- Home
- »
- Biotechnology
- »
-
Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market (2025 - 2030) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Mode (Chemical, Physical), By Application (Research, Therapeutics), By End-use, By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-497-6
- Number of Report Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2024
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Healthcare
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Interactive Charts
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Summary
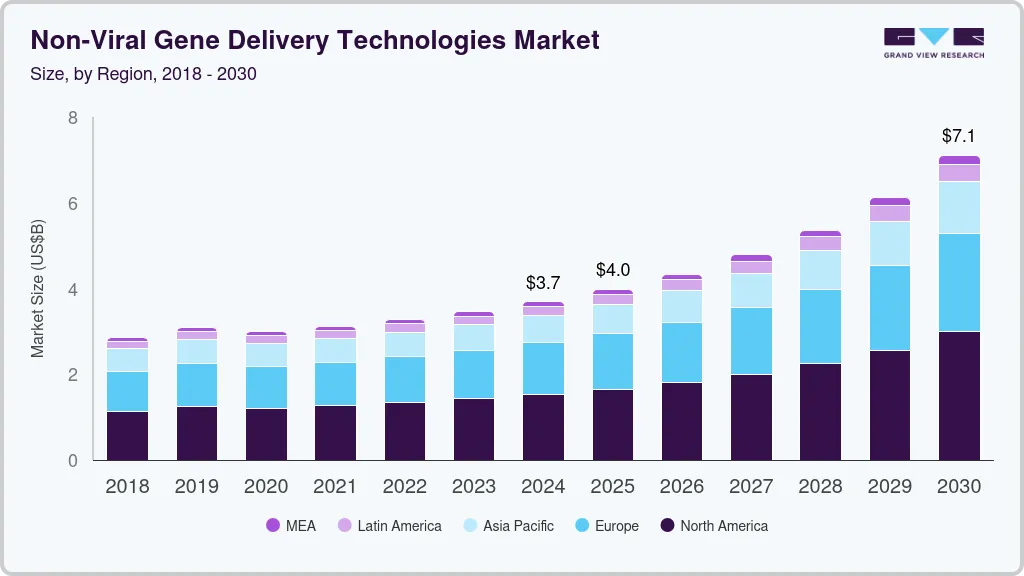
The global non-viral gene delivery technologies market size was estimated at USD 3,695.1 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7,105.3 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 12.3% from 2025 to 2030. The global non-viral gene delivery technologies industry is significantly driven by the ongoing advancements in genome editing technologies and the increasing demand for personalized medicine.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- In terms of region, North America was the largest revenue generating market in 2024.
- Country-wise, UAE is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2030.
- In terms of segment, chemical accounted for a revenue of USD 2,387.9 million in 2024.
- Chemical is the most lucrative mode segment registering the fastest growth during the forecast period.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 3,695.1 Million
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 7,105.3 Million
- CAGR (2025-2030): 12.3%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
The successful integration of non-viral systems, especially lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) and polymer-based vectors, into gene-editing platforms like CRISPR/Cas9 has paved the way for precision therapies targeting complex genetic disorders. This precision medicine trend is accelerating market growth as therapies are being developed for rare genetic diseases, where non-viral vectors offer advantages such as ease of modification and scalability over viral vectors.
Companies like Intellia Therapeutics and Editas Medicine are increasingly focusing on non-viral delivery mechanisms to improve the safety and efficiency of gene-editing therapies, particularly in the realm of in vivo applications.
The COVID-19 pandemic also had a transformative effect on the adoption of non-viral gene delivery technologies. The rapid development and deployment of mRNA vaccines by companies like Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech demonstrated the potential of lipid nanoparticles as effective non-viral delivery systems. This success has not only driven the adoption of non-viral delivery technologies in vaccine development but has also spurred a broader interest in their use for gene therapy in oncology, cardiovascular diseases, and genetic disorders. As the pandemic illustrated the need for rapid, scalable production methods for gene-based therapeutics, the market saw a surge in investments, particularly from public and private sectors eager to develop next-generation gene therapies for a variety of diseases.
The ongoing development of nanomedicines has also contributed significantly to the growth of the market. Nanoparticles, such as gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes, are being explored for their ability to deliver nucleic acids efficiently and provide targeted therapy, a significant advantage for applications in cancer and other hard-to-treat conditions. Companies like Cellectis and Arcturus Therapeutics are exploring the use of novel delivery systems, such as self-assembling RNA nanoparticles, which can improve the stability and delivery efficiency of RNA-based therapeutics. These innovations are expanding the application of non-viral gene delivery beyond traditional gene therapy into more personalized, tissue-targeted approaches.
