- Home
- »
- Advanced Interior Materials
- »
-
U.S. Black Mass Recycling Market, Industry Report, 2033GVR Report cover
![U.S. Black Mass Recycling Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
U.S. Black Mass Recycling Market (2025 - 2033) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Battery Type (Lithium-ion, Nickel-based), By Battery Source (Automotive Batteries, Consumer Electronics, Industrial Batteries), By Recovered Metals, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-617-3
- Number of Report Pages: 80
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2021 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2033
- Industry: Advanced Materials
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
U.S. Black Mass Recycling Market Summary
The U.S. black mass recycling market size was valued at USD 1.16 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.75 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 17.2% from 2025 to 2033. Upward trend in battery disposal creates consistent feedstock for black mass recycling facilities, thus driving market growth in the U.S.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- By battery type, the lithium ion batteries segment is anticipated to register the fastest CAGR of 17.1% from 2025 to 2033.
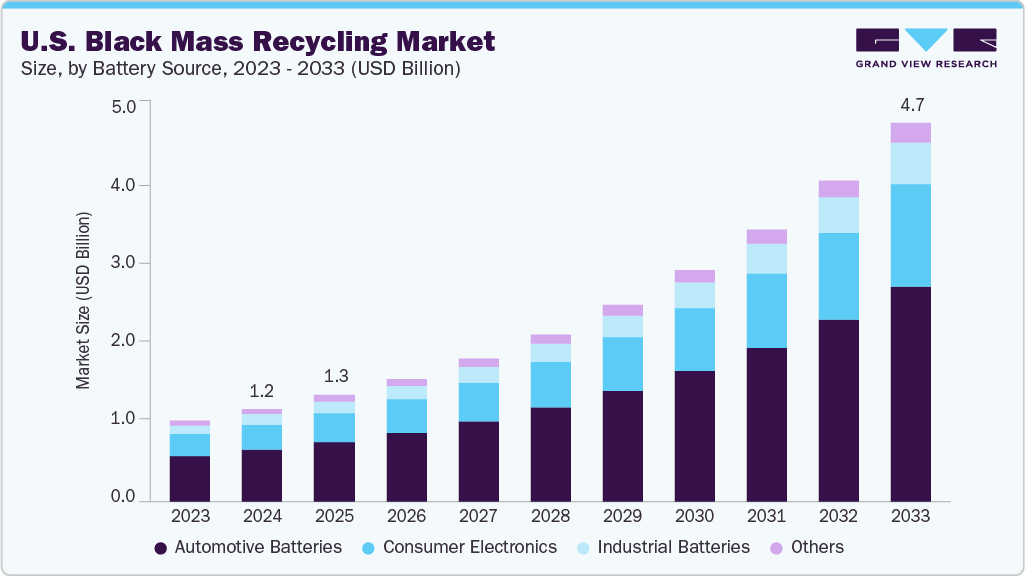
- By battery source, the automotive batteries accounted for the largest market revenue share of over 56.0% in 2024.
- By recovered metal, nickel is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 17.6% over the forecast period in terms of revenue.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 1.16 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 4.75 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2033): 17.2%
The deployment of battery-electric vehicles in the U.S. accelerated in 2024, with automakers scaling production to meet rising consumer and regulatory demands. Companies such as Tesla, Ford, and General Motors significantly ramped domestic EV output, contributing to the expanding EV ecosystem. This surge in production naturally resulted in a larger volume of lithium-ion batteries reaching end-of-life, either through vehicle retirement or manufacturing scrap. As a result, the availability of black mass, comprising valuable battery metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, increased substantially.U.S.-based black mass recyclers have responded with large-scale infrastructure expansion and capital-intensive projects. Redwood Materials announced that by 2026, it aims to produce 100 GWh of cathode-active materials annually, enough to power over one million EVs, using recovered minerals from the black mass. Ascend Elements also advanced its position in 2024 by constructing a USD 65 million recycling facility in Hopkinsville, Kentucky. This plant is projected to process up to 24,000 metric tons of lithium-ion battery material annually. These developments indicate a strategic move towards scaling operations, improving recycling efficiency, and capturing value from a growing domestic battery waste stream.
