- Home
- »
- Distribution & Utilities
- »
-
Middle East Microgrid Market Size, Industry Report, 2033GVR Report cover
![Middle East Microgrid Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Middle East Microgrid Market (2025 - 2033) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Power Source (CHP, Natural Gas, Solar PV), By Connection (Remote, Hybrid), By End Use (Government, Education), By Country, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-710-3
- Number of Report Pages: 110
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2021 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2033
- Industry: Energy & Power
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Middle East Microgrid Market Summary
The Middle East microgrid market was estimated at approximately USD 6.67 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 16.00 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.11% from 2025 to 2033. Microgrid deployment in the region spans renewable, hybrid, and diesel-solar systems, supporting grid-connected and remote applications in industrial, commercial, defense, and community sectors.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- The microgrid market in Saudi Arabia held the largest share of 38.72% in the Middle East region in 2024.
- The microgrid market in the Middle East is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period.
- By power source, solar PV held the largest market share of 33.78% in 2024.
- Based on connection, the remote segment held the largest market share in 2024.
- Based on end use, the government segment held the largest market share in 2024.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 6.67 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 16.00 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2033): 10.11%
National strategies such as Saudi Vision 2030, the UAE’s Energy Strategy 2050, and Oman’s National Energy Strategy are accelerating investments in decentralized energy systems to enhance energy security, reduce transmission losses, and integrate variable renewable repower sources. Countries across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Turkey, and Israel are increasingly adopting microgrids to serve off-grid oil and gas operations, mining sites, islands, and rural communities while improving resilience against grid outages and cyber threats.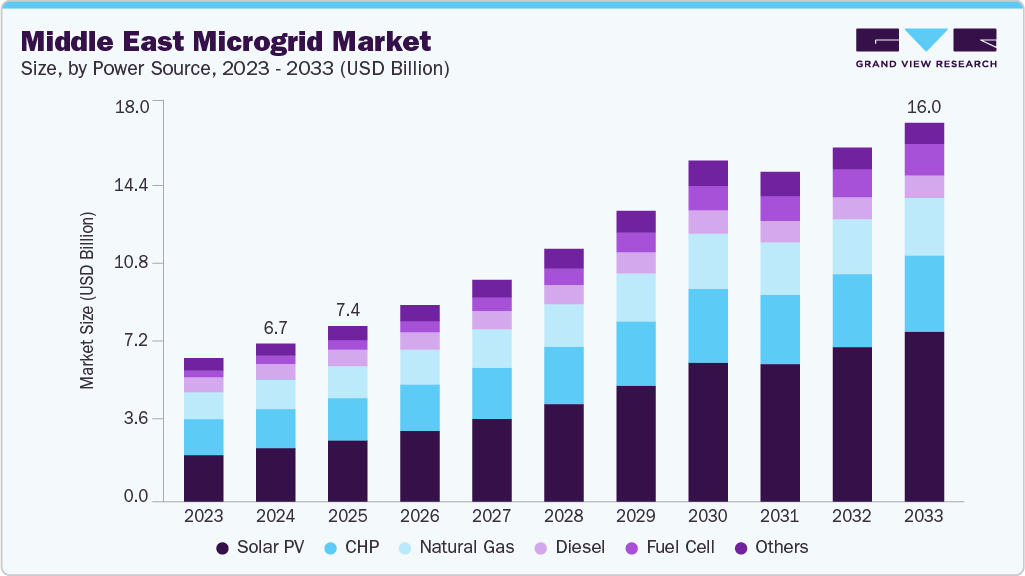
Growth in the market is driven by abundant solar irradiation, falling renewable technology costs, and strong policy support through incentives, public-private partnerships (PPPs), and concessional financing. Advanced technologies such as battery energy storage systems (BESS), smart inverters, and AI-enabled energy management platforms enable more flexible and efficient operations. Hybrid microgrids combining photovoltaic (PV) panels, wind turbines, and diesel or gas generators are gaining traction for delivering round-the-clock power with reduced fuel consumption. Cross-border initiatives like the GCC interconnection expansion and Israel-Europe transmission links are expected to strengthen grid integration and open new opportunities for distributed energy repower sources. With leading companies such as Masdar, ACWA Power, Siemens Energy, and Schneider Electric spearheading large-scale deployments, the Middle East microgrid industry is set for robust and sustained growth over the coming decade.
Drivers, Opportunities & Restraints
The Middle East microgrid industry is driven by strong renewable energy ambitions, energy security priorities, and targeted policy frameworks across the GCC, Levant, and North Africa. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Israel are leveraging their national visions to promote decentralized energy generation, reduce dependence on oil and gas, and enhance grid resilience. The region’s exceptional solar potential and growing interest in hybrid microgrid systems integrating wind, storage, and diesel backup position it as a leader in off-grid and grid-connected solutions. Rising electricity demand from urban expansion, industrial zones, and tourism hubs further accelerates investments in advanced microgrid infrastructure capable of delivering reliable, low-carbon power.
