- Home
- »
- Clinical Diagnostics
- »
-
Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market, Industry Report, 2033GVR Report cover
![Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market (2025 - 2033) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Type (Genetic Biomarkers, Cell-based Biomarkers, Metabolomic Biomarkers), By Application, By End-use, By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-547-6
- Number of Report Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2021 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Healthcare
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Trends
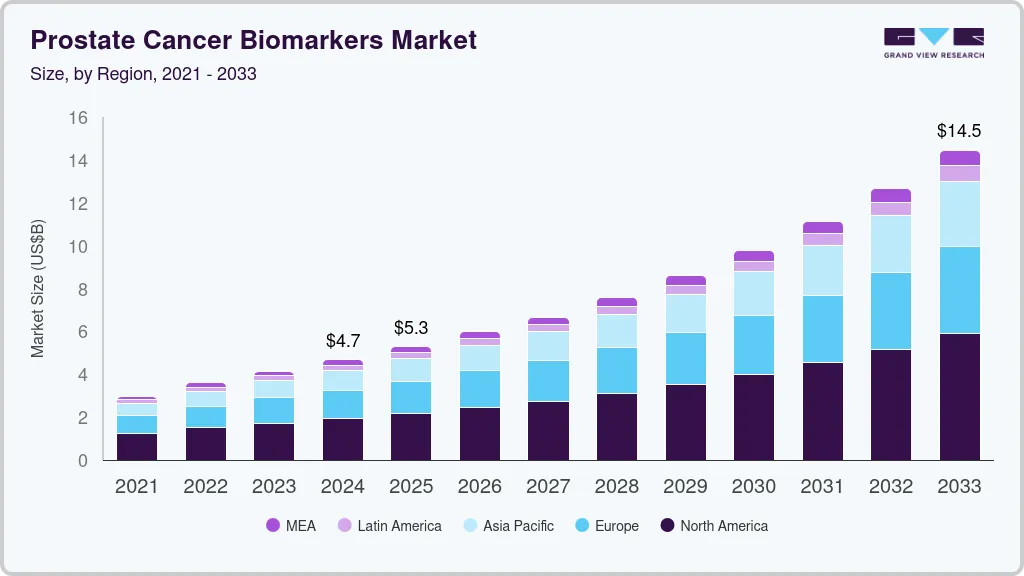
The global prostate cancer biomarkers market size was estimated at USD 4.68 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 14.45 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.4% from 2025 to 2033. Some of the major factors expected to drive the market are the rising incidence of prostate cancer and increasing awareness among physicians & patients regarding early detection. Furthermore, advancements in biomarker technologies and growing research efforts for prostate cancer diagnosis & treatment are further propelling the overall market.
The demand for prostate cancer biomarkers is rising due to the need for accurate and early-stage disease detection and the growing adoption of precision medicine. Factors such as the increasing application of biomarkers in targeted therapies and the development of minimally invasive diagnostic techniques further drive market expansion. Regulatory authorities emphasize the importance of biomarker-based diagnostic tools for improving clinical outcomes, leading to greater biomarker validation and standardization investment.
Advancements in genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic technologies are enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of prostate cancer biomarker detection. Genomic biomarkers, including PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG, improve early diagnosis, while proteomic markers such as PSA and Prostate Health Index (PHI) refine risk stratification. Metabolomic approaches are gaining attention for their potential to distinguish aggressive from indolent prostate cancer. With growing awareness of biomarker-driven diagnostic and prognostic applications, the demand for highly specific and validated prostate cancer biomarkers is expected to continue expanding.
The increasing focus on biomarker-driven diagnostics is transforming prostate cancer detection and management. Advanced biomarker assays contribute to improved risk stratification and support personalized treatment approaches. In January 2025, OncoAssure Ltd announced the clinical validation of its biopsy-based test, OncoAssure Prostate, designed to enhance risk assessment for prostate cancer recurrence. The study, published in BJUI Compass, demonstrated the test’s ability to distinguish between aggressive and low-risk prostate cancers, supporting more precise treatment decisions. These advancements underscore the growing role of biomarker-based diagnostics in improving clinical outcomes and guiding more effective prostate cancer management strategies.