In addition to the advancements in technology, regulatory changes and a more supportive framework for gene therapy approvals are further accelerating market growth. The approval of non-viral gene therapies, such as Inclisiran (Leqvio) for hypercholesterolemia by Novartis, demonstrates the potential for small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapies in treating chronic conditions. This trend is expected to continue as governments and regulatory bodies increasingly prioritize gene therapy and related treatments. Moreover, the rise of biotechnology hubs in Asia-Pacific, including China and India, where biotech infrastructure is rapidly expanding, is fueling the global adoption of non-viral gene delivery technologies. With increasing collaboration between biotech companies and academic research institutions, the market is expected to witness a wave of innovations and therapies in the coming years.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The non-viral gene delivery technologies industry is characterized by rapid innovation, particularly in areas such as lipid nanoparticles, polymers, and CRISPR/Cas9-based delivery. Advances in nanotechnology have led to the development of highly efficient, targeted delivery systems with reduced toxicity. Continuous R&D efforts focus on improving the stability, payload capacity, and specificity of these delivery methods to enhance therapeutic outcomes in genetic disorders, oncology, and immunotherapy.
The regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the non-viral gene delivery technologies industry. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA are evolving their frameworks to accommodate gene therapies, creating both opportunities and challenges. While regulatory approvals for non-viral therapies are becoming more streamlined, the need for comprehensive safety and efficacy data still drives long and rigorous approval processes, especially for new gene-editing technologies like CRISPR.
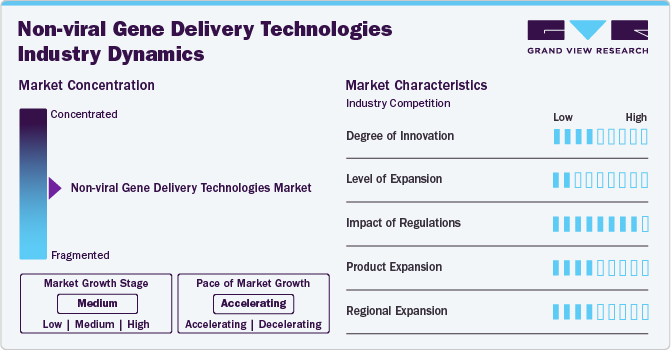
Product expansion in the market is driven by the continuous development of new delivery platforms and targeted therapies. Companies are expanding their portfolios to include a variety of non-viral methods, such as RNA nanoparticles, electroporation systems, and polymeric vectors. This expansion is broadening the scope of applications in areas like oncology, genetic disorders, and vaccination, with products evolving to address unmet medical needs.
Regional expansion of non-viral gene delivery technologies is growing, with a strong focus on North America and Europe due to robust healthcare infrastructures and regulatory support. However, markets in Asia-Pacific, including China and India, are emerging as key growth regions. These regions benefit from increasing investments in biotechnology, gene therapy research, and favorable government policies, positioning them as important players in the global market expansion.
Mode Insights
Based on mode, chemical accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024 and is projected to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. The chemical mode of non-viral gene delivery technologies is driven by the increasing demand for efficient, safe, and scalable gene delivery systems. Chemical methods, such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), polymeric carriers, and lipoplexes, offer several advantages, including the ability to carry larger genetic payloads, reduced immunogenicity, and ease of production.
The growing interest in mRNA-based therapies and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing has further accelerated the use of chemical delivery systems, as they provide a versatile platform for targeting specific cells and tissues. In addition, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of chemical-based delivery methods are crucial for advancing gene therapies for chronic diseases, cancer, and genetic disorders, driving their adoption across the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors.
Application Insights
Based on application, the research segment held the largest revenue share in 2024. The market is driven by the growing need for versatile, efficient, and cost-effective tools to study gene function, expression, and regulation. Non-viral delivery methods, such as lipid nanoparticles, polymeric vectors, and electroporation, offer researchers enhanced control over gene transfer, enabling precise manipulation of cells and tissues without the risks associated with viral vectors. These technologies are crucial for advancing research in gene editing, cancer therapy, and genetic diseases, as they facilitate the delivery of large genetic payloads and facilitate CRISPR-based genome editing. In addition, the shift towards more reproducible and scalable delivery systems supports the growing demand for non-viral methods in academic and commercial research laboratories, further accelerating their adoption in genetic studies.