Opportunities in the market include the deployment of microgrids for remote oil & gas facilities, islanded communities, and military bases, as well as integrating battery energy storage systems (BESS) to improve energy dispatchability. The expansion of green hydrogen pilot projects, cross-border interconnection plans, and AI-driven smart control systems opens new frontiers for scalability and export potential. International joint ventures and technology collaborations enable the adoption of advanced control software, modular microgrid designs, and renewable-hydrogen hybrids. However, market restraints persist in the form of high upfront capital expenditure, particularly for advanced storage and hydrogen integration, coupled with challenges in financing smaller-scale projects. Technical hurdles, such as managing variable renewable generation in extreme climate conditions, and policy inconsistencies between jurisdictions, can slow deployment and affect investor appetite in certain sub-markets.
Power Source Insights
The solar PV segment emerged as the fastest-growing power source category in the market, capturing a revenue share of over 33.78% in 2024. Its rapid expansion is fueled by abundant solar irradiation across the region, falling technology costs, and the ability to deliver clean, renewable energy for various applications. Key installations in countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Jordan drive capacity additions, with deployments spanning residential communities, industrial facilities, commercial complexes, and remote off-grid areas. Landmark projects leveraging utility-scale and distributed solar PV demonstrate the technology’s capability to reduce reliance on fossil fuels while supporting national renewable energy targets. While CHP and other dispatchable sources ensure baseline stability, solar PV plays a central role in reducing operational emissions and diversifying energy supply in regional microgrids.
Supportive government initiatives, attractive feed-in tariffs, and ambitious solar deployment targets further accelerate adoption. Integrating solar PV with battery energy storage systems (BESS), advanced inverters, and smart energy management platforms enhances grid stability, peak load shaving, and energy cost optimization. In addition, the proliferation of modular, containerized solar microgrids for remote communities, mining operations, agricultural sites, and humanitarian projects underscores the technology’s scalability and adaptability. Challenges such as intermittency and land-use constraints are being mitigated through hybrid configurations with CHP, wind, and storage, as well as the adoption of high-efficiency PV modules and tracking systems, cementing solar PV’s position as a cornerstone of the Middle East’s evolving microgrid landscape over the forecast period.
Connection Insights
The remote segment accounted for a significant revenue share of over 39.02% in 2024 and is projected to witness substantial growth over the forecast period. This segment is gaining momentum as governments and private developers focus on delivering reliable, independent power solutions to off-grid and underserved locations, including rural communities, islands, mining operations, oil & gas sites, and border outposts. Countries such as Oman, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE are deploying remote microgrids to reduce diesel dependence, lower fuel transport costs, and enhance energy access in geographically challenging areas. Projects integrating solar PV, wind, energy storage, and, in some cases, hybrid diesel or CHP systems are increasingly implemented to ensure a stable, continuous supply in areas far from centralized grids.
The growth of the remote segment is further supported by advancements in modular and containerized microgrid solutions, which enable faster deployment, scalability, and ease of maintenance in isolated environments. Integrating energy storage systems and intelligent control platforms allows optimized energy usage, improved load management, and minimal operational downtime. Supportive government policies, sustainability targets, and public-private partnerships are accelerating investment in remote microgrid infrastructure, particularly in energy-intensive industries and strategic defense locations. As renewable technology costs decline and hybrid configurations become more efficient, remote microgrids emerge as a critical enabler of energy self-sufficiency, resilience, and low-carbon power generation in the Middle East’s off-grid regions.
End Use Insights
The government segment accounted for a substantial revenue share of over 23.49% in 2024 and is expected to maintain strong growth over the forecast period. This end use segment is expanding rapidly as regional governments prioritize resilient, secure, and sustainable energy solutions for administrative complexes, defense facilities, emergency response centers, and municipal infrastructure. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Oman increasingly deploy microgrid systems to ensure uninterrupted operations for critical government services, integrating solar PV, CHP, and energy storage to enhance energy security and reduce dependence on centralized grids. High-profile projects, including renewable-powered government campuses, smart city control hubs, and hybrid microgrids for strategic defense sites, highlight the sector’s commitment to reliable, efficient, and low-carbon energy systems.