Government support strengthened the momentum in 2024, particularly through financial incentives and loan guarantees. Redwood Materials secured a USD 2 billion loan from the Department of Energy’s Advanced Technology Vehicles Manufacturing program to expand its Nevada-based recycling facility. This governmental backing mitigates financial risk for recycling companies and provides the liquidity needed to expand processing capacities and technologies. Such federal involvement reflects broader national efforts to localize critical mineral supply chains and reduce dependency on overseas sources, particularly amid geopolitical supply risks tied to materials like cobalt and lithium.
A critical enabler of market stability has been the formation of closed-loop partnerships between recyclers and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Redwood Materials’ collaborations with Toyota and Panasonic ensured a reliable stream of battery production scrap and end-of-life batteries for processing. Similarly, Ascend Elements partnered with SK Ecoplant to convert recycled black mass into high-value cathode precursor materials. These agreements ensure recyclers can access consistent input material and help automakers meet sustainability goals by reintegrating recovered minerals into new battery production. Establishing such loops is pivotal to building a circular economy for battery materials within the U.S.
Lastly, stringent regulatory frameworks and rising environmental, social, and governance (ESG) expectations continue to play a central role in 2024. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and other federal and state-level initiatives incentivize domestic recycling and penalize environmentally harmful disposal practices. With increased scrutiny on battery end-of-life management, U.S. recyclers are positioned as essential contributors to a lower-carbon EV supply chain. These policy levers encourage industrial investment and ensure that black mass recycling aligns with broader goals of clean energy transition, resource independence, and long-term sustainability.
Drivers, Opportunities & Restraints
Many battery manufacturing facilities and gigafactories are being built across the U.S., generating large volumes of production scrap. The need to process this scrap efficiently and sustainably supports the black mass recycling industry. Growing awareness among consumers and businesses about responsible battery disposal also fosters greater participation in take-back programs and recycling initiatives. Furthermore, the push for onshore battery production in line with national security and industrial competitiveness goals creates a policy environment favoring domestic material recovery, indirectly boosting demand for black mass processing.
There is a significant opportunity to develop second-life battery applications before recycling, as partial degradation does not always render batteries unusable. Integrating reuse and recycling can extend battery life cycles and increase black mass yield in the long run. Technological innovation in sorting and pre-treatment end-of-life batteries also opens new avenues for efficiency gains and cost reductions in recycling operations. Another growth area is the emergence of regional processing hubs across underserved U.S. states, which could decentralize operations and reduce logistics costs, creating more localized black mass supply chains.
The fragmented regulatory landscape across U.S. states creates inconsistencies in battery collection and transportation rules, making it difficult for recyclers to operate efficiently nationwide. Additionally, high upfront capital expenditure for building hydrometallurgical or integrated processing facilities remains a barrier, especially for startups and mid-sized firms. There are also technical challenges related to processing diverse battery chemistries, such as LFP, NMC, and LCO, within the same facility, which can lead to yield inefficiencies and increased contamination risk.
Battery Type Insights
Lithium-ion batteries segment held the revenue share of 71.8% in 2024. The lithium-ion battery segment is dominant in the U.S. black mass recycling industry, driven by its widespread use in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. These batteries are the primary source of black mass due to their high concentrations of valuable metals such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese. In recent years, the rising deployment of EVs and stationary storage units has substantially increased the volume of spent lithium-ion batteries entering the recycling stream.
Nickel-based batteries is anticipated to register the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Due to cadmium's toxicity, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Department of Transportation (DOT) have set clear guidelines on safely handling and transporting nickel-based batteries, particularly NiCd. These regulations have prompted recyclers to establish specialized processes to ensure compliance while maximizing material recovery. In parallel, rising geopolitical concerns about nickel supply and efforts to localize critical mineral sourcing under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) have reinforced interest in secondary sources of nickel.
Battery Source Insights
Automotive batteries held the revenue share of 56% in 2024. The automotive batteries segment is the largest contributor to the market by source, driven primarily by the rapid growth of the EV sector and the gradual retirement of hybrid and electric vehicle battery packs. In 2024, with over 1.3 million EVs sold in the U.S., the volume of end-of-life automotive lithium-ion batteries entering the recycling stream has increased significantly.