The therapeutics segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Non-viral delivery systems, including lipid nanoparticles, polymer-based carriers, and RNA-based technologies, are essential for delivering gene-based therapies for chronic diseases, genetic disorders, and cancer. Their ability to reduce immunogenicity, provide repeat administration, and carry large genetic payloads makes them ideal for therapeutic interventions. The success of non-viral technologies in mRNA vaccines, such as the COVID-19 vaccines by Moderna and Pfizer, has highlighted their potential in large-scale therapeutic applications. In addition, their adaptability to targeted delivery systems is fueling their adoption in precision medicine, particularly for diseases that require highly specific gene modifications or therapies.
End-use Insights
Based on end use, the research and academic institutes segment held the largest revenue share of 48.11% in 2024 and is projected to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. The market for research and academic institutes is driven by the increasing need for reliable, efficient, and cost-effective methods to explore gene function, expression, and modification.
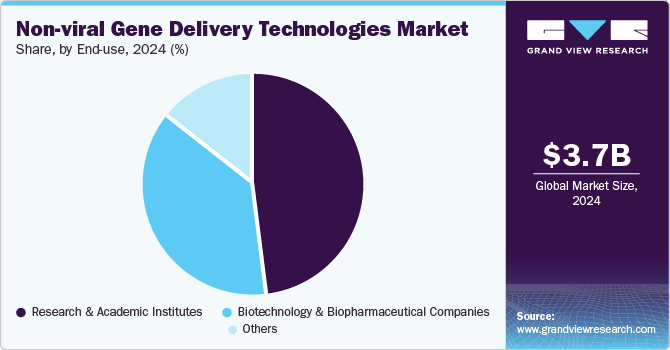
Non-viral systems offer researchers a versatile platform to deliver genes or gene-editing tools like CRISPR/Cas9 without the complexities and risks associated with viral methods. These technologies enable precise control over genetic material delivery, facilitating studies in gene therapy, genetic diseases, cancer, and functional genomics. Furthermore, their ability to support large-scale experiments and reproducible results makes non-viral delivery methods increasingly popular in academic research, accelerating the development of new therapies and advancing basic scientific understanding.
Regional Insights
North America non-viral gene delivery technologies market dominated globally with a share of 41.25% in 2024. Factors behind this growth include the strong research infrastructure, well-established pharmaceuticals and biotechnological sectors, and heavy investments in gene therapy and genetic medicine.
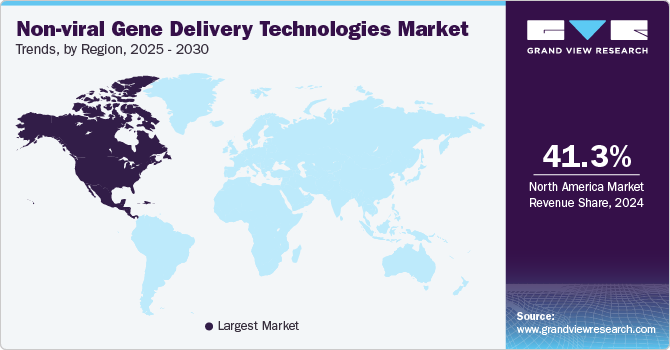
U.S. Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Trends
The U.S. non-viral gene delivery technologies market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for gene therapies and biotech innovations across various therapeutic areas such as oncology, genetic disorders, and chronic diseases. The U.S. benefits from a robust biopharmaceutical industry, strong R&D funding, and a supportive regulatory framework by agencies like the FDA, which have fast-tracked gene therapy approvals. Furthermore, the successful adoption of non-viral systems in mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the use of non-viral gene delivery technologies, pushing for their wider adoption in gene therapy trials and research applications.
Europe Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Trends
The Europe non-viral gene delivery technologies market is driven by a combination of innovative research and the region's expanding focus on personalized medicine and genetic-based therapies. European governments and institutions are increasingly investing in the biotech sector, particularly in the UK, Germany, and France, where non-viral delivery technologies are integrated into research programs targeting diseases like cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and rare genetic conditions. Regulatory support from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has enabled the commercialization of gene therapies, while the region’s collaboration between academia, research institutes, and the pharmaceutical industry accelerates the development and adoption of non-viral delivery systems.
The UK non-viral gene delivery technologies market is experiencing rapid growth driven by government investments in genomic research and a focus on biotech innovation. The UK is a hub for CRISPR research and gene editing, where non-viral delivery technologies are increasingly used for preclinical and clinical trials. In addition, the UK's growing healthcare ecosystem and its push toward adopting personalized medicine are key drivers of demand for efficient and scalable gene delivery systems. The regulatory support from UK authorities also fosters the development of non-viral gene therapies, enhancing their application in research and therapeutics.