Table below presents Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Clinical Trials
Biomarker
Clinical trial phase
Type of cancer
Patients included
Clinical trial ID
TMPRSS2-ERG
Phase II
mCRPC and recurrent PCa
148
NCT01576172
Phase II
Recurrent PCa, stage IV PCa
29
NCT00330161
Phase II
Prostatic adenocarcinoma
148
NCT01682772
Phase I
Advanced or metastatic PCa
113
NCT00749502
Phase I
High risk PCa
65
NCT02588404
Phase I
Localized or locally advanced PCa, biochemical recurrent PCa
84
NCT03421015
Phase II
High risk PCa
208
NCT02573636
TP53
Phase III
mCRPC
750
NCT03903835
Phase I/II
Prostatic neoplasia
36
NCT00900614
Phase III
Localized PCa
7,776
NCT00001469
Phase I
Localized or locally advanced PCa, biochemical recurrent PCa
84
NCT03421015
AR
Phase I
Hormone refractory PCa
140
NCT00510718
Phase II
PCa
45
NCT01990196
Phase II
Recurrent PCa
42
NCT03311555
Phase I
mCRPC
58
NCT01516866
Phase II
Metastatic PCa, CRPC
60
NCT04090528
Phase I
PCa
40
NCT02411786
Phase II
mCRPC
8
NCT02379390
Phase II
Biochemical recurrent PCa
90
NCT01790126
Phase II
Advanced hormone dependent PCa
90
NCT01861236
BRCA2
Phase II
High risk PCa
100
NCT02154672
Phase III
mCRPC
408
NCT03075735
Phase III
Genetic predisposition to PCa
1,700
NCT00261456
Phase II
mCRPC
40
NCT04038502
Phase II
mCRPC
70
NCT03012321
Phase III
mCRPC
387
NCT02987543
PTEN/P13K/AKT/mTOR
Phase II
High risk PCa
208
NCT02573636
Phase III
CRPC
120
NCT03580239
Phase II
PCa previously treated
108
NCT01251861
Phase I
PCa previously treated with enzalutamide
36
NCT03310541
Phase I
Stage III and IV PCa
62
NCT01480154
Phase II
mCRPC
9
NCT02091531
MGMT
NA
NA
NA
NA
DNMT1
Phase I
mCRPC
19
NCT05037500
NA
Prostatic adenocarcinoma
19
NCT01118741
Phase III
Prostatic adenocarcinoma
80
NCT03535675
Phase I
Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate, Recurrent PCa, Stage I, IIA, IIB, III and IV PCa
32
NCT01912820
Phase I/II
Prostate Carcinoma
NA
NCT03709550
JMJD3
NA
NA
NA
NA
KDM4B
NA
NA
NA
NA
CDK9
Phase I
Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
100
NCT05159518
SF3B2
NA
NA
NA
NA
AR-V7
Phase III
Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
953
NCT02438007
AR-V3
NA
NA
NA
NA
HDAC6
NA
NA
NA
NA
PRUNE2
NA
NA
NA
NA
Circulating tumor cells
NA
Prostate Cancer Obesity
67
NCT02453139
Phase II
Patients with PSA 4–10 ng/mL
500
NCT03488706
Phase II
Localized PCa
200
NCT01961713
Phase II
mCRPC
11
NCT00887640
Phase II
Advanced PCa
24
NCT02552394
Phase II
mCRPC
140
NCT03050866
Phase I
PCa
60
NCT02450435
cell-free DNA
Phase III
Metastatic PCa
1038
NCT00134056
Phase I
PCa
12
NCT04081428
Phase II
Metastatic PCa
300
NCT02853097
Phase II
PCa
68
NCT02941029
Phase II
PCa
30
NCT03284684
Extracellular vesicles
NA
PCa
108
NCT04298398
miRNAs
Phase II
mCRPC
40
NCT02471469
Phase II
mCRPC
46
NCT04188275
Phase III
High risk PCa
300
NCT01220427
Phase I
PCa
240
NCT03911999
Phase I
PCa
60
NCT02366494
lncRNAS
NA
Prostatic neoplasia
507
NCT01024959
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The degree of innovation in prostate cancer biomarkers is advancing rapidly, driving improvements in early detection, risk assessment, and personalized treatment strategies. Emerging biomarkers such as PCA3, TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, and the Prostate Health Index (PHI) enhance diagnostic accuracy beyond traditional PSA testing. Innovations in liquid biopsy technologies, such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and extracellular vesicles, provide non-invasive options for real-time monitoring of disease progression. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven biomarker analysis is refining predictive models, enabling more precise identification of aggressive versus indolent prostate cancer. These advancements are transforming clinical decision-making, optimizing therapeutic approaches, and improving patient outcomes while reducing unnecessary interventions.