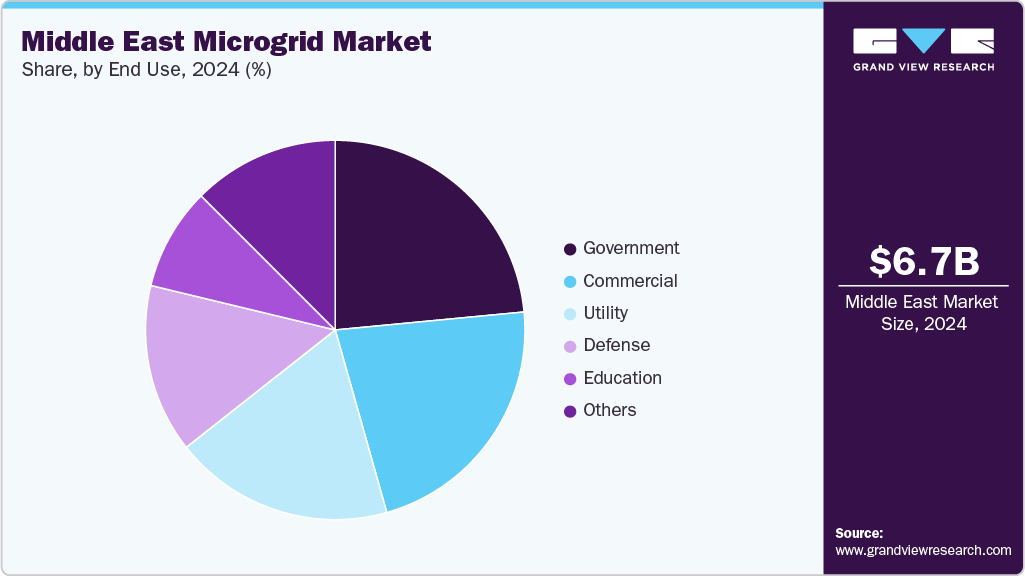
National energy transition strategies, carbon neutrality goals, and the need for operational continuity in mission-critical environments further drive the growth of microgrids in the government sector. Advanced control systems, real-time monitoring platforms, and hybrid configurations combining renewable and dispatchable sources enable governments to optimize power generation, manage peak demand, and improve disaster resilience. Policy mandates for renewable energy adoption, budget allocations for sustainable infrastructure, and strategic partnerships with global technology providers are accelerating investment in government microgrid projects. As Middle Eastern nations continue to modernize public infrastructure, enhance energy independence, and strengthen national security, the government segment will remain a pivotal driver of microgrid deployment across the region over the forecast period.
Country Insights
Saudi Arabia microgrid industry held the largest revenue share in the Middle East region in 2024, accounting for over 38.72%, driven by its ambitious energy diversification strategy under Vision 2030 and its commitment to becoming a global clean energy leader. The Kingdom is investing heavily in utility-scale solar, wind, and green hydrogen projects, with flagship initiatives such as NEOM, the Red Sea Project, and the Sakaka PV plant serving as cornerstones of its renewable expansion. The Renewable Energy Project Development Office (REPDO) continues to organize structured auctions that attract international developers and ensure transparent, competitive pricing, significantly boosting installed microgrid and renewable capacity nationwide.
Saudi Arabia’s renewable energy potential, particularly in solar irradiance and northwestern wind corridors, is among the highest in the Middle East. While utility-scale solar remains dominant, wind energy is gradually gaining traction, supported by detailed feasibility studies and technological innovation. The Kingdom is also making substantial progress in green hydrogen, exemplified by NEOM’s USD 8.4 billion green hydrogen plant, which is poised to become a global benchmark. Well-defined policy frameworks, investor-friendly regulations, and sovereign-backed funding mechanisms reinforce Saudi Arabia’s regional microgrid market leadership. With growing momentum in project execution, international collaboration, and technological deployment, the country is expected to maintain its dominant position throughout the forecast period.
The UAE microgrid industry is a key player in the Middle East, underpinned by its leadership in solar deployment and forward-looking national policies through the UAE Energy Strategy 2050. The country has scaled up utility-scale solar PV and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) projects, including the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park, one of the world’s largest integrated solar facilities. Abu Dhabi and Dubai continue to lead in distributed solar systems, digital grid enhancements, and microgrid integration via initiatives such as Shams Dubai and the Abu Dhabi Clean Energy Strategy.
Beyond solar, the UAE is actively developing a green hydrogen economy, with export-oriented projects in collaboration with international partners. Strong regulatory support, low-cost project financing, and an open market for foreign investment further enhance the country’s microgrid growth prospects.