France non-viral gene delivery technologies market growth is largely fueled by the country’s emphasis on biotechnology and genomics. France has become a leading player in genetic research, with institutes focusing on rare diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders. Non-viral gene delivery systems, such as lipid nanoparticles and polymeric carriers, are gaining traction as efficient, scalable alternatives to viral vectors. Furthermore, government-backed research programs and a strong pharmaceutical sector contribute to the growing adoption of non-viral delivery methods in both academic research and clinical applications.
Germany non-viral gene delivery technologies market is at the forefront in Europe, driven by its well-established biotechnology industry, robust research funding, and advanced manufacturing capabilities. The country’s focus on personalized medicine and genetic-based therapeutics has led to increased investments in non-viral delivery technologies. As Germany’s pharmaceutical and academic sectors continue to explore novel gene therapies for complex diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and genetic disorders, the demand for safe and efficient delivery systems is rising. The regulatory framework in Germany, supported by the European Medicines Agency, also enables the development of non-viral gene therapies.
Asia Pacific Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Trends
Asia Pacific non-viral gene delivery technologies market growth is driven by the adoption of the expanding biotech infrastructure, increasing investments in genetic therapies, and the demand for advanced gene-editing technologies like CRISPR/Cas9. Countries like Japan, China, and India are seeing rapid growth in the biotech sector, with a focus on genetic disorders, cancer research, and mRNA-based therapeutics. The affordability, scalability, and reduced immunogenicity of non-viral gene delivery technologies make them attractive options in these markets. Government policies supporting biotech research and clinical trials further boost market adoption.
The non-viral gene delivery technologies market in China is expanding rapidly due to the country’s focus on advancing genetic engineering and gene therapies. Government investments in biotech and life sciences, coupled with China's large patient population, drive the demand for non-viral delivery systems, particularly for cancer therapies and rare diseases. China's regulatory support for innovative gene therapies and its increasing participation in global clinical trials have accelerated the adoption of non-viral gene delivery technologies. The country's advancements in CRISPR technology also contribute to the growing utilization of non-viral vectors.
The non-viral gene delivery technologies market in Japan is leading the way in the Asia-Pacific region, with strong government support for biotech research and genetic therapies. Japan's established reputation in pharmaceuticals and healthcare innovation, alongside increasing investments in gene-editing technologies and mRNA-based therapies, propels the adoption of non-viral gene delivery systems. These systems are particularly important for targeted therapies in oncology, genetic disorders, and neurological conditions. Japan’s stringent regulatory framework ensures high standards for the development of non-viral gene therapies, further encouraging market growth.
The non-viral gene delivery technologies market in India is growing due to increased investments in biotechnology and a strong focus on affordable healthcare solutions. India’s large patient population, especially in areas of genetic diseases and cancer, drives the demand for more effective and scalable gene delivery systems. The rise of biotech startups and increasing collaboration between academia and the pharmaceutical industry further contribute to the adoption of non-viral delivery technologies in gene therapies. India's expanding clinical trial infrastructure is also providing more opportunities for the application of these technologies in therapeutic settings.
Middle East & Africa Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Trends
The Middle East & Africa non-viral gene delivery technologies market is witnessing growth due to increased investments in biotechnology and healthcare infrastructure development. Countries like the United Arab Emirates and Qatar are making substantial efforts to diversify their economies, with a focus on biotech and genetic medicine. The growing need for advanced gene therapies in areas such as oncology and genetic diseases is driving the demand for non-viral delivery methods. In addition, the Middle East’s collaboration with global biotech companies fosters the adoption of innovative gene delivery technologies in research and therapeutic applications.
The market for non-viral gene delivery technologies in Saudi Arabia is expanding due to the country’s emphasis on healthcare modernization and biotech innovation. The Saudi government’s efforts to diversify its economy through the Vision 2030 initiative have led to increased investments in the biotech sector, with a focus on genomic research and precision medicine. As the country seeks to address growing healthcare challenges, particularly in the areas of genetic disorders and cancer, non-viral gene delivery systems are seen as promising tools for safe and scalable gene therapies.
The market for non-viral gene delivery technologies in Kuwait is supported by the adoption of the country’s increasing focus on genomic research and biotechnology development. Kuwait is investing heavily in healthcare infrastructure and personalized medicine. The rising demand for gene therapies and the focus on rare diseases and cancer have led to the use of non-viral delivery methods in research and therapeutic applications. As the region continues to modernize its healthcare systems and collaborate with global biotech companies, the adoption of non-viral gene delivery systems is expected to grow.