Consumer electronics is anticipated to register the fastest CAGR over the forecast period, primarily due to the widespread use of lithium-ion batteries in devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, smartwatches, and wireless accessories. As product life cycles shorten and device ownership per capita increases, a rising volume of small-format batteries is discarded yearly. For instance, Apple reported collecting over 40,000 metric tons of used electronics in the U.S. in 2024 through its recycling and trade-in programs, some of which contained lithium-ion batteries contributing to black mass recovery.
Recovered Metal Insights
Nickel held the revenue share of 36.2% in 2024. Recycling companies are increasingly investing in hydrometallurgical technologies capable of efficiently separating and purifying nickel from complex battery compositions. In 2024, U.S. firms like Redwood Materials and Ascend Elements highlighted their ability to recover over 95% of contained nickel from black mass streams, reinforcing the technical feasibility of high-yield recovery. This trend aligns with broader federal goals under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) to localize critical mineral supply chains. With battery-grade nickel prices remaining volatile and global supply chains concentrated in a few countries, the recovery of nickel from black mass is expected to become even more crucial in ensuring raw material availability for domestic cathode manufacturing and enhancing the long-term sustainability of the U.S. battery ecosystem.
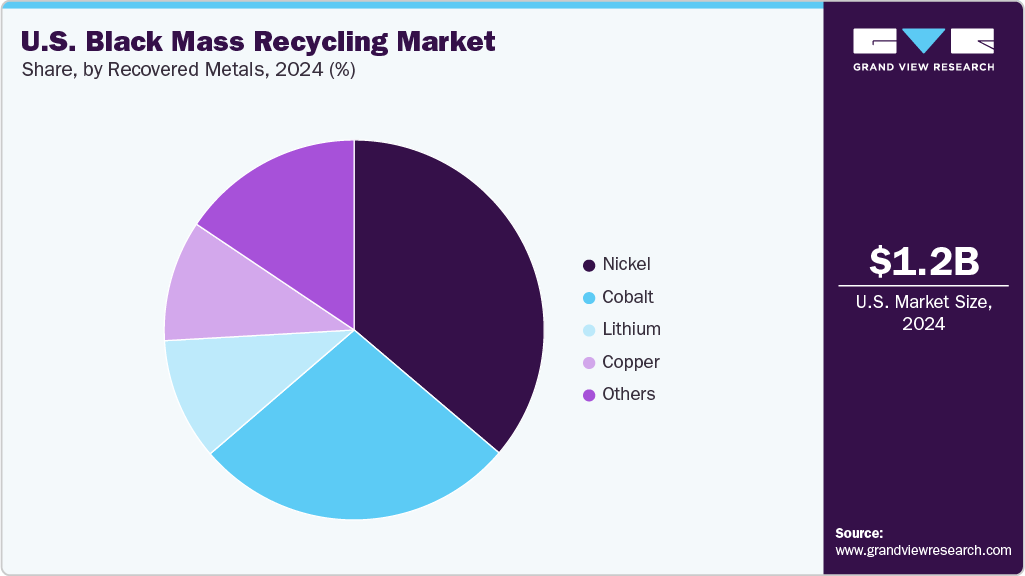
Lithium is anticipated to grow significantly over the forecast period. Technological advancements in the U.S. have enabled recyclers to significantly improve lithium recovery rates, especially through hydrometallurgical processes that selectively extract lithium from complex battery chemistries like NMC and LFP. In 2024, companies such as Li-Cycle reported consistent progress in extracting lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide at commercially viable scales from black mass. These outputs can be reused to produce new cathodes, support circular economy initiatives, and reduce environmental impacts associated with primary lithium extraction.
Key U.S. Black Mass Recycling Company Insights
Some of the key players operating in the market include Ascend Elements, Inc., Redwood Materials Inc., and others.
-
Ascend Elements, Inc. is a U.S.-based leader in transforming end-of-life lithium-ion batteries and manufacturing scrap into premium battery materials. Headquartered in Massachusetts and with facilities in Georgia and Kentucky, the company has developed a patented Hydro‑to‑Cathode process that directly converts black mass into cathode precursor active material (pCAM), effectively bypassing traditional multi-step hydrometallurgical pathways.