The level of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in the prostate cancer biomarkers industry is moderate but steadily rising as companies seek to expand their diagnostic capabilities and strengthen their biomarker portfolios. Several diagnostic and biotech firms engage in strategic acquisitions to access novel biomarker technologies, proprietary assays, and advanced molecular platforms. Collaborations between diagnostic and precision medicine firms are also shaping the competitive landscape, reflecting a growing interest in integrated biomarker solutions for prostate cancer. While large-scale acquisitions remain limited, targeted M&A efforts increasingly focus on enhancing expertise in genomics, liquid biopsy, and AI-based analytics for prostate cancer diagnostics.
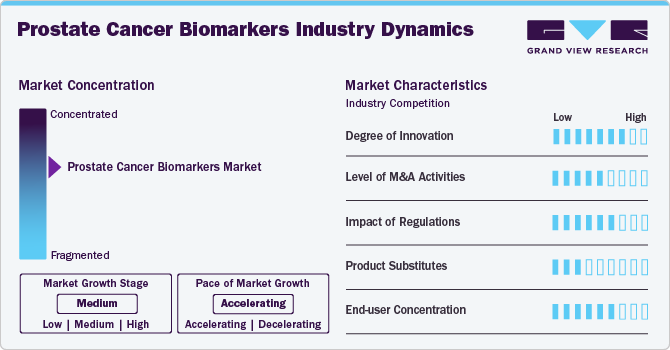
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence the development, approval, and commercialization of prostate cancer biomarkers. Authorities such as the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), and PMDA (Japan) enforce rigorous standards to ensure biomarker accuracy, analytical reliability, and clinical relevance. The FDA’s Biomarker Qualification Program offers a structured path for biomarker acceptance but requires robust evidence, which can extend the time to market. Similarly, the EU’s In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) has reclassified many diagnostic tests, increasing the burden of documentation and compliance for prostate cancer biomarker developers. In parallel, regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe govern patient data used in biomarker research, impacting study design and data accessibility. These evolving requirements shape innovation timelines and influence the strategic direction of diagnostic development.
The market faces competition from several conventional and emerging diagnostic approaches. Traditional methods such as digital rectal examination (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, and multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) continue to serve as primary tools in prostate cancer screening and diagnosis. These techniques, while accessible and cost-effective, often lack the precision of newer biomarker-based tests. In addition, tissue biopsies and genomic profiling—when used without biomarker integration—can offer diagnostic insights but may not fully support risk stratification or treatment personalization. In cost-sensitive healthcare systems, the reliance on these established tools may limit the adoption of newer biomarker technologies, particularly where reimbursement frameworks are not well aligned with advanced diagnostics.
The market is expanding geographically due to rising investments in cancer diagnostics, increasing awareness of early detection, and ongoing research efforts. In North America, the use of biomarker-based tests is supported by established screening programs, access to advanced technologies, and regulatory initiatives. Europe is witnessing steady growth through government-backed cancer research and public health strategies. In Asia-Pacific, awareness and adoption of these tests are growing as healthcare systems improve and research activities increase in countries such as China, Japan, and India. Latin America and the Middle East are gradually adopting biomarker diagnostics with support from improvements in healthcare infrastructure and focused efforts to enhance cancer detection, contributing to broader market growth across regions.