Key Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Company Insights
The market players operating in the non-viral gene delivery technologies industry are adopting product approval to increase the reach of their products in the market and improve the availability of their products in diverse geographical areas, along with expansion as a strategy to enhance production/research activities. In addition, several market players are acquiring smaller players to strengthen their market position. This strategy enables companies to increase their capabilities, expand their product portfolios, and improve their competencies.
Key Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the non-viral gene delivery technologies market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- GenScript
- Danaher
- Merck KGaA
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Altogen Biosystems
- Lonza
- Sonidel
- SIRION BIOTECH GmbH
- Innovative Cell Technologies, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
In October 2024, Poseida Therapeutics presented new preclinical data that supported the use of non-viral gene editing with P-KLKB1-101 for treating hereditary angioedema.
-
In September 2024, ProBio and UCI Therapeutics announced the signing of a strategic cooperation memorandum of understanding (MOU) aimed at advancing NK cell gene introduction technology. Under this MOU, both companies have committed to enhancing their collaboration in the development of both viral and non-viral methods.
-
In March 2023, Moderna, Inc. and Generation Bio Co. announced a strategic collaboration to combine Moderna's biological and technical expertise with Generation Bio's core technologies in non-viral genetic medicine. This partnership aims to enhance the application of both companies' platforms by developing innovative nucleic acid therapeutics, including those targeting immune cells, to accelerate the progress of their respective non-viral genetic medicine pipelines.
Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 3.98 billion
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 7.11 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 12.29% from 2025 to 2030
Actual data
2018 - 2024
Forecast period
2025 - 2030
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million/billion, and CAGR from 2025 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Mode, application, end-use, region
Regional scope
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Australia; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia, UAE; Kuwait
Key companies profiled
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., GenScript, Danaher, Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Altogen Biosystems, Lonza, Sonidel, SIRION BIOTECH GmbH
Innovative Cell Technologies, Inc.
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Non-viral Gene Delivery Technologies Market Report Segmentation
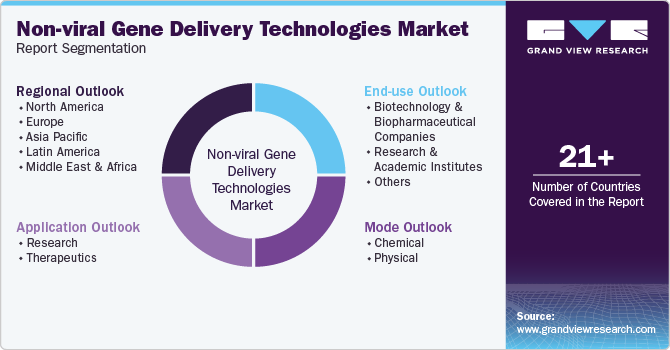
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global non-viral gene delivery technologies market report based on mode, application, end-use, and region:
-
Mode Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Chemical
-
LNPs
-
Polymers
-
Others
-
-
Physical
-
Electroporation
-
Microinjection
-
Others
-
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Research
-
Therapeutics
-
Gene Therapy
-
Cell Therapy
-
Vaccines
-
-
-
End-use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Biotechnology and Biopharmaceutical Companies
-
Research and Academic Institutes
-
Others
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Denmark
-
Sweden
-
Norway
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
Japan
-
India
-
South Korea
-
Australia
-
Thailand
-
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
South Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
UAE
-
Kuwait
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global non-viral gene delivery technologies market size was estimated at USD 3.70 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 3.98 billion in 2025.
b. The global non-viral gene delivery technologies market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 12.29% from 2025 to 2030 to reach USD 7.11 billion by 2030.
b. The North American region dominated the market share of 41.25% in 2024. The region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, enabling the rapid adoption of innovative gene delivery techniques. Growing interest in precision medicine and increasing clinical trials focused on genetic disorders further boost market growth. Additionally, government initiatives and funding for genomic research contribute to the expanding use of non-viral delivery technologies.
b. Some key players operating in the non-viral gene delivery technologies market include Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., GenScript, Danaher, Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Altogen Biosystems, Lonza, Sonidel, SIRION BIOTECH GmbH, Innovative Cell Technologies, Inc.
b. The market's growth is driven by the growing demand for safe, scalable, and cost-effective alternatives to viral vectors in gene therapy and research. Unlike viral methods, non-viral technologies such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), polymers, and electroporation offer lower immunogenicity and reduced manufacturing complexities. These attributes make them highly suitable for large-scale applications, including mRNA-based vaccines and CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing therapies.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.