-
Redwood Materials Inc. is a privately held U.S. company founded in 2017 in Nevada. Its mission is a fully circular supply chain for lithium-ion batteries, collecting end-of-life batteries and production scrap, extracting critical minerals, and remanufacturing them into new battery components. Redwood recovers approximately 95% of metals such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, and copper from recycled batteries and aims to produce enough cathode active material to power about one million EVs (circa 100 GWh) annually.
Key U.S. Black Mass Recycling Companies:
- American Battery Technology Company
- Aqua Metals, Inc.
- Ascend Elements, Inc.
- ECOBAT
- Elemental Holding S.A.
- Green Li-ion Pte Ltd.
- Lifecycle Renewables
- RecycLiCo Battery Materials Inc.
- Redwood Materials Inc.
- Retrieve
Recent Development
-
In April 2025, Redwood Materials announced that its Nevada facility began commercial-scale production of cathode active material (CAM) from recycled lithium-ion batteries. This plant, one of the largest in North America, now uses hydrometallurgical processes to process end-of-life and production scrap materials, converting them into metal-rich black mass. The operation achieves recovery rates of around 98% for critical metals, including lithium, nickel, cobalt, and copper, enough to supply approximately 100 GWh of CAM annually for 1.3 million EVs.
-
In September 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy awarded USD 3 billion to 25 battery manufacturing projects across 14 states, specifically targeting black mass processing and critical minerals recovery as part of its Clean Manufacturing tax credit framework. These projects aim to enhance the U.S.’s capacity to convert battery waste into battery-grade materials, reducing reliance on foreign supply chains.
U.S. Black Mass Recycling Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 1.33 billion
Revenue forecast in 2033
USD 4.75 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 17.2% from 2025 to 2033
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2021 - 2023
Forecast period
2025 - 2033
Quantitative Units
Revenue in USD million/billion, volume in kilotons, and CAGR from 2025 to 2033
Report coverage
Volume forecast, revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Battery source, recovered metal, battery type
Country scope
U.S.
Key companies profiled
Redwood Materials Inc.; Ascend Elements, Inc.; American Battery Technology Company; Aqua Metals, Inc.; RecycLiCo Battery Materials Inc.; Retrieve; Green Li-ion Pte Ltd.; Lifecycle Renewables; Elemental Holding S.A.; ECOBAT
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts' working days). You can add or alter the country, regional, and segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
U.S. Black Mass Recycling Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue and volume growth at the country level and analyzes the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For the purpose of this study, Grand View Research has segmented the U.S. black mass recycling market report by battery type, battery source, and recovered metal.
-
Battery Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million; Volume, Kilotons; 2021 - 2033)
-
Lithium-Ion Batteries
-
Nickel-Based Batteries
-
-
Battery Source Outlook (Revenue, USD Million; Volume, Kilotons; 2021 - 2033)
-
Automotive Batteries
-
Consumer Electronics
-
Industrial Batteries
-
Others
-
-
Recovered Metal Outlook (Revenue, USD Million; Volume, Kilotons; 2021 - 2033)
-
Nickel
-
Cobalt
-
Lithium
-
Copper
-
Others
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The U.S. black mass recycling market size was estimated at USD 1.16 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.33 billion in 2025.
b. The U.S. black mass recycling market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 17.2% from 2025 to 2033 to reach USD 4.75 billion by 2033.
b. The lithium ion batteries segment dominated the market with a revenue share of 71.8% in 2024.
b. Some of the key players of the U.S. black mass recycling market are Redwood Materials Inc., Ascend Elements, Inc., American Battery Technology Company, Aqua Metals, Inc., RecycLiCo Battery Materials Inc., Retrieve, Green Li-ion Pte Ltd., Lifecycle Renewables, Elemental Holding S.A., ECOBAT, and others.
b. The key factor that is driving the growth of the U.S. black mass recycling market is driven by the increasing demand for lithium-ion batteries, coupled with the need for a sustainable and domestic supply of critical battery materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.