The microgrid industry in the Israel is expanding steadily, supported by government backing, international financing, and untapped solar and wind resources. Projects like the Benban Solar Park demonstrate Israel’s commitment to renewable integration. The government’s Integrated Sustainable Energy Strategy (ISES) aims for a 42% share of microgrid and renewable energy in the national mix by 2035. Large-scale solar, onshore wind, and cross-border energy interconnections with Africa and Europe reinforce Israel’s role as a clean energy corridor. The rise of Independent Power Producers (IPPs) and well-defined regulatory frameworks enhances investor confidence, positioning Israel as a notable contributor to regional microgrid capacity.
The Oman microgrid market is emerging as a promising market in the Middle East, with strategic emphasis on solar, wind, and green hydrogen deployment. Under Oman Vision 2040, the country targets 30% electricity generation from renewables by 2030. Vast deserts support solar PV deployment, while the southern Dhofar region offers strong wind potential. Oman is also a regional frontrunner in green hydrogen projects, led by initiatives such as Hydrogen Oman (Hydrom), which have attracted multiple international consortia. Despite some challenges in grid capacity and policy implementation, regulatory improvements and pilot microgrid projects are laying the groundwork for long-term growth.
Qatar’s microgrid industry’s initiatives are gaining momentum and are aligned with the Qatar National Vision 2030 and carbon neutrality targets. The 800 MW Al Kharsaah Solar PV Plant, inaugurated in 2022, marks a major step toward renewable adoption. The country is exploring hydrogen and carbon capture integration to reduce emissions in its gas-heavy power sector. While fossil fuels remain dominant, strengthened regulatory support and international collaborations are expected to drive further microgrid investments, particularly in urban and industrial expansion areas.
Key Middle East Microgrid Company Insights:
Some of the key players operating in the Middle East microgrid industry include ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG, General Electric Company, among others. These companies are actively involved in delivering advanced microgrid solutions, integrating renewable energy repower sources, and optimizing energy management systems to enhance grid reliability and sustainability in the region.
Key Middle East Microgrid Companies:
- ABB Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- General Electric Company
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- ENGIE SA
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Tesla Inc.
Recent Developments
-
In March 2025, ENGIE SA launched the development of a 300 MW solar-plus-storage microgrid project in the United Arab Emirates, designed to serve remote communities and industrial zones in Abu Dhabi’s Al Dhafra region. The project will combine solar PV generation with advanced lithium-ion battery systems to ensure round-the-clock power availability, cutting annual carbon emissions by over 1.5 million tons. This initiative aligns with the UAE’s Energy Strategy 2050 and highlights ENGIE’s role in driving microgrid adoption across the Middle East through innovative, large-scale clean energy deployments.
Middle East Microgrid Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 7.40 billion
Revenue forecast in 2033
USD 16.00 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 10.11% from 2025 to 2033
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2021 - 2023
Forecast period
2025 - 2033
Quantitative Units
Volume in MW, Revenue in USD million, and CAGR from 2025 to 2033
Report coverage
Revenue & volume forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Power Source, connection, end use and country
Country scope
UAE; Saudi Arabia; Israel; Oman; Qatar
Key companies profiled
ABB Ltd.; Schneider Electric SE; Siemens AG; General Electric Company; Honeywell International Inc.; Hitachi Energy Ltd.; Eaton Corporation plc; ENGIE SA; Yokogawa Electric Corporation; Tesla Inc.
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Middle East Microgrid Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the Middle East microgrid market report based on power source, connection, end use, and country.
-
Power Source Outlook (Volume, MW; Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
CHP
-
Natural Gas
-
Solar PV
-
Diesel
-
Fuel Cell
-
Others
-
-
Connection Outlook (Volume, MW; Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Remote
-
Grid Connected
-
Hybrid
-
-
End Use Outlook (Volume, MW; Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Government
-
Education
-
Commercial
-
Utility
-
Defense
-
Others
-
-
Country Outlook (Volume, MW; Revenue, USD Million, 2021 - 2033)
-
Middle East
-
UAE
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Israel
-
Oman
-
Qatar
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The Middle East microgrid market size was estimated at USD 6.67 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 7.40 billion in 2025.
b. The Middle East microgrid market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 10.11% from 2025 to 2033 to reach USD 16.00 billion by 2033.
b. Based on the power source segment, solar PV microgrid held the largest revenue share of 33.78% in the Middle East microgrid market in 2024, supported by the region’s increasing investment in modernizing and strengthening national power infrastructure.
b. Some of the key vendors operating in the Middle East microgrid market include Masdar; ACWA Power International; EDF Renewables; Engie; Siemens Energy AG; ABB Ltd.; Schneider Electric SE; General Electric Company; and Hitachi Energy Ltd., among others.
b. The key factors driving the Middle East microgrid market include ambitious national energy transition strategies, rising electricity demand, and the urgent need for resilient power systems in both urban and remote locations. Governments across the region, particularly in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman, are prioritizing distributed energy solutions to complement large-scale renewable projects.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.