Type Insights
Protein biomarkers dominated the market, accounting for a share of 57.7% in 2024. Protein biomarkers are essential in prostate cancer diagnostics, enabling early detection and monitoring of disease progression by identifying abnormal protein expression patterns. The rising demand for personalized medicine and targeted therapies drives the adoption of protein-based diagnostic tools. Technological advancements such as mass spectrometry and immunoassays have improved the accuracy and efficiency of protein analysis in biological fluids like blood and urine. These developments support broader clinical adoption and research applications, strengthening the segment’s contribution to the market.
Metabolomic biomarkers are expected to grow fastest, with a CAGR of 14.1% over the forecast period. The rising interest in understanding metabolic changes associated with prostate cancer is driving the growth of this segment. Metabolomic biomarkers provide insights into disease mechanisms by analyzing small molecule profiles in biofluids such as urine, serum, and plasma. These markers support early detection and offer the potential for distinguishing aggressive from indolent cancer forms. Advances in analytical techniques like NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry have improved the detection and quantification of metabolic changes. Growing investments in precision oncology and increasing use of metabolomics in research and clinical trials are further accelerating the segment’s expansion.
Applications Insights
Screening and early detection dominated the market, accounting for a share of 45.1% in 2024. This segment's growth is driven by the rising need for timely identification of prostate cancer to improve treatment outcomes and reduce disease burden. Biomarkers play a vital role in detecting cancer at an early stage, often before symptoms appear, allowing for more effective and less invasive interventions. Integrating biomarker-based tests in routine health check-ups and screening programs is increasing across hospitals and diagnostic centers. Advances in non-invasive testing methods, such as liquid biopsies and multiplex assays, also improve detection accuracy and patient compliance. These developments support the growing adoption of biomarkers in prostate cancer screening and early diagnosis.
Companion diagnostics is expected to grow fastest at a CAGR of 14.5% over the forecast period. This segment is gaining traction due to the increasing need for personalized treatment strategies in prostate cancer management. Companion diagnostics help identify patients most likely to benefit from targeted therapies based on specific biomarker profiles. These tools improve treatment accuracy and reduce the risk of adverse effects by guiding therapeutic decisions. Advances in molecular testing and regulatory support for precision medicine drive the development and approval of companion diagnostic tests. With more targeted therapies entering the market, the demand for reliable biomarker-based companion diagnostics is expected to grow steadily, supporting this segment’s expansion.
End Use Insights
Hospitals and diagnostic laboratories dominated the market, accounting for a share of 63.2% in 2024. These facilities are central to adopting and applying prostate cancer biomarkers, as they handle large volumes of diagnostic testing and patient monitoring. Their role in early detection, treatment planning, and ongoing disease surveillance supports the growing use of biomarker-based diagnostics. With advancements in clinical workflows and access to improved testing platforms, hospitals, and labs can process biomarker tests faster and more accurately. The emphasis on personalized care and integration of molecular diagnostics into routine practice continues to strengthen the position of this segment in the market.
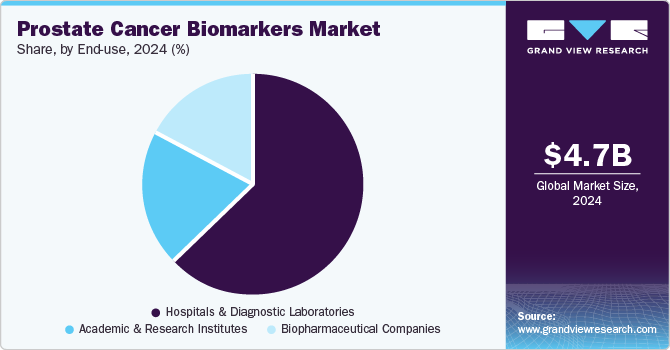
Academic and research institutes are expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 14.4% over the forecast period. These institutions are actively involved in discovering and validating prostate cancer biomarkers, contributing significantly to translational research and clinical innovation. With strong academic networks and access to research funding, they are advancing biomarker studies through collaborative projects and clinical trials. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and precision diagnostics encourages the adoption of novel biomarkers in academic research. Moreover, partnerships with healthcare providers and biotech firms help translate research findings into practical diagnostic tools, supporting the segment's steady growth.
