constrained by budgetary oversight and formulary restrictions. Increasing attention to hospital-acquired infections and antimicrobial stewardship is influencing prescribing behavior, particularly in tertiary hospitals, which is expected to support selective growth in systemic antifungal use over time.
Middle East & Africa Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The antifungal drugs market in the MEA is heterogeneous, reflecting wide disparities in healthcare infrastructure, access, and disease burden across countries. Superficial fungal infections drive demand for topical and oral antifungals, particularly in regions with hot climates, while systemic antifungal use is largely concentrated in urban hospitals and private healthcare facilities managing complex cases. Public-sector purchasing dominates in many markets, shaping access and pricing structures.
Limited diagnostic capabilities and constrained healthcare budgets in parts of the region influence treatment patterns, often favoring empiric therapy with established antifungal agents. However, gradual investments in hospital infrastructure, infection control, and specialist care in select countries are supporting incremental growth in systemic antifungal utilization, particularly in tertiary and private healthcare settings.
Saudi Arabia antifungal drugs market is supported by substantial public healthcare spending, expanding hospital capacity, and growing emphasis on infection prevention and control. Demand for systemic antifungals is concentrated in government and tertiary hospitals, driven by ICU expansion, surgical procedures, and treatment of immunocompromised patients. Retail and outpatient demand for topical and oral antifungals remains stable, supported by high awareness and access to pharmacy services.
Market development is influenced by centralized procurement, formulary oversight, and national healthcare transformation initiatives aimed at improving quality and efficiency. Increasing focus on antimicrobial stewardship and hospital accreditation standards is shaping prescribing practices, with greater emphasis on appropriate antifungal selection and diagnostic confirmation. These factors are expected to support controlled but sustained demand growth across hospital and outpatient segments.
Key Antifungal Drugs Company Insights
The global market is characterized by the presence of multinational pharmaceutical companies and large generic manufacturers with established antifungal portfolios spanning systemic and topical therapies. Bausch Health Companies Inc. has a strong presence in dermatology-focused antifungal products, while Pfizer Inc. and Merck & Co., Inc. maintain leadership in systemic antifungals used in invasive fungal infections. Bayer and Kenvue are prominent in the OTC and consumer health segment with widely distributed topical antifungal brands. GSK plc. and Janssen Pharmaceuticals have historical and ongoing involvement in antifungal molecules that continue to be marketed in various regions. Sandoz and GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS INC., USA play a significant role through generic antifungal formulations, supporting large-volume global supply. Astellas Pharma US, Inc. remains a key player in hospital-focused antifungal treatments, particularly for severe and invasive infections. Collectively, these companies account for a substantial share of commercially available antifungal products across major global markets.
Key Antifungal Drugs Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the antifungal drugs market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Bausch Health Companies Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Bayer
- Kenvue
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- GSK plc.
- Sandoz
- GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS INC., USA
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- Astellas Pharma US, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
In August 2024, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals launched micafungin for injection in the U.S. market, enabling the company to expand its systemic antifungal portfolio and address invasive fungal infections in hospital settings following regulatory approval.
-
In December 2023, the U.S. FDA approved expanded labeling for CRESEMBA (isavuconazonium sulfate) to include pediatric indications for invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis, broadening the clinical use of Astellas’ antifungal agent.
-
In September 2024, the European Medicines Agency reaffirmed authorization of VFEND (voriconazole) for treating invasive aspergillosis and serious fungal infections across Europe, supporting continued clinical utilization of Pfizer’s systemic antifungal therapy.
Antifungal Drugs Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2026
USD 17.55 billion
Revenue forecast in 2033
USD 23.39 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 4.19% from 2026 to 2033
Base year for estimation
2025
Historical data
2021 - 2024
Forecast period
2026 - 2033
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million/billion and CAGR from 2026 to 2033
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, trends
Segments covered
Drug class, indication, dosage form, distribution channel, region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; UK; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; UAE; Kuwait
Key company profiled
Bausch Health Companies Inc.; Pfizer Inc.; Bayer; Kenvue; Merck & Co., Inc.; GSK plc.; Sandoz; GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS INC., USA; Janssen Pharmaceuticals; Astellas Pharma US, Inc.
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Antifungal Drugs Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global antifungal drugs market report based on drug class, indication, dosage form, distribution channel, and region:
-
Drug Class Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2021 - 2033)
-
Azoles
-
Echinocandins
-
Polyenes
-
Allylamines
-
Others
-
-
Indication Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2021 - 2033)
-
Dermatophytosis
-
Aspergillosis
-
Candidiasis
-
Others
-
-
Dosage Form Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2021 - 2033)
-
Oral Drugs
-
Ointments
-
Powders
-
Others
-
-
Distribution Channel Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2021 - 2033)
-
Hospital Pharmacies
-
Retail Pharmacies
-
Others
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2021 - 2033)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
UK
-
Germany
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Denmark
-
Sweden
-
Norway
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
Japan
-
China
-
India
-
Australia
-
South Korea
-
Thailand
-
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
South Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
UAE
-
Kuwait
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global antifungal drugs market size was estimated at USD 16.93 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 17.55 billion in 2026.
b. The global antifungal drugs market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.19% from 2026 to 2033 to reach USD 23.39 billion by 2033.
b. North America dominated the antifungal drugs market with a share of 40.32% in 2025. This is attributable to an increase in the development of innovative drugs, and high awareness regarding fungal diseases and its treatment.
b. Some key players operating in the antifungal drugs market include Novartis AG, Pfizer, Inc., Bayer AG, Sanofi S.A., Merck & Co., Inc., GSK plc, Abbott Laboratories, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Astellas Pharma, Inc.
b. Key factors that are driving the antifungal drugs market growth include the introduction of new antifungal drugs, frequent government initiatives, and a high prevalence of fungal infections in emerging economies.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.