Regional Insights
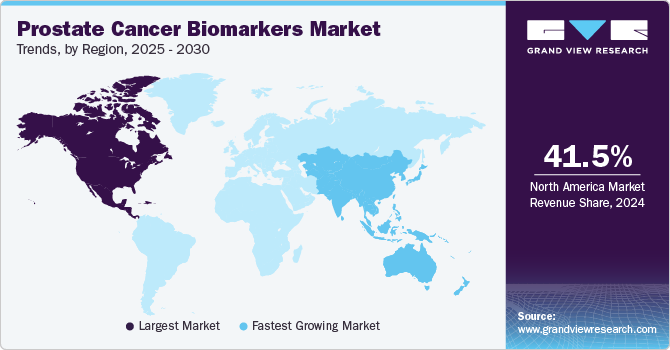
North America accounted for the largest share of 41.47% in 2024 and is anticipated to register steady growth over the forecast period. The increasing recognition of biomarkers in guiding prostate cancer diagnostics and therapy decisions contributes to market expansion. In addition, strong support from local regulatory agencies is helping facilitate the development and validation of biomarker-based tests. These agencies are actively involved in promoting awareness of precision medicine and its role in improving prostate cancer outcomes, which is encouraging broader adoption across healthcare systems in the region.
U.S. Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Trends
The U.S. accounted for a substantial share of the North American prostate cancer biomarkers market in 2024, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, significant research funding, and the increasing adoption of biomarker-based diagnostics. The market is bolstered by high awareness and institutional support for early detection and precision medicine in prostate cancer care. Research organizations and academic institutions actively engage in studies to validate novel biomarkers, enhancing clinical confidence in these diagnostic tools.
For instance, in February 2022, Datar Cancer Genetics Inc. received the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's Breakthrough Device Designation for its 'TriNetra-Prostate blood test, designed to detect early-stage prostate cancer. This test demonstrated high accuracy (>99%) without false positives and requires only a 5 mL blood sample. It is indicated for males aged 55-69 years with serum PSA of 3 ng/mL or higher. The test identifies prostate adenocarcinoma-specific Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in the blood, potentially reducing the need for invasive biopsies among individuals with benign prostate conditions and improving detection rates among those with prostate cancer.
Europe Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Trends
The Europe prostate cancer biomarkers market is growing steadily with rising awareness about early cancer detection and personalized treatment. Governments across countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are supporting research and encouraging the use of advanced diagnostic tools. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is helping by providing clear guidelines supporting biomarkers' use in drug development. Research partnerships across universities, hospitals, and companies are also helping discover new and more accurate biomarkers. With better access to non-invasive tests like liquid biopsies and wider insurance coverage, the use of prostate cancer biomarkers is gradually increasing across the region.
The prostate cancer biomarkers market in France is growing with support from national research programs and strong public-private partnerships. The government has invested in projects focused on improving cancer diagnostics, helping research centers like Inserm work closely with biotech companies. There is also a push to use digital tools and artificial intelligence in labs to make biomarker testing faster and more accurate. France’s well-developed clinical trial network and partnerships with international pharmaceutical companies are also helping expand access to advanced biomarker-based tests. This progress supports early detection and more personalized treatment approaches across the country.
The prostate cancer biomarkers market in Germany is showing steady growth due to strong research capabilities, well-established healthcare systems, and rising interest in early cancer detection. Government-backed programs and partnerships between universities, hospitals, and diagnostic companies support developing and using biomarker-based tests. The German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) plays a key role in promoting biomarker research through national initiatives focused on precision oncology. There is growing use of genetic and protein-based biomarkers in hospitals to improve diagnosis and treatment planning for prostate cancer. Ongoing clinical studies and access to advanced lab technologies are also helping expand the market. These factors contribute to the wider adoption of prostate cancer biomarkers nationwide.
Asia Pacific Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Trends
The Asia Pacific prostate cancer biomarkers market is expected to register the fastest CAGR of 14.1% during the forecast period, supported by a growing aging population, rising cancer awareness, and greater emphasis on early diagnosis. Countries such as Japan, China, and South Korea are making notable progress in biomarker research through public health initiatives and institutional collaborations. Japan focuses on improving non-invasive diagnostics, while China is strengthening its biomarker testing capabilities through increased R&D investments.
India is also witnessing a gradual shift toward personalized medicine, with hospitals and diagnostic centers adopting biomarker-based approaches for improved disease detection. With healthcare infrastructure improving and clinical research activities expanding across the region, biomarker integration in prostate cancer diagnostics is expected to gain more traction.
The Japan prostate cancer biomarkers market is expanding with growing awareness of early detection and personalized cancer care. The country’s aging population and focus on precision medicine have encouraged research on genetic and protein-based biomarkers. National institutions such as RIKEN and the National Cancer Center are supporting studies aimed at improving prostate cancer diagnosis through non-invasive biomarker tests. The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) is streamlining the approval of innovative diagnostics, which is helping more hospitals and labs adopt these technologies. This supportive environment contributes to steadily adopting prostate cancer biomarkers across Japan.
Latin America Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Trends
Latin America prostate cancer biomarkers market is growing with better access to diagnostic services and increasing efforts in cancer awareness. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina focus on early detection strategies through biomarker-based testing. In Brazil, research centers like Fiocruz support the development of diagnostic tools to improve prostate cancer outcomes. Mexico is encouraging academic and private sector partnerships to enhance biomarker research, while Argentina’s CONICET is contributing to studies on genetic and protein markers for cancer detection. These regional efforts and gradual improvements in healthcare infrastructure are helping expand the prostate cancer biomarkers market across Latin America.
The prostate cancer biomarkers market in Brazil is progressing with support from national research institutions, growing awareness, and efforts to improve early cancer detection. Organizations such as Fiocruz and the University of São Paulo are involved in biomarker research focused on improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning for prostate cancer. Government funding bodies like FAPESP and CAPES are encouraging research in precision medicine, contributing to local innovation. Collaborations between public hospitals and biotech firms are also helping expand access to biomarker-based diagnostics. These combined efforts are driving the adoption of prostate cancer biomarkers across Brazil’s healthcare sector.
Middle East & Africa Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Trends
The prostate cancer biomarkers market in the Middle East & Africa is gradually expanding with increasing efforts to improve early cancer detection, modernize healthcare systems, and promote research in precision oncology. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE support prostate cancer diagnostics through national health strategies and collaborations with global institutions. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 encourages investment in biomarker-based innovations, including those focused on prostate cancer. In Africa, institutions like the University of Cape Town are exploring biomarker applications to enhance prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. While these developments create opportunities, challenges such as limited access to specialized testing and uneven research funding continue to affect wider market adoption.
The prostate cancer biomarkers market in Saudi Arabia is expanding with a growing emphasis on early cancer detection, precision medicine, and healthcare modernization. National health programs under Vision 2030 prioritize research and innovation in oncology, creating a favorable environment for biomarker-based diagnostics. Government-backed institutions such as King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre are involved in developing and validating prostate cancer biomarkers for clinical use. Additionally, partnerships with international research organizations are helping advance diagnostic capabilities. These efforts, along with improved access to laboratory infrastructure and a strong focus on personalized care, are contributing to the growth of the prostate cancer biomarkers market in the country.
Key Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Company Insights
Major market players engage in various strategies, such as distribution agreements, mergers and acquisitions, and expansions. Most crucially, they exhibit a high degree of innovation in product research and development to improve their market penetration.
Key Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the prostate cancer biomarkers market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Exact Sciences Corporation
- Myriad Genetics, Inc.
- Bio-Techne
- ExoDx
- OPKO Health,Inc.
- mdxhealth
- Veracyte, Inc.
- Beckman Coulter, Inc.
- Nucleix
- DiaCarta
Recent Developments
-
In February 2025, Myriad Genetics partnered with PATHOMIQ to exclusively license PATHOMIQ_PRAD, an AI-driven technology platform for prostate cancer, in the U.S. This partnership integrates AI-enabled diagnostics into Myriad's oncology portfolio, supporting more informed treatment decisions before and after prostate cancer therapy. By leveraging advanced artificial intelligence, the collaboration aims to strengthen diagnostic precision in prostate cancer care, aligning with evolving needs in the Prostate Cancer Biomarker market.
-
In February 2024, DiaCarta entered a strategic collaboration with OncoAssure Ltd to commercialize a prostate cancer prognostic test. This 6-gene expression assay evaluates the risk of aggressive disease following diagnosis and estimates the probability of biochemical recurrence within five years post-surgery. The partnership utilizes DiaCarta's clinical diagnostic capabilities to support validation and market expansion of the test, contributing to more tailored prostate cancer management through biomarker-based risk stratification.
Prostate Cancer Biomarkers Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 5.3 billion
Revenue forecast in 2033
USD 14.45 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 13.4% from 2025 to 2033
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2021 - 2023
Forecast period
2025 - 2033
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2033
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Type, application, end use, region
Regional scope
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; UK; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; India; China; Japan; Australia; Thailand; South Korea; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; UAE; South Africa; Kuwait
Key companies profiled
Exact Sciences Corporation; Myriad Genetics, Inc.; Bio-Techne; ExoDx; OPKO Health, Inc.; mdxhealth; Veracyte, Inc.; Beckman Coulter, Inc.; Nucleix; DiaCarta; Genomic Health
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Prostate Cancer Biomarker Market Report Segmentation
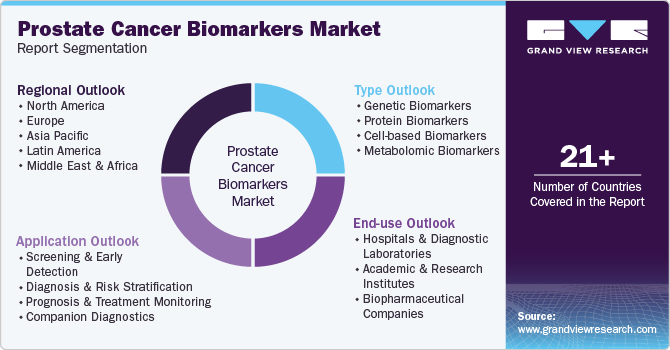
This report forecasts revenue growth and provides an analysis on the market trends in each of the sub-markets from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global prostate cancer biomarkers market report on the basis of type, application, end use, and region:
-
Type Outlook (USD Million; 2021 - 2033)
-
Genetic Biomarkers
-
Protein Biomarkers
-
Cell-based Biomarkers
-
Metabolomic Biomarkers
-
-
Application Outlook (USD Million; 2021 - 2033)
-
Screening and Early Detection
-
Diagnosis and Risk Stratification
-
Prognosis and Treatment Monitoring
-
Companion Diagnostics
-
-
End Use Outlook (USD Million; 2021 - 2033)
-
Hospitals & Diagnostic Laboratories
-
Academic & Research Institutes
-
Biopharmaceutical Companies
-
-
Regional Outlook (USD Million; 2021 - 2033)
-
North America
-
U.S
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
UK
-
Germany
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Denmark
-
Sweden
-
Norway
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
India
-
China
-
Japan
-
Australia
-
South Korea
-
Thailand
-
-
Latin America
-
Argentina
-
Brazil
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
UAE
-
South Africa
-
Kuwait
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global prostate cancer biomarker market size was estimated at USD 4.7 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 5.3 billion in 2025.
b. The global prostate cancer biomarker market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.1% from 2025 to 2030 to reach USD 9.8 billion by 2030.
b. The protein biomarkers segment dominated the global prostate cancer biomarker market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 57.73% in 2024.
b. Some key players operating in the prostate cancer biomarker market include Exact Sciences Corporation; Myriad Genetics, Inc.; Bio-Techne; ExoDx; OPKO Health, Inc.; mdxhealth; Veracyte, Inc.; and Beckman Coulter, Inc
b. Key factors that are driving the prostate cancer biomarker market growth include rising incidence of prostate cancer and increasing awareness among physicians & patients regarding early detection. Furthermore, advancements in biomarker technologies and growing research efforts for prostate cancer diagnosis & treatment are further propelling the overall market..
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.